It is possible to install an All in One (AIO) Cooler as an intake or exhaust by simply changing the direction of the radiator fans. While both modes will cool down your CPU, the way they do so is somewhat different.
Generally, using AIO as intake is better for the CPU and using it as exhaust is better for other components like the GPU. However, there’s only a slight difference in the cooling performance since it is not just the radiator fan but the whole airflow inside the case that maintains the temperature.
You actually need to pay more attention to the ease of installation as well as the proper placement of the radiator to make your choice.
I always use the AIO as an intake if I am setting up the radiator on the front and as an exhaust when I place the radiator on the top. I have used many PCs with both intake and exhaust AIO coolers this way, and I found little difference in the performance.
Most AIOs fitted better in one configuration over the other in my PC cases, so I would always choose the better fit for my setup.
Factors that Affect AIO Configuration
Which AIO configuration is better for your setup depends on several factors. You need to pay attention to the ideal placement, installation difficulty, and case airflow, along with the cooling efficiency of these configurations.
Placement
Traditionally, the front/bottom fans on a PC are intake, and the rear/top fans are exhaust. It is the configuration that gives the most cooling efficiency as hot air rises to the top.

So, if you want to set up an AIO radiator as an intake, you need to set it up on the front or the right-side panel. It’s a very bad idea to install it on the bottom panel as it will cause air bubbles to get trapped at the pump that is at a higher point. This will affect your cooling performance and create pump noises.
Similarly, if you want to use an AIO as an exhaust, you need to install its radiator on the top panel directly over the CPU. You can also use the rear panel, but it’s not as common as the IO shield on most motherboards can obstruct the radiator.
Cooling Efficiency
Generally, using an AIO as intake will help cool the CPU slightly more as cooler air passes through the radiator fins. On the other hand, the radiator will introduce slightly warmer air inside the case as the air absorbs heat from the coolant in the radiator.
When you are using it as exhaust, the warmer air from inside the case passes through the radiator. So it won’t be as effective in cooling the liquid and consequently the CPU. But since the warmer air goes outside, it does not heat up other internal components like the GPU as intake AIO does.
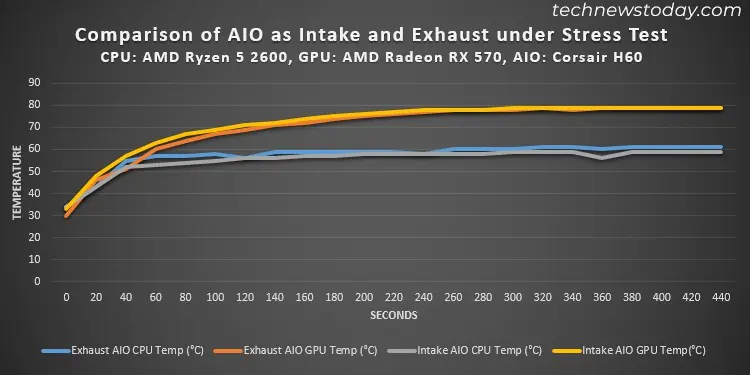
A slight difference in CPU temperature does not affect its performance, but the same is not true for a GPU. It’s always better to have it at the lowest possible temperature if you are into gaming or graphics processing for the best performance. So it might be better to set up AIO as an exhaust in such scenarios.
Regardless, if you use enough case fans, the difference in CPU/GPU temperatures is not that much for both cases (only about 2-5°C). So you actually don’t need to worry too much about the cooling performance.
Installation
The components on the motherboard and PC case matter more while setting AIO radiators as intake or exhaust if you have already bought a compatible AIO cooler.
You can place the AIO radiator in any orientation that doesn’t cause air bubbles to gather at the pump. However, you need to make sure that you are not bending the tubes too much or you can cause the coolant to leak through the gaskets.
Depending on your AIO’s tube, the profile of the PC components, case size, and position of the fan slots on the case, it may not be a good idea to mount your AIO in a certain way.

Since the cooling efficiency is not that different with enough case fans, you should choose a setup that doesn’t stretch, bend or squeeze the tubes. Exhaust is a good option for AIOs with shorter tubes as the top panel is closer to the CPU. Similarly, intake is the better choice with longer tubes.
The number of available fan slots for exhaust and intake also matter. For example, if your PC case comes with only one fan slot on the top, you can’t mount a two fan radiator as exhaust.

Case Airflow
Whenever airflow inside the case is concerned, you should treat the radiator fans same as case fans but with lower efficiency. The radiator slightly introduces turbulence and heats up the air passing through it.
So you need to balance the number of intake and exhaust case fans depending on how you set up the AIO. You must also have enough fan slots on the panels to set up all these case fans.
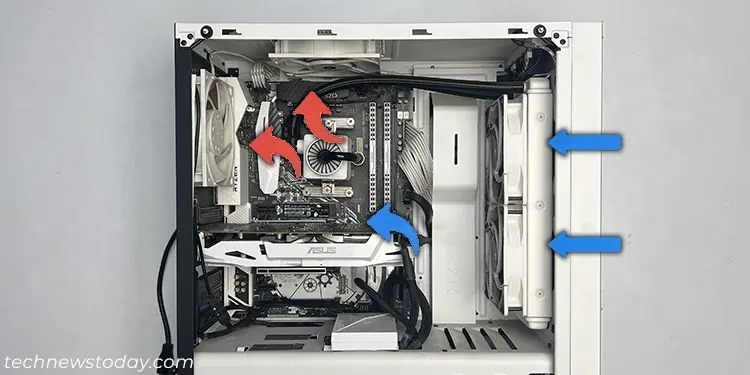
If you are using the AIO as an intake on the front panel, it’s better to have other intake fans on the bottom or side and exhaust on both the back and the top. If you are using it as an exhaust on the top, you need another exhaust at the back and enough intake fans on the front panel.
Which Configuration Should You Use?
In practice, using AIO radiators as intake or exhaust does not have any significant differences in the performance.
So what you should do is choose the radiator placement (front or top) depending on your motherboard and case. If the radiator fits most comfortably on the top, you should use it as an exhaust, and if it fits well on the front panel, use it as an intake.
You should just make sure to have enough case fans in the proper places to properly maintain the airflow inside the case. If the radiator fits in both panels without any significant tube bends, you can choose any configuration you like.