So, maybe you just updated your BIOS through your manufacturer’s website, and maybe now, the Windows screen won’t load, and youre left with only a black screen.
This is a fairly common issue that many users have faced at one time or the other. And most of the time, it’s either because of an improper BIOS update or due to a damaged motherboard. Black screen after BIOS is a confusing issue, mainly because youre left with no GUI and no instructions at all.
If you can somehow access the safe mode, youre in luck, as a fresh Windows installation or a startup repair can fix your problem. However, this will not be the case for a majority of users and in this scenario, you have to resort to other methods.
Fortunately, you’re in luck as this guide is prepared just for you. We have listed all the possible ways through which you can fix your black screen and return back to Windows normally. So, continue till the end to understand and troubleshoot your problem.
What Causes a Black Screen After BIOS?
- Corrupted peripherals
- Corrupted display drivers
- Corrupted MBR
- Power supply problems
- Overheating
How to Fix the Black Screen After BIOS?
Black screen after BIOS should be taken as a big deal because most of the time, you don’t even know what exactly caused it to happen.
However, we have listed all the fixes you can follow to try and solve your problem. If one method doesn’t work for you, be sure to follow every last one until the end.
Verify if Your System Is Responsive
First thing’s first, check if your system is responsive or not. If it’s not responsive, then that’s a totally different problem. However, if it is, then there’s usually something we can do about it.
So, press Win + Ctrl + Shift + B on your keyboard and notice if you hear a beep or not. If your computer is responsive, then you’ll hear a beep because the aforementioned key combination restarts your graphics driver.
Ensure Your Cables and Monitor Are Connected Properly
Whenever you face the problem of a black screen on your system, before diving into complicated steps, ensure that your monitor and cables are connected properly. So, unplug your monitor and firmly plug it back on again.
Furthermore, you can also check using a different monitor/cable and a different connection method (for eg. switch to DisplayPort instead of HDMI).
Unplug Your External Peripherals
If it’s an external peripheral that’s causing the issue, this method shall help you detect and fix your problem. So, follow the steps shown below:
- Turn off your computer.
- Unplug all your external devices (keyboards, mouse, speakers, external HDD, etc.).
- Now, turn on your computer and see if the black screen issue still persists.
- If there is no black screen anymore, then connect your devices back to your system one by one.
This can help you detect which device is corrupted and possibly set you on a path to fixing it. - If you happen to find the corrupted device, you should update this device’s driver to fix its misbehavior.
Check for Faulty GPU
A faulty and misbehaving graphical processing unit can often cause the screen to go black on your system. GPUs can crash when it is dirty, damaged, or overheated. This is not an unusual scenario and in this case, you should first remove your graphics card and see if the screen lights back up.
Luckily, we here have a dedicated article on how to remove your graphics card the right way. So, have a look at this guide to fix your issue.
Resume Your Interrupted BIOS Update
Black screen after BIOS usually means that your BIOS update failed halfway through. So, if that’s the case, resuming your BIOS update is the only way to move forward.
Listed below are the exact step to continue your BIOS update with three different cases. So, depending on what’s going on in your system, follow the steps shown.
If the Screen Is Completely Black
If the screen in front of you is completely black, without any letters or options, removing your batteries and reattaching them could help you fix your problem.
However, this method only works if your system has removable batteries. So, considering this, follow the steps below:
- Turn off your computer.
- Unplug your AC Adapter.
- Hold the power button for about 40 seconds to dissipate the remaining electricity from your system.
- Remove your battery.
- Now, reattach the battery, plug the AC Adapter back on and turn on your computer.
- Now, the BIOS update shall be automatically resumed.
- Do Not remove the AC adapter or interfere with the update process until it completes.
If Your System Restarts and Displays Some Instructions
In case your computer restarts and returns you with three to four steps of instructions, then follow the steps shown below to resume your BIOS update:
- With the help of another system, download the BIOS file depending on your computer’s model.
- Copy this file on your USB, in the root directory. The USB file format should be FAT32.
- Now, turn off your computer and then, hold the power button for about 15-20 seconds.
- Plug in your AC Adapter.
- Insert the USB drive with the BIOS file.
- Now, turn on your computer. The BIOS update process shall now be resumed.
If Your System Restarts and Displays Texts With a Yes/No Option
In case your computer restarts and displays texts with yes/no options, then follow the steps shown below to resume your BIOS update:
- Wait for a minimum of 60 seconds.
- Connect your AC Adapter.
- Click Yes on the screen. The BIOS update process shall now be resumed.
Perform a Startup Repair
Startup repair is a feature provided by the Windows OS that detects and troubleshoots problems that may arise during Windows startup. It can fix some of the common issues that are preventing your system from logging into the OS.
However, to perform a startup repair, you’ll have to access the Windows Recovery Environment.
If You Have a Recovery Drive
If you previously created a recovery drive, it can be useful for you now. If so, then follow the steps shown below:
- Turn off your computer.
- Connect your recovery drive.
- Turn on your computer.
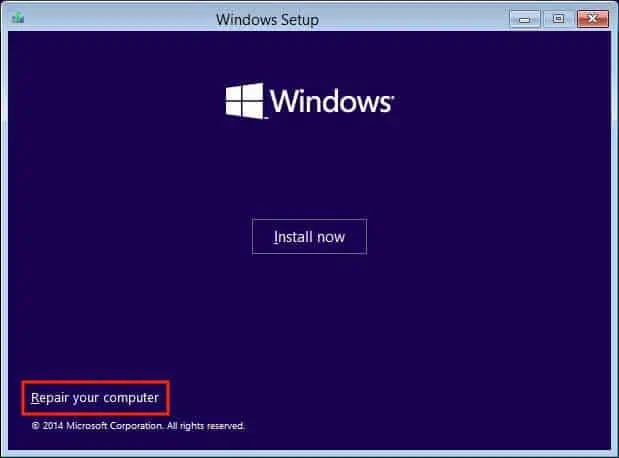
- Select Repair your computer.

