Let’s say you want to open a website, for instance, www.technewstoday.com on a web browser. The Domain Name System (DNS) on your network translates this URL or hostname into the specific IP address of the web server. Your browser will then use this address to connect to the website.
Your Windows Operating System also saves this information in a DNS resolver cache so that the DNS server does not have to go through name resolution again in the future. But sometimes you may need to delete this cache, especially if you are unable to access some websites.
Depending on your situation, you may also need to reset other components of the internet such as the TCP/IP configuration.
How DNS Works?
Different levels of DNS servers work together to help you load a webpage or website. The web browser’s request first goes to the DNS recursive resolver which queries the Root Nameserver, the Top Level Domain (TLS) Nameserver, and the Domain or Authoritative Nameserver.
Each preceding nameserver sends the next nameserver’s address to the resolver and the Authoritative Nameserver returns the IP address of the required web server. The browser then sends an HTTP or HTTPS request to this address to initiate communication and load the webpage.
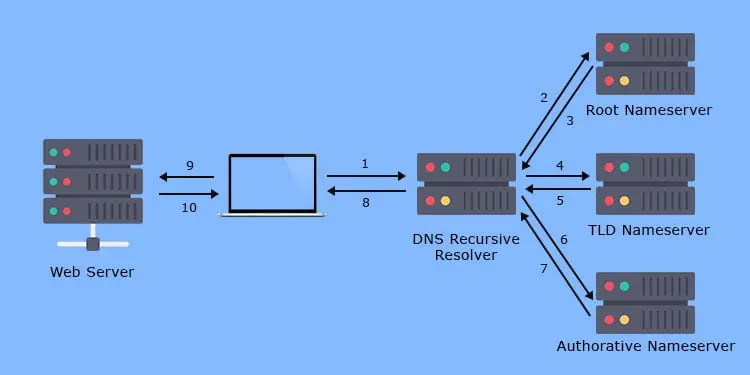
Since it is a lengthy process, your computer stores the DNS records of the latest visited addresses in the DNS resolver cache. So, after entering the domain name on the browser, it first views this cache and if the cache can resolve the IP address, the browser directly sends the HTTP or HTTPS request to the DNS server.
How to Flush DNS?
Sometimes, the web servers change their IP address. In such a case, the incorrect data in the DNS cache will cause the browser to attempt to connect to an invalid address. As a result, you can’t open the web pages at all.
This is why most ISPs regularly refresh the DNS cache to avoid storing outdated information. However, your Windows system does not clear the cache regularly, so you may encounter connection issues while trying to load a website. So, it’s better to manually clear the cache whenever you run into such issues.
On your computer, there are two levels of DNS cache. One is the cache data stored by the operating system and the other is the dedicated cache of your web browser.
You can clear the DNS cache on Windows through the administrator-level Command Prompt.
- Open Run by pressing Win + R.
- Type
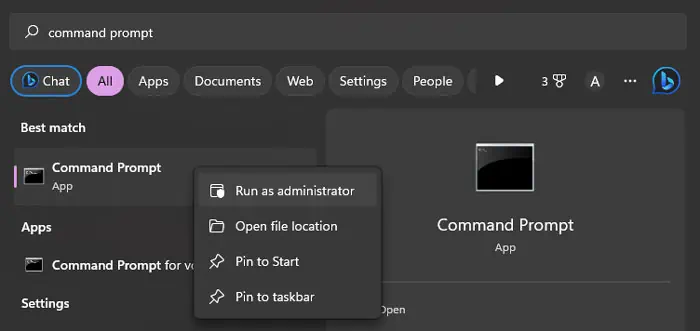
cmdand press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open the Elevated Command Prompt. - You can also search for
command prompt, right-click on the program and select Run as administrator.
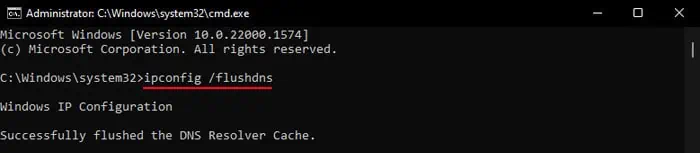
- Type and enter the command
ipconfig /flushdnsto clear the DNS cache records.
Then, to clear the dedicated DNS cache of your web browsers, follow these steps on your browser:
On Google Chrome/Opera/Microsoft Edge/Brave
- Open the web browser.
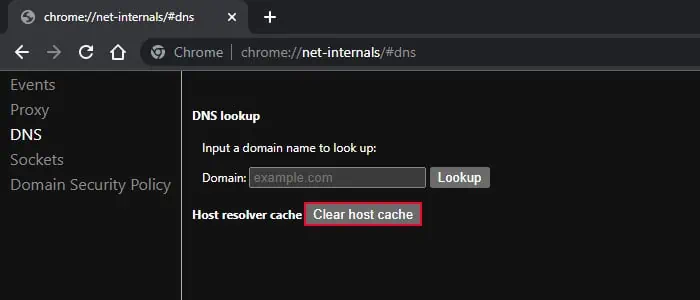
- Type
about://net-internals/#dnson the address bar and press Enter. - Click on Clear host cache.

