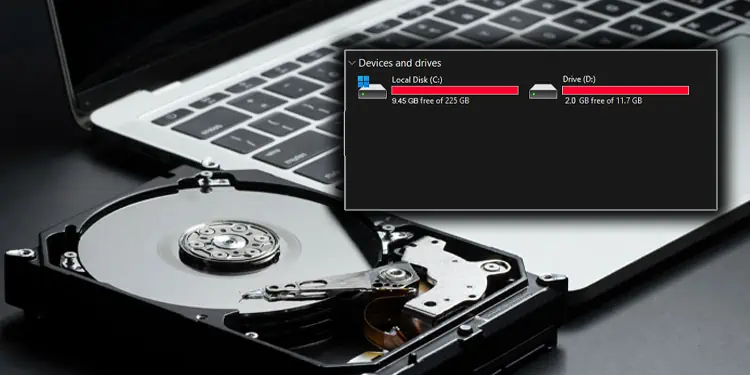
The performance of a computer starts to degrade when the storage device begins to fill up. So, it is always a good idea to periodically clean up your storage device. Furthermore, your system’s performance will decrease significantly if the primary drive is full.
Sometimes when clearing storage, File Explorer may indicate that the hard drive is full even when you don’t have files and folders taking up as much storage space. This could happen due to installed applications or hidden files inside your drive.
In the case of a primary storage device, crucial system files could take up storage space. There are a few things you can do to locate and clean up these unnecessary files, so let’s start!
Uninstall Applications and Delete Files
Before we begin to remove system files, make sure you uninstall any unused applications and files that are taking up huge storage space.
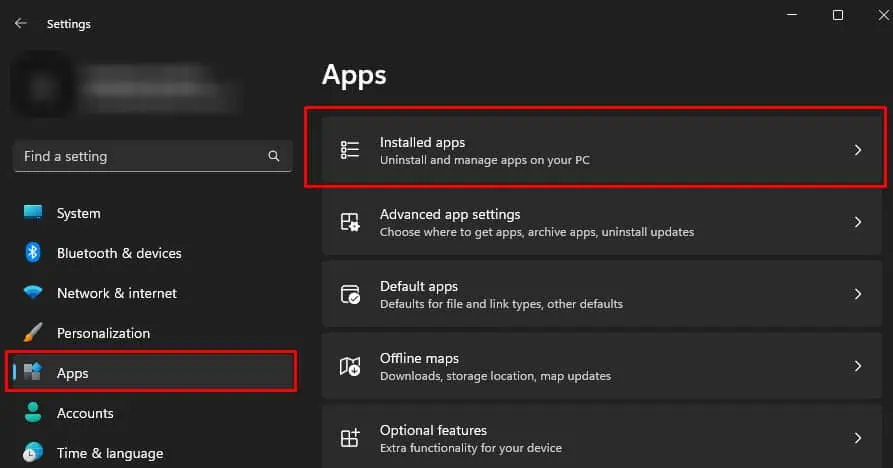
- Press Windows + I key. This will open Settings.
- Go to Apps.
- Click on Installed Apps to get details about all the applications installed on your system.

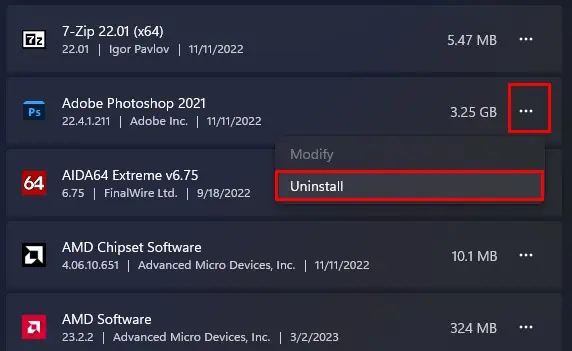
- Here, scroll through the applications installed on your system.
- Click on the three horizontal dots on the application that you want to remove.
- Click on Uninstall. Now follow the uninstall process.

