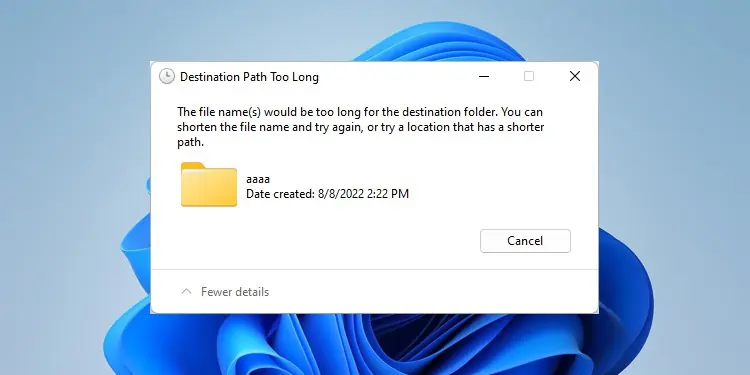
Windows has a limitation of 255-260 characters for the path length of a folder. If while transferring a folder, the new path length of the folder or any subfolder were to exceed this number, Windows does not allow transferring the files at all. Instead, it’ll give you the “Destination Path Too Long” error message.
The full path includes the drive letter, colon, name components together with backslashes as well as a terminating null character. For instance, C:\Windows is the full path of the Windows folder and it’s path length is 11.
People often encounter this issue while moving or copying saved web pages where the supporting files have very long names. They are not able to transfer some files which causes issues while viewing the web document.
In such cases, there are a few things you can do to avoid or resolve this issue, which we provide in this guide.
How to Fix Destination Path Too Long Error
There are a few ways to resolve the Destination Path Too Long Error while transferring a file on Windows. Go through the possible solutions we have mentioned below and apply one according to your preference.
Rename Folder/File
The first thing you should do is rename the folders with long names along the destination path. You should also change all long names in the source folder and it’s subsequent files and subfolders. Since Windows has a maximum limit of 256 for a path, make sure the directory length (after copying/moving) of any folder or subfolder does not exceed this number.
Use Command-line Interface to Move/Copy Files
It is possible to use the robocopy utility to move or copy your files and folders while disregarding the maximum path limit.
However, robocopy is not exactly a tool intended to copy or move but synchronize two folders. So it actually transfers the contents of the source folder to the destination folder instead of transferring the source folder itself.
Here’s how you can use this CLI tool to avoid the “Destination Path Too Long” error:
- Open Run by pressing Win + R.
- Type
cmdand press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open Command Prompt as administrator. - Enter the following command to copy the contents of a folder to another location:
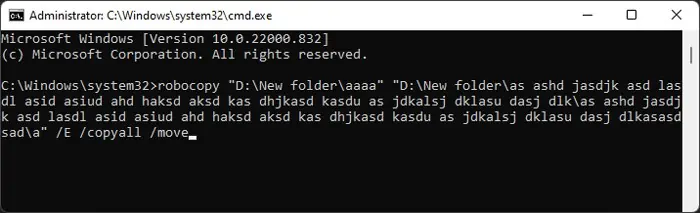
robocopy “Source folder path” “Destination folder path” /E /copyall
Make sure to replace the folder paths. - To move the contents of the source folder, append the flag /move to the command. i.e.,
robocopy “Source folder path” “Destination folder path” /E /copyall /move
- If you find it difficult to enter the paths, there’s an easy way to do so:
- Navigate to the folders in the File Explorer.
- Right-click on the folder and select Copy as path (Don’t copy with Ctrl + C).
- On the Command Prompt, press Ctrl + V or right-click when you need to enter the path.
Substitute the Path
Another way to resolve this issue is to substitute a long part of the path with a shorter path. In this process, you link the destination folder’s path to a new drive or another location. So, when you add files/folders to the new location, your system will update the previous location as well.
If the new path is shorter than the max path limit, this method bypasses the above error. However, if the folder you are copying itself contains subfolders with long names (more than the limit), this method may not work.
There are mainly three ways to substitute the path on a Windows OS using built-in tools. You can pick any one of them.
Substitute the Path With Virtual Drive Letter
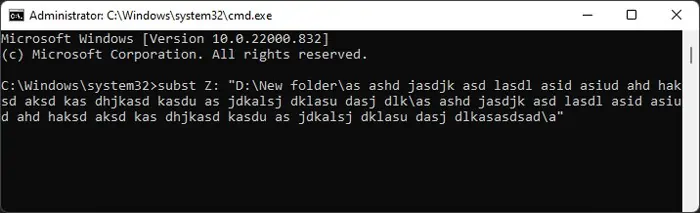
This method creates a virtual drive and links it to a folder, the destination folder in this case. You need to use the Subst command on the Command Prompt to create a substitute drive.
