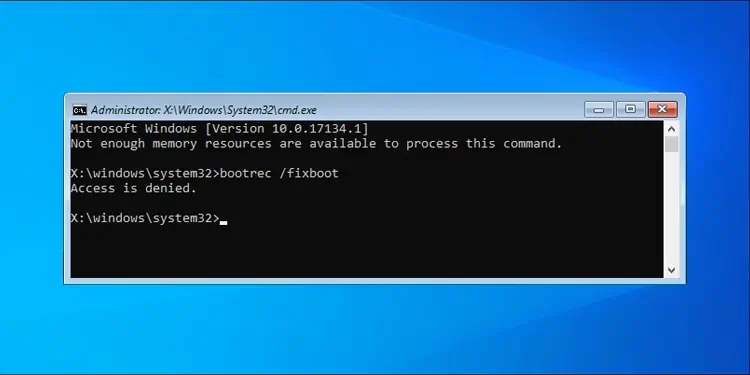
The Bootrec /FixBoot Access Is Denied error occurs when you try to repair a UEFI boot loader with this command.
The function of the FixBoot switch is to write a new boot sector to the system partition. But in UEFI systems, the EFI System Partition (ESP) is unmounted by default. As FixBoot can’t access the system partition, it fails and returns the Access Is Denied error.
You can use diskpart to manually assign a mount point to the EFI System Partition. After doing so, you should be able to use FixBoot without any issues. Alternatively, you can instead use BCDBoot to repair the EFI Boot Loader.
One more thing to note is that this error is very common in Windows versions 1707, 1709, and 1803. If your PC is running any of these versions, then we recommend that you use Windows Version 1703’s image to create a bootable media and copy the BCD.
Mount ESP with Diskpart and Repair
You can use diskpart to assign a drive letter to the EFI System Partition, then use FixBoot or BCDBoot to perform the repair. Here are the steps to do so:
- In winRE, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Command Prompt.
- Execute the following commands:
diskpart
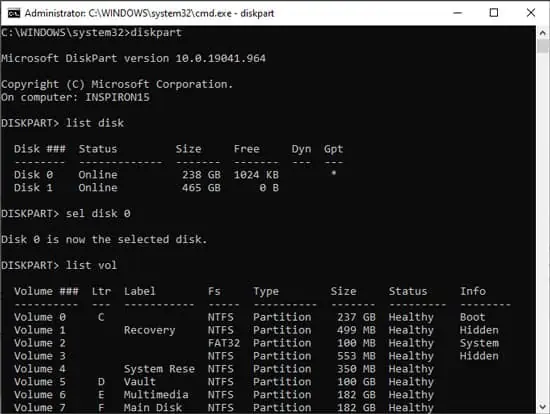
list disk - Determine the disk Windows is installed on and check if it has an asterisk (*) or not in the Gpt column. If it’s present, you can continue with the steps below. But if there is no asterisk, you should instead check the Repair Boot Sector on MBR Disk section at the end.

- Replace 0 with the Windows disk if different and execute the following commands:
sel disk 0
list vol - From the list of volumes, find the UEFI volume. You can recognize it by its usual size (100MB), FAT32 in Fs section, Boot in the Label section, or System in the Info section.
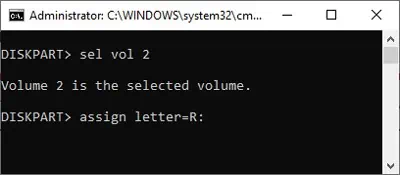
- The EFI System Partition is Volume 2 on my PC, so we’ll use that for tutorial purposes. Change it accordingly if yours is different in the steps below. Also, replace R: with a drive letter that’s not in use if necessary.
- Execute the following commands:
sel vol 2
assign letter=R:
- Type
exitand press Enter. - Execute the following commands:
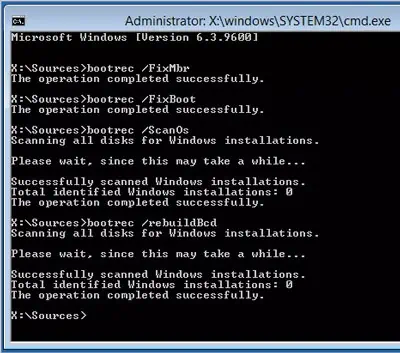
bootrec /FixMBR
bootrec /FixBoot
bootrec /ScanOs
bootrec /RebuildBcd
- If you’re able to run FixBoot now, you can stop here. But if you’re still encountering the same error, use the commands listed below instead.
- Type the following command and replace R: with the EFI partition’s letter if different.
cd /d R:\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\ - If you receive a The system cannot find the path specified error message, run the same command on alternative paths:
cd /d R:\Boot\
cd /d R:\ESD\Windows\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\ - Type
bcdboot C:\Windows /s R: /f UEFIand press Enter. - Rename the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) for backup purposes with the following command:
ren BCD BCD.bak - Recreate the BCD with the following command:
Bcdboot C:\Windows /s x: /f ALL - Type
exitand press Enter. - Restart your computer and check if you can boot properly now.
Delete ESP and Use Automatic Repair Tool
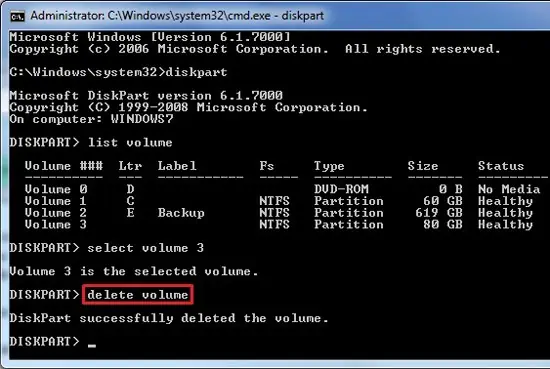
The Automatic Repair tool is the go-to option to combat any kind of startup issue. But before using it, you should delete the system partition to ensure that a corrupt EFI system partition (ESP) isn’t the issue. Here are the steps to do so:
- First, use Windows Version 1703’s ISO to create a bootable disk or USB.
- Boot from the media and select Repair your computer.