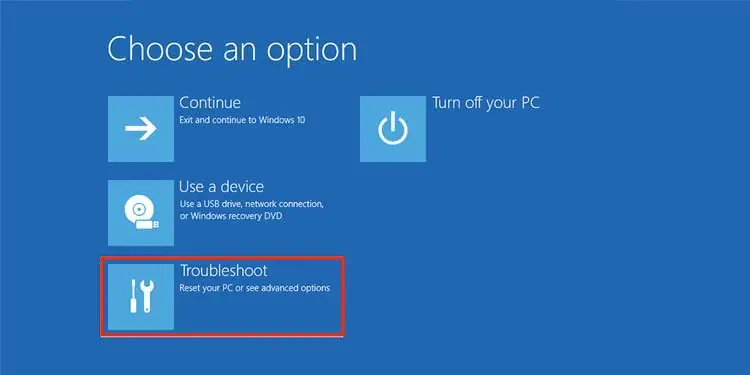
You’ll now be directed towards the Windows Recovery Environment. - Select Troubleshoot.
- Go to Advanced Options.
- Click on Start-up Repair.

- Follow the on-screen instructions to continue.
If You Don’t Have a Recovery Drive
If you don’t have a recovery drive, you’ll need to download the Windows installation file first and then copy it on a USB. Once this is done, follow the steps below:
- Turn off your computer.
- Connect your recovery drive.
- Turn on your computer.
- Select Repair your computer.
You’ll now be directed towards the Windows Recovery Environment. - Select Troubleshoot.

- Go to Advanced Options.
- Click on Start-up Repair.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to continue.
Repair Boot Record
The MBR (Master Boot Record) stores information about the location of your OS on your disk drive. A damaged boot record results in Windows not starting up properly and hence, a black screen. The MBR is created when you install Windows for the first time.
For this method, you’ll need the Windows installation file on an external drive (USB), as the MBR is created during the Windows setup process. The steps below show how you can repair your boot record.
- Turn off your computer.
- Connect your recovery drive.
- Turn on your computer.
- Click on Repair your computer.
- Select Troubleshoot.
- Go to Advanced Options.
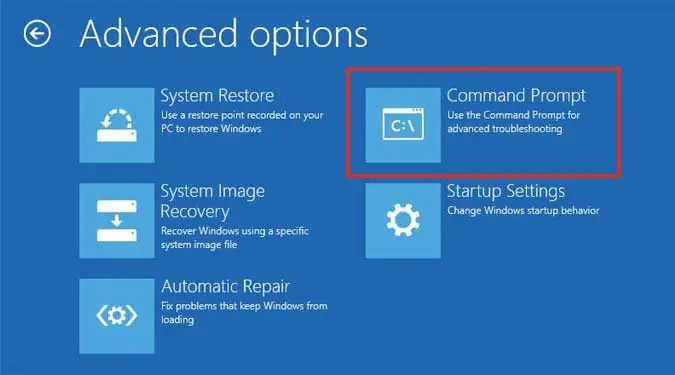
- Click on Command Prompt.

