Before 2020, when DDR5 was yet to be released, DDR4 memory was the perfect and the only choice when it came to choosing a memory module for your PC. It offered a great price-to-performance ratio. And choosing a DDR4 RAM with higher capacity and frequency was great for the long run.
However, with the release of DDR5 memory, most users are confused whether to switch to the newer technology or stick to the same older-gen DDR4 memory sticks.
In this article, we’ll break down the pros and cons of DDR4 and DDR5 memory in simple terms and help you make an informed decision about which memory module to choose from.
Let’s get started!
DDR4 RAM

DDR4 memory was the perfect choice for RAM for most, if not all, users before the release of DDR5. DDR4 offered much higher transfer rates with lower CAS latency. And running RAM on a dual channel would further improve the memory bandwidth.
DDR4 RAM provided data transfer rates from 2133 MT/s to 5333 MT/s (MegaTransfers per Second). And with a single stick of memory supporting up to a capacity of 256GB, DDR4 also used to run in 1.2V, which was 20% lower power consumption compared to the previous generation DDR3 memory.
Furthermore, the prices of DDR4 memory are relatively cheap when compared to the same capacity DDR5 sticks. This price-to-performance ratio of DDR4 RAM makes it a great choice, especially if you are on a budget.
- Offers great performance on a budget.
- Has a lower CAS Latency and memory timings compared to the newer generation, DDR5.
- A higher frequency and capacity DDR4 RAM is still somewhat future proof although being a decade-old technology.
- A newer CPU and motherboard will not support DDR4 memory sticks in the foreseeable future.
- Top-of-the-line DDR4 memory is still expensive or in a similar range compared to the entry line DDR5 memory.
DDR5 RAM

DDR5 is the latest generation of Double Data Rate memory chips which offers much higher memory frequency with even higher capacity in a single stick.
DDR5 RAM supports data transfer rates ranging from 4800 MT/s to 8000 MT/s. This number is extremely high compared to a DDR4 RAM’s speed. DDR5 also uses just 1.1V, which is almost 10% lower when compared to the DDR4 voltage requirement.
These higher transfer rates offered by DDR5 are great when the CPU is constantly accessing the memory. You will see a massive performance boost when running CPU-intensive applications. Other times, not so much.
- Higher transfer rates compared to DDR4.
- Future proof.
- Low power requirement
- Technology is new and many applications are still not able to utilize DDR5 full capability.
- Higher CAS latency and memory timings.
- Requires an entirely new motherboard and CPU that supports DDR5.
DDR4 Vs DDR5
Now, let us look at a few other parameters to see which is better, DDR4 or DDR5 ?
Channel Architecture
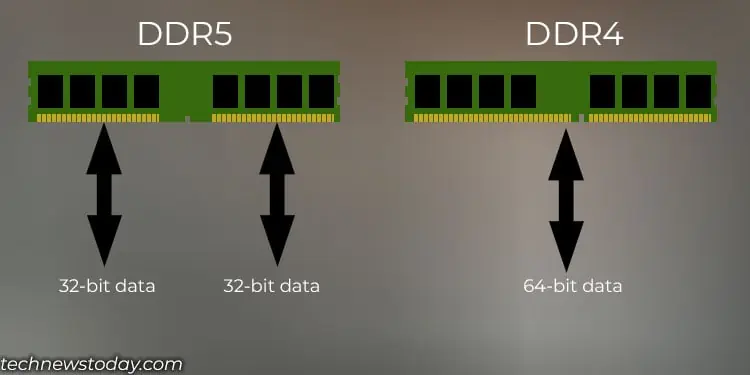
DDR4 RAM architecture allows it to use a single 64-bit bus to transfer data to the CPU. And if the memory modules are in a dual-channel arrangement, a multi-core CPU can access both memory modules in parallel through the two memory channels.
Meanwhile, the memory controller within the processor handles the distribution of memory requests among the available channels and modules, improving the overall memory performance.
DDR4 memory first collects data to a 64-bit bus buffer before transferring data to the CPU. Once the buffer is full, the RAM then transfers this 64-bit data through a 64-bit data bus to the CPU. However, it’s not always that the 64-bit buffer is full.
If the buffer is only partially filled, the remaining is filled with junk data to transfer the information to the CPU. This takes time, and thus, the latency increases.
DDR5 also uses the same 64-bit data bus to transfer data. However, the bus is further divided into two 32-bit sub-channels that operate independently.
So, even if the 64-bit bus is partially filled, data are sent without having to fill it with junk data. This decreases the latency on DDR5 modules.
You can also find DDR4 and DDR5 memory with ECC (Error Correcting Code). However, these memory are primarily used on server, data center or workstations where data integrity is crucial.
DDR4 memory with ECC uses a single 8-bit ECC bus. On the other hand DDR5 with ECC uses two 8-bit ECC bus, one per single sub channel.
Winner: DDR5
Power Management