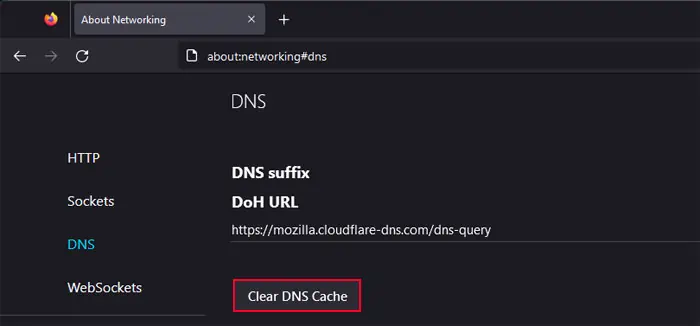
On Mozilla Firefox
- Open Mozilla Firefox and click on the address bar.
- Type
about:networking#dnsand press Enter. - Select Clear DNS Cache.

Other Ways to Reset an Internet Connection
While flushing the DNS is the most common way to reset an Internet connection, other network aspects also affect Internet connectivity. So, if you can’t resolve your issue after clearing the DNS, I recommend trying out these methods for a more complete Internet connection or network reset.
Power Cycle Router/Modem
The router is the device that uses the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server to assign the IP addresses to your computer. So, if the DHCP is not working properly, you need to power cycle the router to refresh its DHCP configuration. Doing so may also reassign your computer with a new IP address.
- Disconnect the computer from the modem or the router. You can also power it off.
- Power off or unplug the modem and router.

- Wait for 20 seconds and power up or plug in the main router/modem.
- Wait about a minute and then power up any secondary router.
- Wait a minute more and then connect your computer to the internet.
- You may need to restart your computer in some situations if you didn’t power it off earlier.
Reset TCP/IP Stack
You can also reset the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol stack altogether to reset all Internet configurations on Windows. It should resolve all internet connectivity issues on your computer’s end.
- Open the Elevated Command Prompt if you closed it earlier.
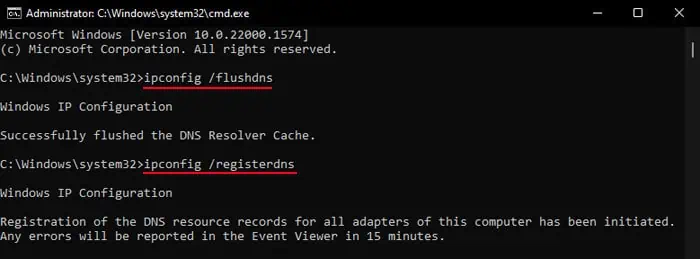
- If you didn’t flush the DNS earlier or used the internet since then, flush the DNS again using the command:
ipconfig /flushdns - Now, use the command below to re-register or refresh the DNS records of the computer:
ipconfig /registerdns
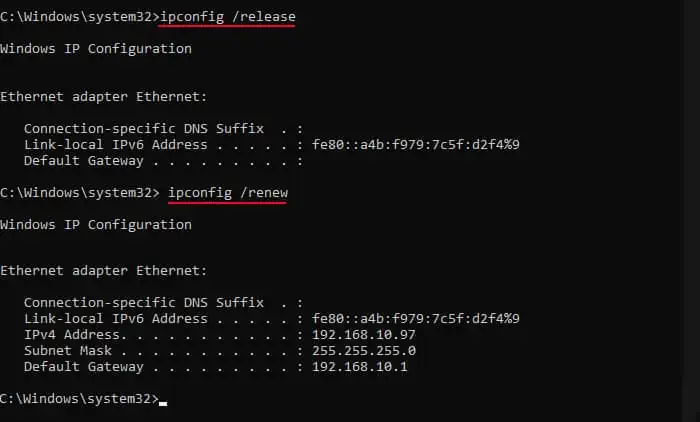
- Next, type the following commands and press Enter after each to refresh or renew the IP address of your computer.
ipconfig /releaseipconfig /renew
- Finally, you need to reset the Winsock catalog and the TCP IP to refresh other network configurations. Use the commands below to do so.
netsh winsock resetnetsh int ip reset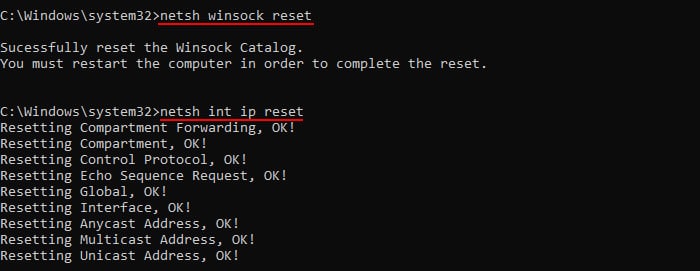
- Restart your computer.
Reset Network Adapter
Apart from the improper internet settings, issues with your network adapter’s (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) configuration can also cause connection problems. As such, you can reset this configuration altogether as well.
However, keep in mind that it will reinstall all network adapters, disconnect you from all networks and reset the VPN/Proxy software as well as any virtual networks.
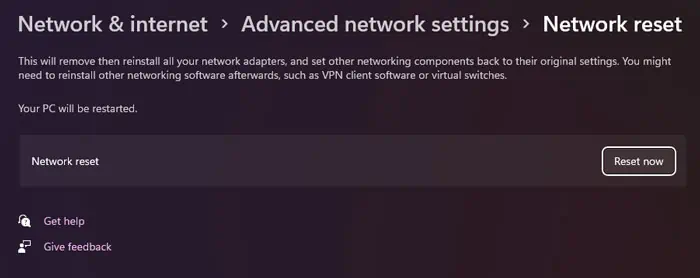
- Open Windows Settings by pressing the Windows key + I.
- Go to Network & internet > Advanced network settings > Network Reset.
- Click on Reset now.

- Confirm with Yes.