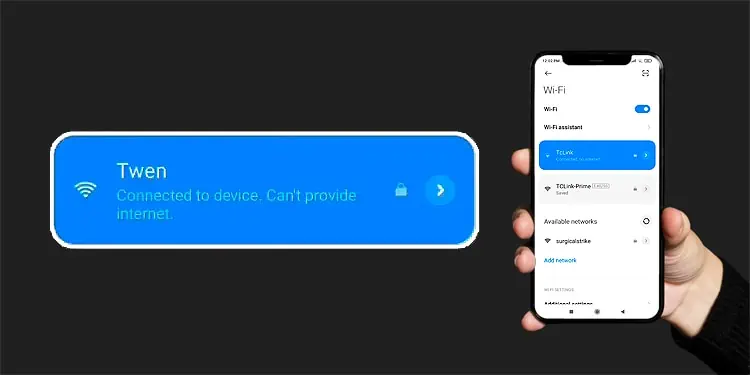
Sometimes, your phone will connect to a network, but you won’t actually have internet access. Android devices like Pixel and Xiaomi indicate this state with the “Connected to device. Can’t Provide Internet.” error message.
Often, restarting your phone and router is all that’s needed to fix this problem. In case the error persists, you can follow the troubleshooting steps from this article (in the order shown) to get internet access again.
Step 1: Verify Internet Access on Network
When troubleshooting, you should start by figuring out whether the problem is network-wide or specific to your device. Simply test internet access on any other device to do this.
If only your device is having internet access issues, skip ahead to Step 2.
On the other hand, if your entire network doesn’t have internet access, you should first check the router’s indicator lights or those on the modem if you’re using one. This will help you determine the possible causes, which include:
- Loose internet cable
- Incorrect router operation mode
- Faulty hardware (router, modem, internet line)
- Service outage in the area
Reseating all the connections, restarting the router/modem, and factory resetting the router (if required) will generally get your internet working. But if these fixes don’t help, you should contact your ISP for support.
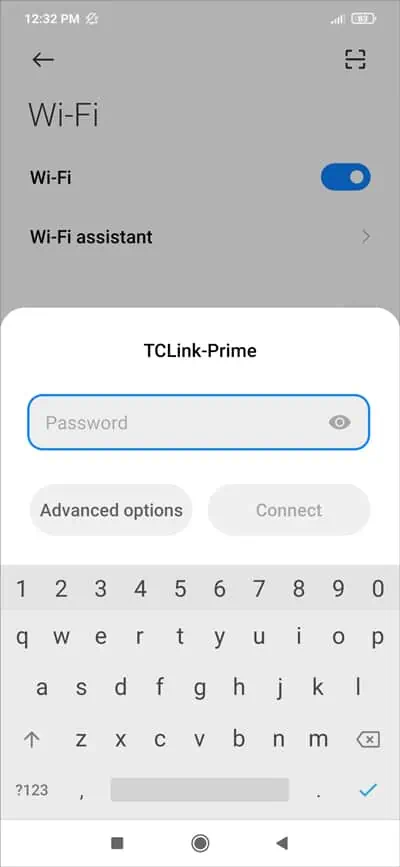
Step 2: Forget Network and Reconnect
Assuming the problem is on your device only, forgetting the network and reconnecting to it could fix the issue. To do this,
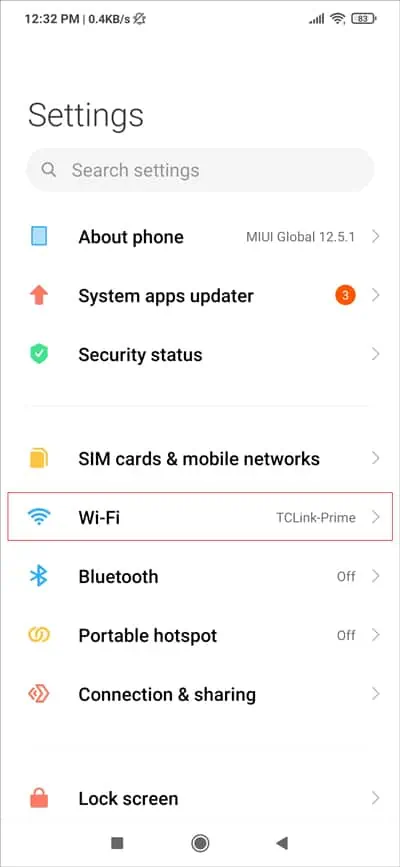
- Launch the Settings app and tap on Wi-Fi.