- Type the following commands, press enter after each one, and wait for the operation to complete:
bootrec /fixmbr
bootrec /fixboot
bootrec /scanos
bootrec /rebuildbcd - Remove your USB drive.
- Type Exit and press enter.
- Restart your computer.
Rollback Your Graphics Driver
This step requires you to boot your system using safe mode. To do this, you need a recovery drive with a Windows installation file. So, considering this, follow the steps shown below to update your graphics driver.
- Turn off your computer.
- Connect your recovery drive.
- Turn on your computer.
- Click on Repair your computer.
- Select Troubleshoot.
- Go to Advanced Options.
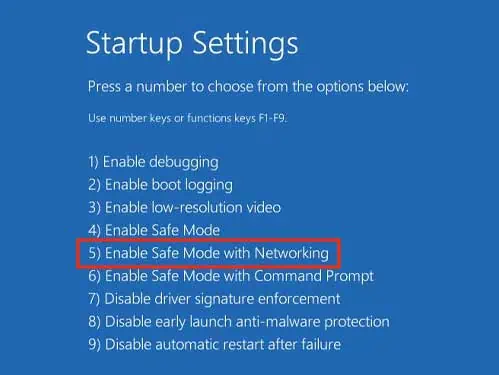
- Click on Start-up Settings.
- Then, select Restart.
- Once your system restarts, select Safe Mode with Networking by pressing the F5 key.

- Now, press Win + X and click on Device Manager.
- Expand Display adapters.
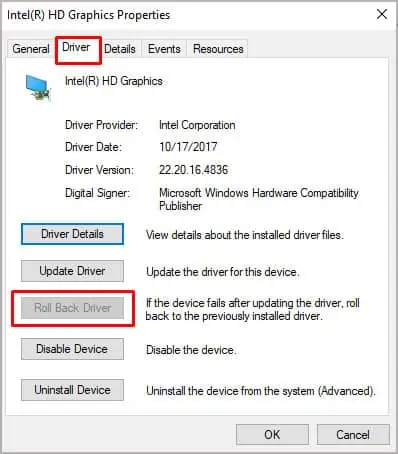
- Right-click on your graphics driver and select Properties.
- Navigate to the Driver tab.
- Click on Roll Back Driver.

Reinstall Your Graphics Driver
If the Roll Back feature isn’t available to you, you can try and reinstall your graphics driver. Here’s how to do so:
- Boot into Safe Mode with Networking as guided above.

- Now, press Win + X and click on Device Manager.
- Expand Display adapters.
- Right-click on your graphics driver and select Uninstall.
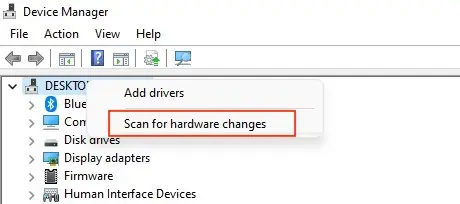
- Now, right-click on your computer’s name and select Scan for hardware changes.

- Follow the on-screen instructions to reinstall your graphics driver.
Repair/Replace your Corruptive Peripherals
Corruptive motherboard and disk drives are often known to cause a black screen after backing out of BIOS. This might indicate a problem with your CMOS memory or your CMOS battery. Luckily, this usually can be fixed. So, take your computer to the nearest repair center and see what happens on your internal peripherals.
And if unfortunately, that’s not the problem, then the only thing you can do is hope that it’s not beyond repair.