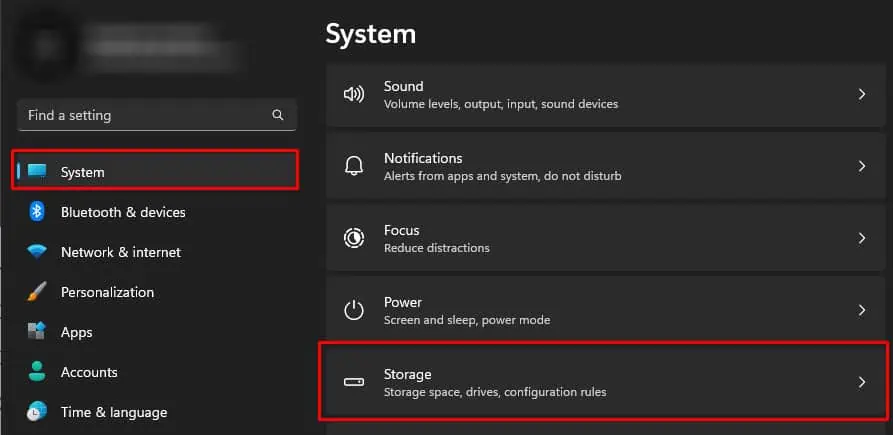
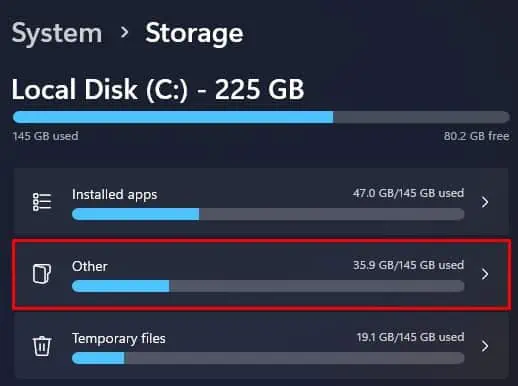
- Now, go to System > Storage.

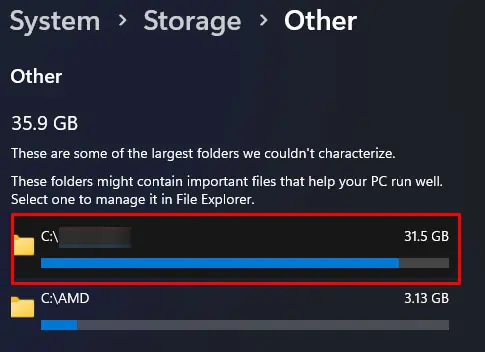
- Click on Other to get the storage detail on large folders.

- Click on folder location to open it in File Explorer.

- Delete these files and folders if they are not necessary.
Once you delete unnecessary files, they will be stored in the Recycle bin if you have not deleted them permanently. The Recycle bin also stores unnecessary files when uninstalling an application.
The data stored in the recycle bin will also take the same amount of storage. So you need to delete files from the Recycle bin as well.
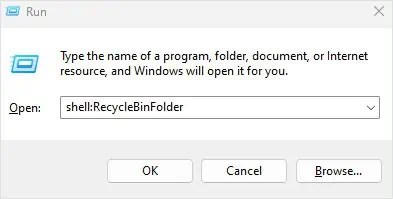
- Open Run by pressing the Windows + R key simultaneously.
- Type
shell:RecycleBinFolderand then press Enter. This will open the Recycle Bin window.
- Here, select all files and delete them to remove these files from the system permanently.
Check File Allocation on Hard Drive
One downside to using Settings to locate folders is that it only displays large folders that Windows couldn’t categorize. You can use Windirstats to get a visual representation of all the hard drives connected to the system.
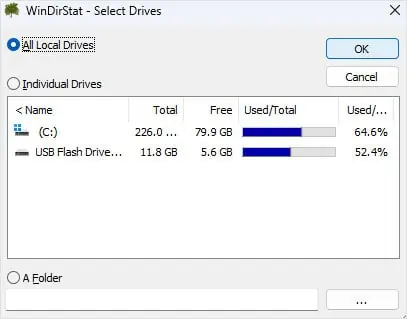
- Download WinDirStats and install the application.
- Run WinDirStats.
- Check All Local Drives and click on OK.