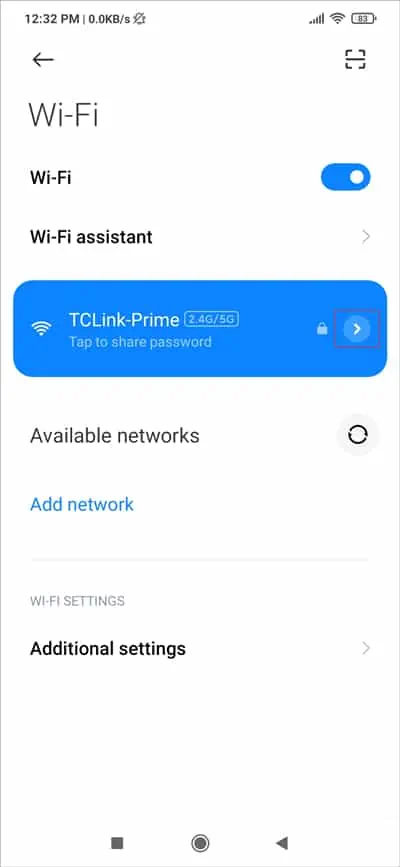
- Connect to the Wi-Fi network and tap the Details arrow.

- Tap Forget Network from the bottom and press Ok to confirm.

- Now, tap the network again and enter the password to reconnect.

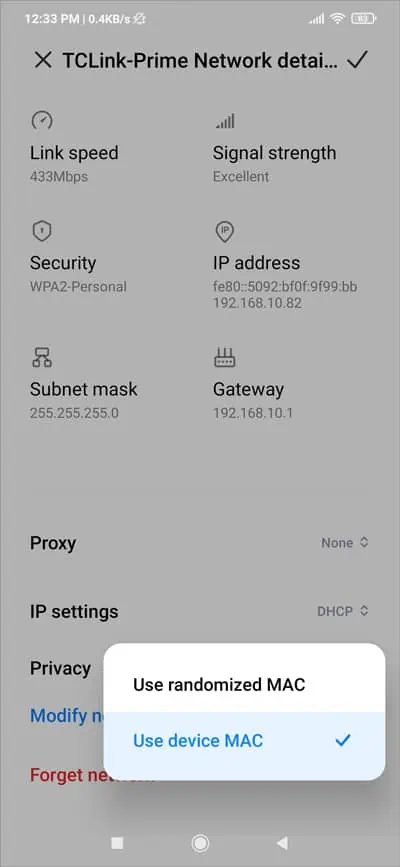
Step 3: Change Network Configurations
The Randomized MAC setting, as well as invalid DNS settings, can also cause this error. To resolve the problem in such cases,
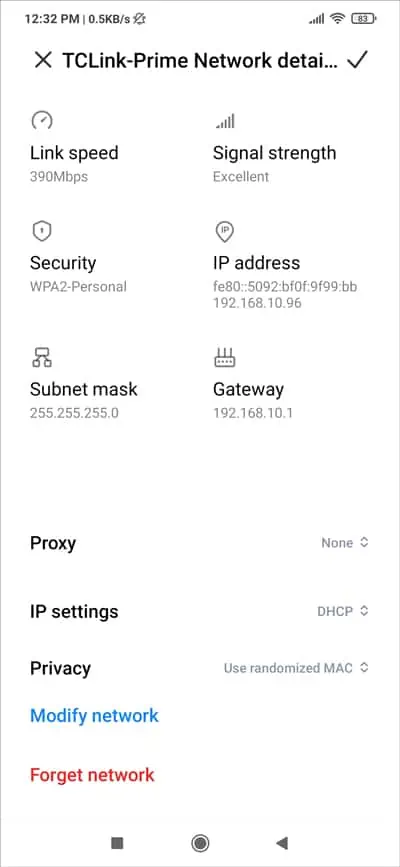
- Go to Settings > WiFi > Network Details again.
- In the Privacy field, select Use device MAC and press Save.

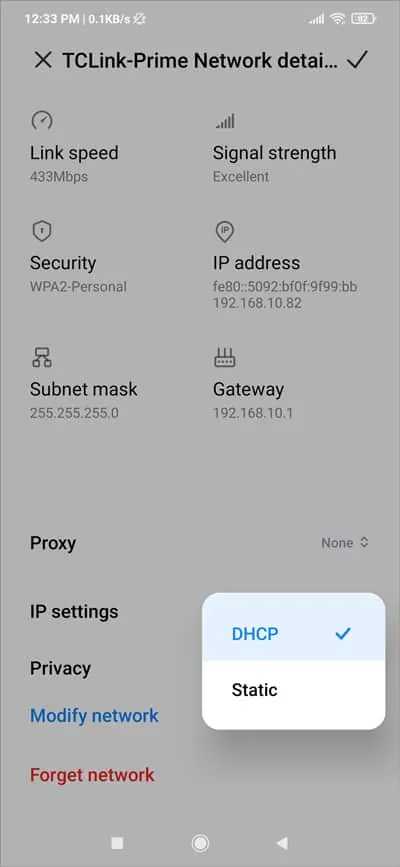
- Check if the internet works now. If it doesn’t, tap IP settings. If this was set to Static, try DHCP now and vice-versa.