- Select Command Prompt and use diskpart to delete the system partition.

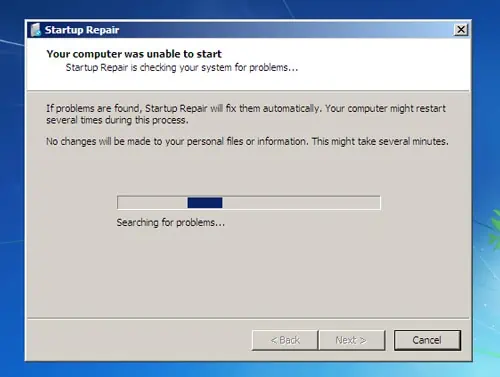
- Now, exit cmd and use the Startup Repair tool.
- Login to your account when prompted to proceed with the repair.
- Wait for the automatic repair tool to do its job. This will typically take 5 – 15 minutes on most systems.

If the repair tool resolves the issue, great. If not, you’ll see a message along the lines of Startup Repair couldn’t repair your PC. In this case, select Advanced Options and try out the other solutions from our guide.
Uninstall Latest Updates
A common issue that users often report is that Windows won’t boot after an update. In cases like this, uninstalling the latest update is generally enough to resolve the issue. Here are the exact steps to do so:
- In winRE, select Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Uninstall Updates.

- Select Uninstall Latest Quality Update and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Repeat the same steps to uninstall the feature update as well.

- Restart your PC and check if you can boot properly.
Clean Install OS
If the issue is still not resolved, a clean reinstall of the OS is likely the final option. Keep in mind that this will remove everything from your PC. So, if you don’t want to lose your files, you may want to hold off on this temporarily. Here are the steps to clean install Windows:
- Insert a Windows Installation Disk or USB.
- In the setup wizard, select Next > Install Now.
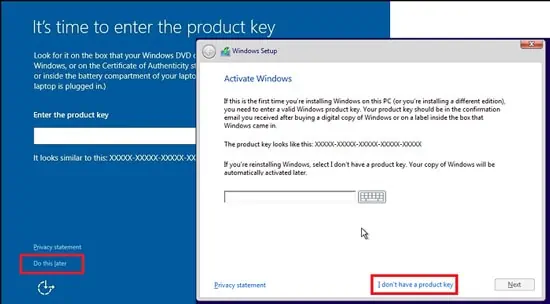
- When prompted for the product key, select the Do this later or I don’t have a product key option.

- Select the OS Edition, accept the license terms, and select Custom: Install Windows Only (Advanced).
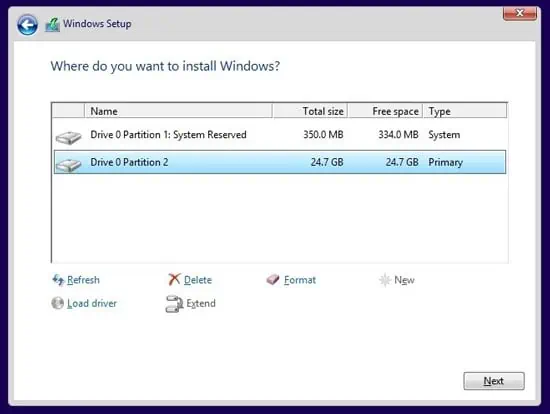
- Select a drive and press Delete. Repeat this until there is only one unallocated drive left.

- Select the unallocated drive and press New > Apply > OK.
- Select the newly created Primary Partition and press Next.

- Windows will now install and your PC may reboot a few times during the process.