- Wait a few moments for the application to analyze your drives.
Here, you will see a visual representation of all your file sizes on the hard drive. The areas with the largest rectangle represent large folders.
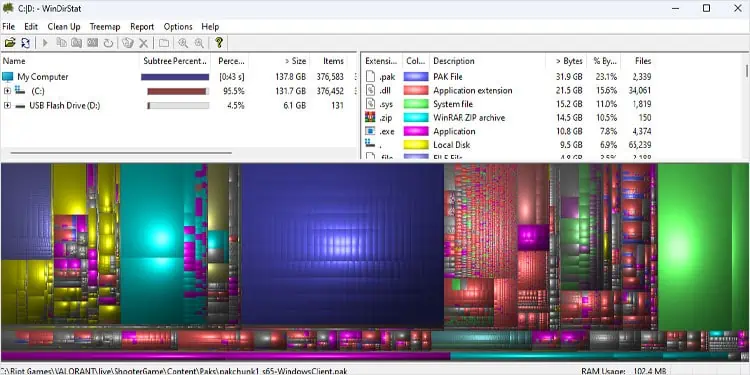
Review these folders and remove or relocate any unnecessary data inside the drive that is low on storage.
Set Page File Size
The Page file is a specified area on the hard drive that the Operating System uses if it runs out of Memory. The OS sets aside this storage area and cannot use it to store personal files. So, you can decrease the total page file size on a drive. By doing this, the system will have extra storage for your files.
- Press the Windows + I key to open Settings.
- Go to System, and scroll down to About.

- Click on Advanced System Settings.

- Under Performance, click on Settings.

- Go to the Advanced tab.
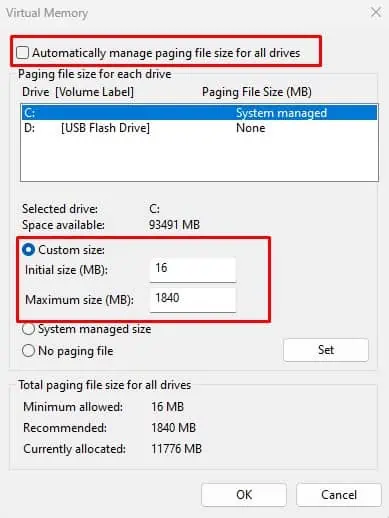
- Under Virtual memory, click on Change.

- Uncheck Automatically manage paging file size for all drives.
- Check Custom Size and set the Initial size to the Minimum allowed file size and Maximum size as Recommended page file size.

- Click on OK.
Delete Temporary Files
An application or the Operating system itself can create temporary files to store temporary information. When the application is running, it can use these files to perform specific tasks related to the application.
However, once the application closes, it automatically deletes these temp files. Try closing any application that might be creating these temp files and check if it clears the hard drive.
Sometimes, the application does not delete these files. These files are not required but take up space in the hard drive. So you need to delete them manually.
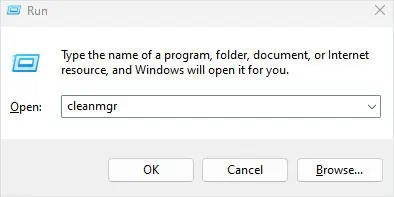
- Press the Windows + R key to open Run.
- Type
cleanmgrand press Enter.
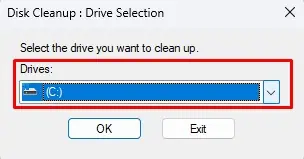
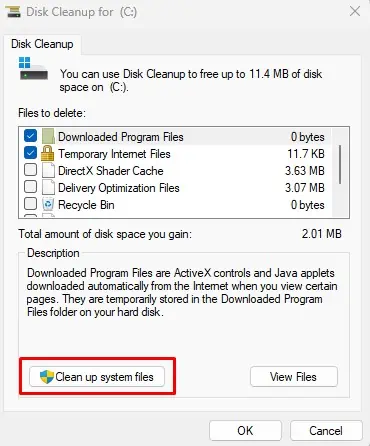
- Select the drive which you want to clean and click on OK to open the Disk Cleanup window.

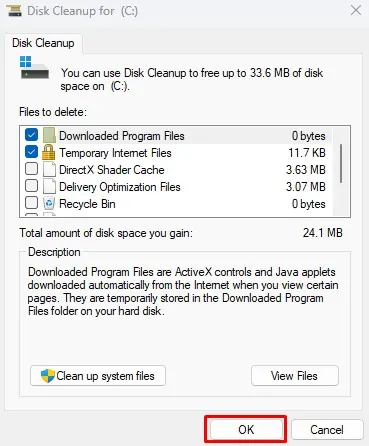
- Select the unnecessary files that are taking up hard drive space.
- Select OK, and then click on Delete files. All these are temporary files so you can safely delete them.