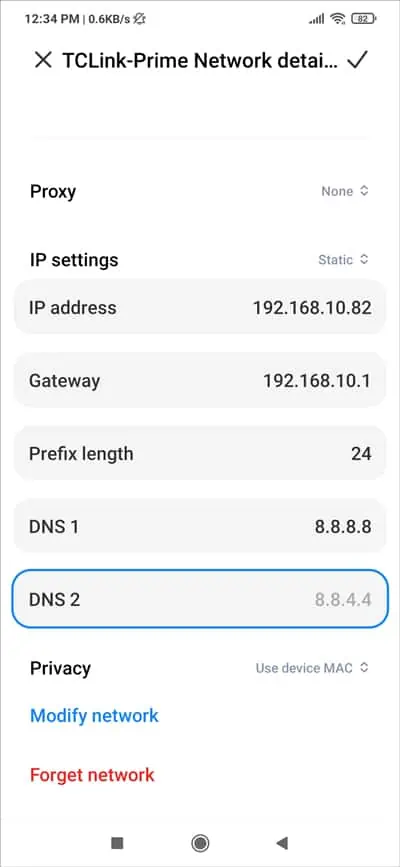
- For Static IP assignment, change the IP address (last digit only) and use 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 as the DNS server addresses.

- Tap the check mark from the top-right to save the changes and test if the internet works.
Step 4: Check Router Settings
Resetting the router to factory defaults is the easiest way to get rid of any configurations that could be preventing internet access on your device. But the method is a bit destructive, so if you don’t want to lose your custom settings, you can check the possible culprits individually in the sections below.
Disable Mesh/Extenders
If you’re using a mesh system or just multiple extenders, the roaming could be the reason for this issue.
Mesh systems usually allow you to ‘Disable Mesh’ for specific clients. This is meant for stationary devices like cameras that work best by connecting to the closest node rather than roaming between nodes.
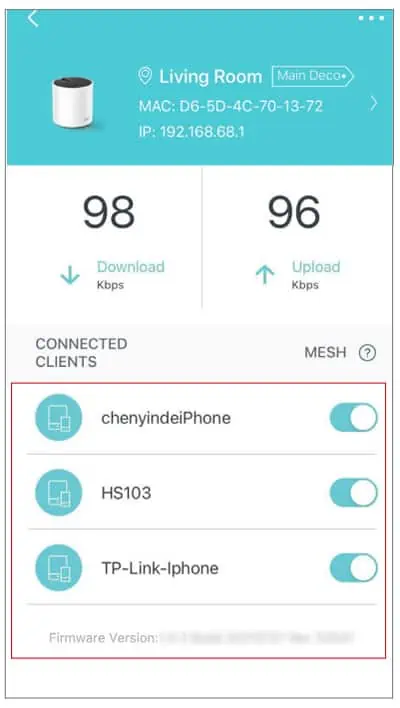
You can use this option to disable mesh for your phone. With that done, your phone should connect directly to the main router rather than any of the nodes, which should fix the issue.
The same idea applies to systems with multiple extenders. Rather than connecting to the extenders, connect directly to the main router and see if that helps.
MAC Address Filtering / Access Control
This one only applies if you’re not the admin of the current network. Check with the network owner/admin to ensure settings like MAC Address Filtering, Parental Controls, or Access Control aren’t set up. If your device is restricted due to these, it will connect to the network but won’t have internet access.
What If The Internet Still Doesn’t Work?
At this point, you’ll either have to contact your ISP for support or take your phone to the service center. If you want to make a last-ditch effort before that, I can recommend a couple of options.
First, remove the SIM or replace it with a different one temporarily. While this may seem unrelated (and a bit impractical), I’ve seen this help numerous users, so it’s worth trying.
Next, assuming this internet access issue is on a specific Wi-Fi network only (e.g., your home Wi-Fi), you could try updating the router firmware. If a firmware bug is causing this problem, there’s a good chance it’s patched in newer revisions.