The easiest way to tell if your desktop has Wi-Fi is by checking the back side of your chassis for Wi-Fi support. Your desktop might have a built-in Wi-Fi module, a PCIe Wi-Fi adapter, or a USB Wi-Fi receiver installed. Alternatively, you may find a port labeled “Wi-Fi” on the back of the computer.
But there are cases where the Wi-Fi adapter or its driver is disabled in your system. This will restrict the OS from accessing Wi-Fi, leading you to think that the desktop does not have Wi-Fi. So you need to perform several steps to determine if your desktop has Wi-Fi.
Check Motherboard Manual

Although you can check if your desktop has Wi-Fi from the back of the CPU case, it’s not always that you have complete access to the CPU case. In such a situation, you can use the motherboard’s or the desktop’s user manual.
Your motherboard user manual contains every detail about the motherboard, its supported component, and how to connect each component. Using the manual, you can check if your motherboard supports Wi-Fi.
The manual will have a section explaining the steps to connect the Wi-Fi antenna to the motherboard if it supports Wi-Fi. But it is highly likely that your desktop does not have Wi-Fi if the user manual does not mention anything about Wi-Fi.
Check System Tray Icon
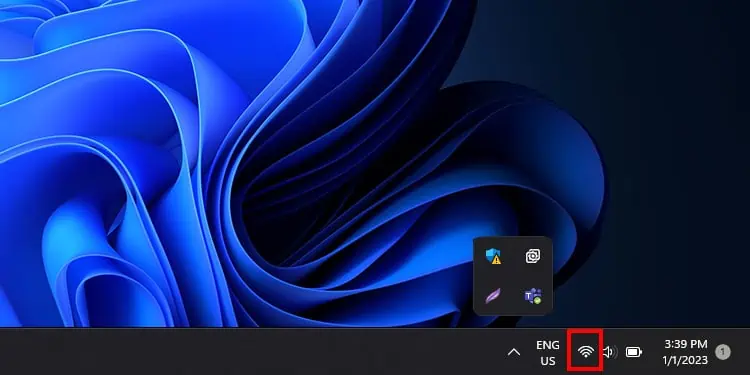
The System Tray Icon contains important Windows functionalities such as sound, keyboard input type, date/time, and most importantly, Wi-Fi. You can rest assured if you see a Wi-Fi icon because your desktop has Wi-Fi.
Check Windows Settings
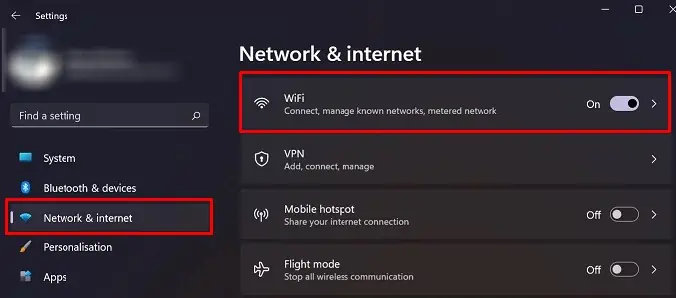
Network and internet settings in Windows allow you to access and change any network-related settings. This includes Wi-Fi as well. If you do not see Wi-Fi listed on the Network and Internet settings, your desktop does not support Wi-Fi.
- Press the Windows + I key to open Settings.
- On the left panel click Network & internet.

Now, on the left panel, you will see a list of network settings. If the list contains Wi-Fi, your desktop has Wi-Fi. Enable it to connect to a network wirelessly.
You will not see Wi-Fi in Windows settings if it is disabled from the Control Panel. In that case, you need to check Network Connections as well.
Check Network Connections
Network connections contain the list of all your system’s built-in or connected network devices. Besides this, you can also disable/enable each device driver, manage its properties and diagnose the device. Using Network connections, you can determine whether your system has Wi-Fi.
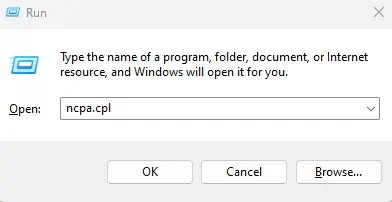
- Press the Windows + R key to open Run.
- Type
ncpa.cpland press Enter to open the Network Connections window.
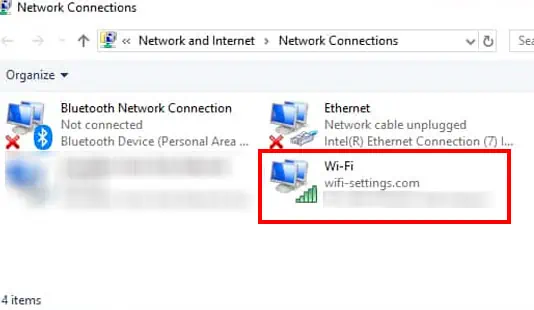
- Here, check if Wi-Fi is listed.

If you see Wi-Fi is among the network devices, your desktop has Wi-Fi. However, if the Network adapter driver is removed/disabled from the system, Network Connections will not display Wi-Fi on the list of network devices.
To ensure this is not the case, we recommend you check if the device is removed from the Device Manager or disabled from the BIOS.
Check Device Manager
When uninstalling a driver using Device Manager, the OS will not acknowledge the device. Even if the device is connected, you cannot access its functionalities. The same goes for the Wi-Fi driver.
You cannot access Wi-Fi settings if the Wi-Fi driver is uninstalled or not installed at all.
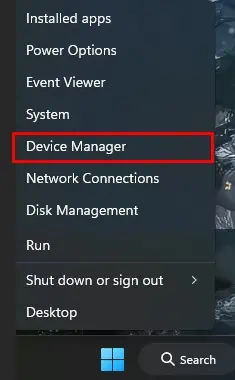
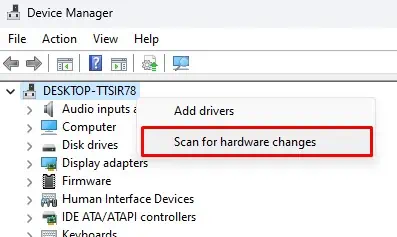
- Press the Windows + X key and select Device Manager.

- Right-click on the top of the list where you see the Desktop name.
- Click on Scan for hardware changes. By doing this, the Device Manager will automatically check the system for drivers and install them.

- Now, Check Network connections to see if you see Wi-Fi.
Check BIOS
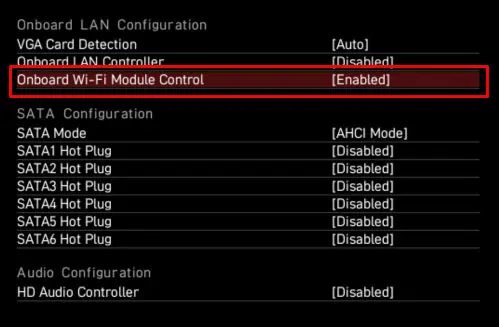
BIOS, or the Basic Input Output System, allows users to access and change the settings related to hardware connected to the motherboard. You can also enable and disable Wireless LAN or WLAN using the BIOS. If disabled, your OS will not detect the Wi-Fi adapter.
You need to enable WLAN in the BIOS to ensure that the OS uses Wi-Fi.
- Repeatedly press the BIOS key during startup to enter the system BIOS. The BIOS key could be any of the function keys or the delete key.
- Navigate and find settings such as, WLAN, OnBoard WLan Controller or WLAN enable and Enable it.

- Save and exit the BIOS.
- Boot into the OS and check if the Network Connections displays Wi-Fi.