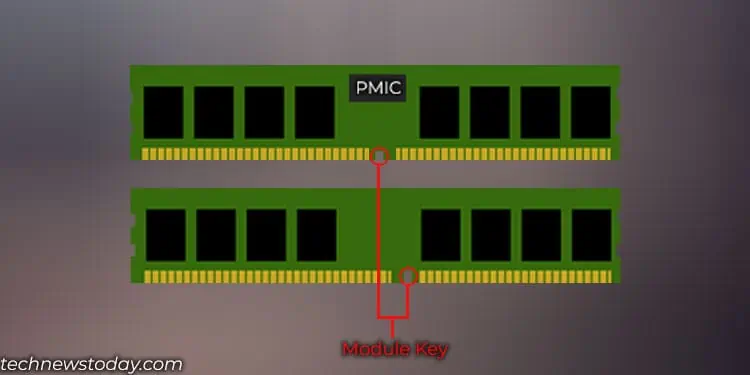
Power management on the DDR4 module was done through a Power Management Integrated Circuit (PMIC) that was available on the motherboard. On DDR5, this PMIC chip is embedded into the memory module.
The PMIC supplies power to each DDR chip on the memory. The signal from PMIC degrades further away from the DDR chip. Moving it to the memory module improves signal integrity which ramps up the memory speed.
Winner: DDR5
Transfer Rates and Latency
Right off the bat, the DDR4 frequency on its top-tier memory module is almost equal to the frequency on the DDR5 entry memory module. With improved power management, DDR5 allows data transfer rates to reach 4000 MT/s to 8000 MT/s. This number is extremely high compared to DDR4’s 2133 to 5333 MT/s.
However, with the increase in transfer rate, the CAS Latency (CL) also increases. CAS Latency refers to the amount of time (in clock cycle) required for the RAM to access data and transfer it to the memory controller. Lower CL is better.
DDR4 memory has a lower frequency and CL ranging from 13 to 22, whereas DDR5 has a higher frequency and CL higher than 22.
Winner: DDR5 in terms of transfer rate. DDR4 in terms of latency.
CPU and Motherboard Compatibility
Talking about compatibility, neither of these devices is backward or forward-compatible. The DDR4 memory module requires a DDR4 memory slot and the DDR5 module requires a DDR5 slot.
As of now, most motherboards you find in the market supports DDR4. However, motherboards that support DDR5 are mostly high-end motherboards.
Furthermore, the CPU also needs to support the memory type. Right now, Ryzen’s 7000 series and Intel’s 12th and 13th gen support DDR5 technology. So, if you are planning to get DDR5 RAM, you also need to match it with the motherboard and the CPU.
If you are upgrading your current system, we have a detailed article on choosing the correct memory for your system.
Winner: DDR4(For now)
Pricing
When you compare prices of DDR4 and DDR5 memory modules with similar capacity and frequency, the price of DDR5 memory looks somewhat lower than DDR4 modules.
The performance of a top-tier(expensive) DDR4 memory module, on paper, is almost equal to the performance of an entry-level (relatively cheap) DDR5 memory.
However, the cost of the latest CPU and motherboard that support DDR5 outweighs the price of the CPU and motherboard that support DDR4.
In total, you will end up paying a lot more when you use DDR5 memory.
Winner: DDR4
Future Proofing

There is no doubt that DDR4 technology has improved a lot since the time of its release. Still, today, these memory modules offer a much higher price-to-performance ratio.
However, with the release of DDR5 memory, DDR4 RAMs will inevitably become obsolete not so far ahead in the future. Even today, most motherboard manufacturing companies have already stopped the production of boards that support DDR4 and have already switched to DDR5.
And there is also a possibility that the 14th generation Intel CPU, Meteor Lake, might not support DDR4 memory.
Winner: DDR5
Final Thoughts
So, should you upgrade to DDR5? If you are building a new PC or upgrading one and have the budget, definitely choose DDR5 as it will be future-proof for more than a couple of years.
But if you are on a budget, choosing DDR5 RAM means you would need to get the latest CPU and motherboard that supports DDR5, which are quite expensive.
All CPUs in the market now except Ryzen 7000 series and 13th gen Intel support DDR4. And the price for the motherboard that supports these CPUs are not so expensive either. These CPUs will perform better and are also quite future-proof as well.
Besides pricing, DDR4 motherboards also offer gaming performance close to DDR5 memory. So, if you’re getting a PC mainly for gaming, you cannot go wrong with DDR4 Memory.
However, if your main priority is performing CPU-heavy tasks, like video/photo editing and 3D rendering videos, DDR5 will be a good choice in the long run.

