All, if not most, motherboard and CPU allow the memory to run on dual channel if configured correctly. However, if you have gotten a pre-built PC, the memory module might be set to run on a single channel, lowering your system’s memory bandwidth.
Running RAM on a dual-channel setup doubles the memory bandwidth giving you a huge performance boost when running a CPU-intensive program. When you have two identical memory modules using alternate DIMM slots (A2 and B2) on the motherboard, the system is likely running a dual-channel setup.
However, the system might not give maximum performance on dual channel mode if there is a mismatch in capacity or frequency. And if the DRAM bus width does not match, the system may not run on dual channels even if you have the correct memory module arrangement.
So, here is how you can check if the memory is running on a dual-channel mode for maximum performance.
Via CPU-Z
CPU-Z is a great application to check your system specs on both desktops and laptops. In our case, you can use it to check whether the system is running in dual or single-channel mode.
- Go to CPU-Z’s official website and click on Setup English.

- Click on Download.

- Run the executable file once the download completes.
- Follow the installation process and Run CPU-Z
- Go to the Memory tab.
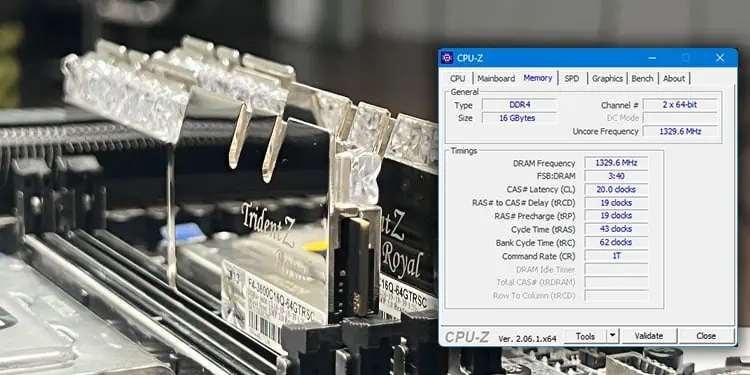
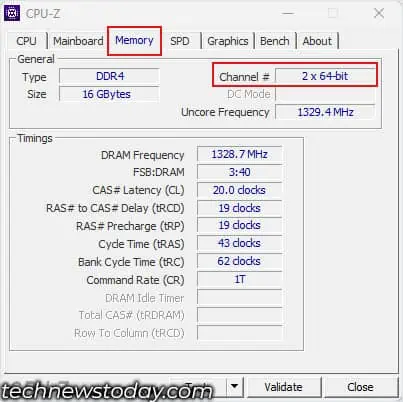
- Here check Channel #.

If it says 2 x 64-bit or dual, the memory runs on dual-channel mode. If it says 1 x 64-bit, it is running on single-channel mode. Here, you can also get the actual frequency of your DDR RAM.
CPU-Z will also indicate 2 x 64-bit or dual if the system is on Flex or Asynchronous Dual Channel mode. When you have two memory sticks of different capacities on dual channel slots, the system runs on Asynchronous or Flex dual channel mode.
In this mode, a lower-sized memory stick will run on a dual channel with a higher-capacity memory. Once the memory usage exceeds double the memory size of the lower RAM, the remaining memory will run on single-channel mode.
For example, if you have a system that runs on 4GB and an 8GB memory stick. The first 8GB (4GB RAM and 4 out of 8GB RAM) will run on a dual channel. Once the system starts to use more than 8GB, the remaining 4 out of 8GB modules will run on a single channel.
Although running on a dual channel, the memory module will only be able to maximize performance when you have two identical memory modules.
You can confirm this by checking your BIOS.
Check from BIOS
BIOS (Basic Input Output System) contains all the information about the hardware connected to the system. And you can access your motherboard BIOS to check the memory slot occupied and its capacity.
- Turn off the PC and turn it back on.
- Repeatedly press the BIOS key during startup. The BIOS key will be different depending on the motherboard. On most PCs, the BIOS key is the delete key or one of the function keys.
- Once you are in the BIOS, search for system or memory settings. Again, BIOS settings are different depending on the motherboard so you need to navigate the BIOS to find the correct setting.