However, one thing you should keep in mind is that you should not use the admin level Command Prompt.
For some unknown reason, if you use this command with the Elevated Command Prompt, you can only access the new virtual drive from the Prompt itself. But if you run the command from an unprivileged Command Prompt, you can access the drive from the File Explorer as well.
Although this has been a subject of discussion on lots of public forums, no any convincing reason has been found yet, as to why this happens. If you know the exact mechanism behind this, do let us know in the comments.
Regardless, here’s how you can associate the path with a drive letter:
- Open Run.
- Type
cmdand press Enter. - Enter the command
subst Z: “Full path of the destination folder”. You can replace the drive letter (Z:) with any unused letter in your system.
Then, copy or move any folder/file you want to the new drive using the File Explorer. If you open the destination folder using the original path, you’ll find that it now contains the transferred folders/files as well.
If you want to delete the virtual drive, you can enter the command subst Z: /d
Share Folder and Map to Network Drive
Another method is to share the destination folder and map it to a network drive. To do so,
- Navigate to the destination folder using the File Explorer and right-click on it.
- Go to the Sharing tab and click Share.
- Select the user account and click Share again.
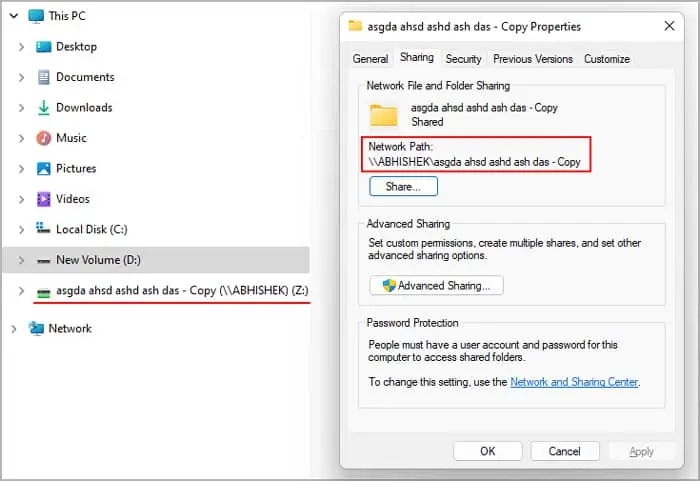
- Copy the path under Network Path.

- Click Apply and OK.
- Now, right-click This PC on the File Explorer’s navigation panel and select Map network drive or Show more options > Map network drive.
- Select a new drive letter and paste the Network Path from step on the Folder textbox.
- Click Finish.
Now you can find the shared folder mapped as a network drive inside This PC ->Network Locations. Any folders you transfer to this location will appear on the destination folder.
Create Symbolic Link
You can also create a symbolic link to the destination folder. While the previous methods created new virtual drives for the folder, this method can associate any folder with another. To create a symbolic link:
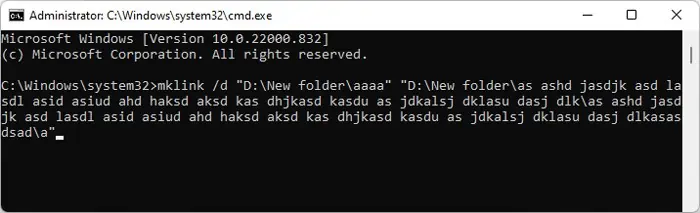
- Open Run and enter
cmd. - Enter the command
mklink /d “New Short Path” “Destination Path”while replacing the paths.
Similar to the above methods, transferring any file or folder to the new path will only consider the new path’s length.
Using Compression Tools
Some third-party compression tools like WinRAR and 7-zip also allow transferring files and folders along with compressing and decompressing them. The also don’t follow the 256 or 260 path character limit while transferring the files, so using them is an easy way to avoid this issue.
The exact process for each programs is different. However, we have listed the steps you need for the 7-Zip File Manager below.
- Open the 7-Zip File Manager using the search function (Win + S).
- Navigate to the the folder you want to transfer.
- Right-click on the folder and select Move To or Copy To.
- Enter the destination path. You can also click on the three-dot icon, browse the folder and click OK.
- Click OK to copy or move the folder.
For other apps, try performing similar steps.