If the motherboard has two memory slots, and both of them are equipped with identical RAM sticks, the system is running on dual channel mode with maximum performance.
These are the requirements for maximum performance and system stability when using a dual-channel setup.
- Both RAM sticks should run on the same frequency.
- Both RAM should have the same capacity.
- Both RAM should have the same number of chips,
- Both RAM should have a memory chip on one or both sides.
- Both RAM should have the same CAS Latency and memory timings.
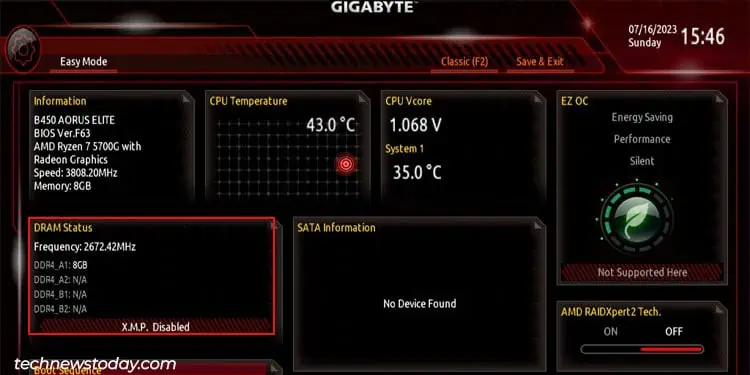
If the motherboard has four memory slots, you will likely see these four writings, DIMM_A1, DIMM_A2, DIMM_B1, and DIMM_B2 in the BIOS.
It should also display memory module details depending on the DIMM slot occupied. These details include memory frequency, timings, and capacity.
If both the memory are identical and occupy slots DIMM_A2 and DIMM_B2 or DIMM_A1 and DIMM_B1 the CPU is in dual channel mode.
If the memory capacity is different but the modules occupy alternate slots (A2 and B2), the memory is running on asynchronous dual-channel mode.
Check the Motherboard
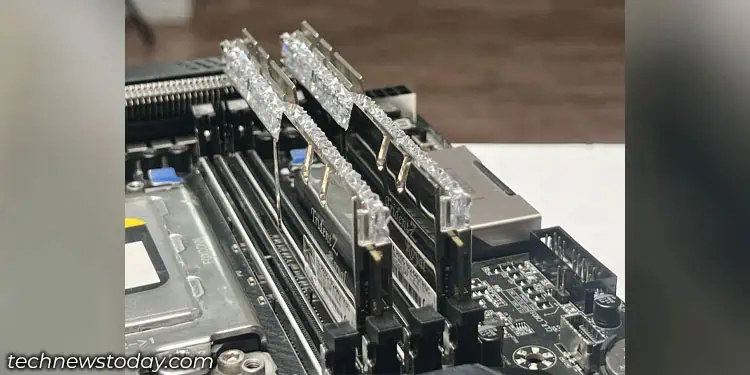
The motherboard will have two, four, eight, or even sixteen DIMM slots. However, general-purpose or gaming motherboards will have two or four memory slots. You can also check these slots and memory arrangement by accessing the motherboard physically to determine whether the RAM is running on dual channel mode.
First, check the number of DIMM slots available on your PC.
- Remove all the screws holding the side panel.

- Take the side panel out of the CPU case.

- Here, check the number of DIMM slots. These memory slot are located near the CPU socket.

If you see identical memory modules occupying alternate slots or color-paired slots (A2 B2 or A1 B1), the system is in dual-channel mode. If you have all four memory slots occupied with identical memory sticks, both channel A and B will work on the dual channel.
If the motherboard has two identical memory sticks but are placed successively, you need to re-arrange them in order to run them in dual channel mode. You can refer to the motherboard user manual to install the memory module in the correct slot.
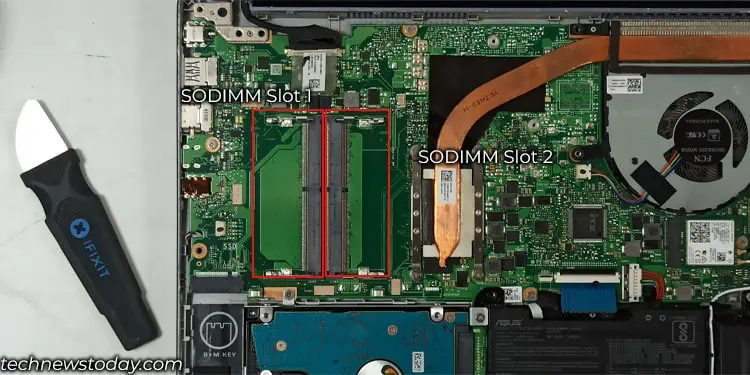
In the case of laptops, these devices usually have two memory slots. And you can check dual or single channels directly from CPU-Z. However, some latest laptop motherboards might only have one memory slot and the other memory module is soldered into the motherboard itself.
In such cases, the system will only run in dual-channel mode if the second memory module is identical to the memory stick that is soldered on to the board.
To check the number of memory slots on the motherboard of your laptop, you first need to remove the back plate.
- Remove any screws that hold the back plate.

- Take a pry tool and insert it in the small opening between the backplate and the rest of the laptop.

- Turn the pry tool to unclip the black plate from the laptop.
- Repeat this step all across the laptop.
- Gently take the backplate out to access the laptop’s motherboard.
- Now, check the memory slots.

If both slots are occupied, and your total memory capacity is 2, 4, 6, 8, 16, or 32 GB and so on, the system is running on dual channel mode.