- Once all the files are deleted, open the Disk Cleanup window again using Run.
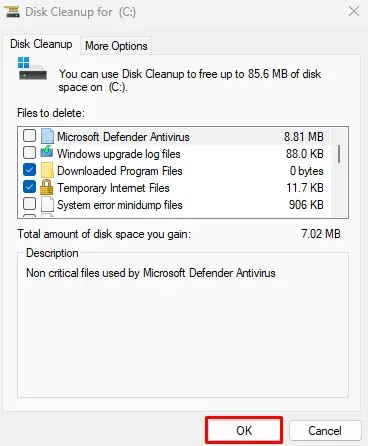
- Click on Clean up system files.

- Again, select the drive you want to clean and click OK.
- Select files that are taking up hard disk space.

- Click on OK and click on Delete files.
Windows Explorer also has some temporary files that you need to delete. These temporary files are small and do not take up huge space, but if you have not cleaned the temporary files in a long time, these files will take a considerable amount of storage.
Check Download Folder
By default, anything you download from the internet will be saved in the current user’s download folder. Windows Settings will not automatically delete these files as they may contain personal files and folders. However, there may be several files and folders that you may not need. So you should check the download folder and delete the unused files.
- Open File Explorer by pressing the Windows + E key simultaneously.
- Go to
C:\Users.
- Select a user account.
- Click on Continue if it asks for permission.
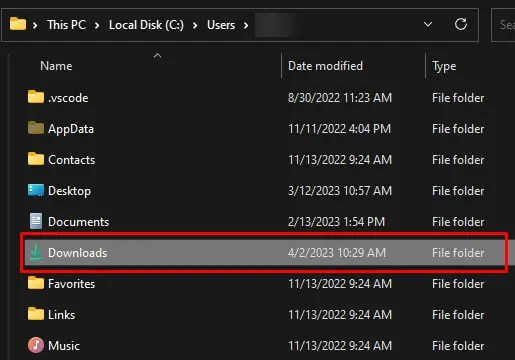
- Go to the Downloads folder.

- Here, right-click on the empty area and click on Sort by.
- Select Size, and set it to Descending. Windows will now set the file with the largest size on the top.
- Check if any unnecessary file/folder takes up huge space and permanently delete it.
If the default download location is on a drive with lower storage, you can change the default download location.
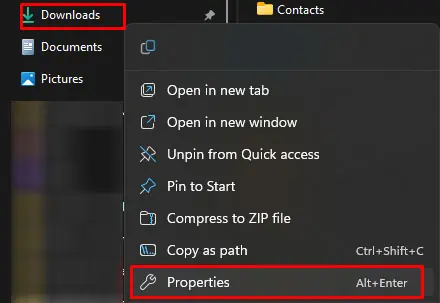
- Press the Windows + E key. This will open file explorer.
- On the left panel, right-click on Downloads.
- Select Properties.

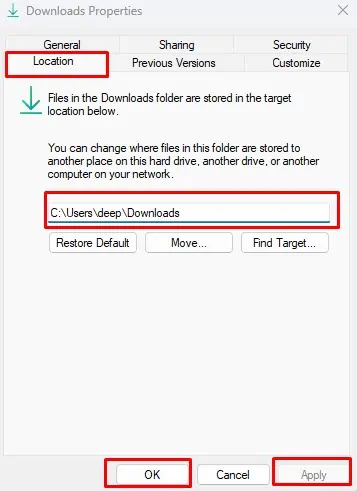
- Go to the Location tab.
- Here, set a file location on another drive where you want to save downloaded files.

- Click on Apply and then OK.
Allocate Restore Point Size
When you create a restore point, it saves the current snapshot of Windows settings and saves it on the hard drive. One single restore point will take about 5 to 10 MB of disc space. If you have several restore points on your system, it will take more hard drive space accordingly.
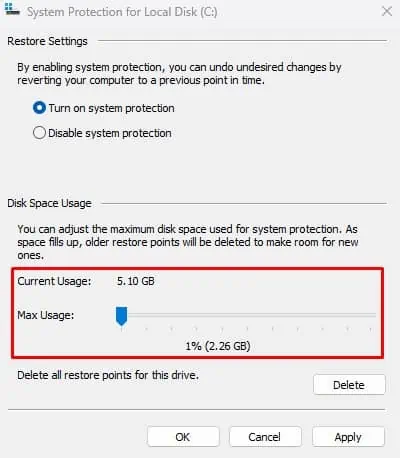
Although the system automatically deletes old restore points to create space for new ones, it is best to set the maximum disk space usage of the restore point to 1-3 GB.
- Open Windows Settings.
- Go to System > About.

- Click on Advanced system settings.

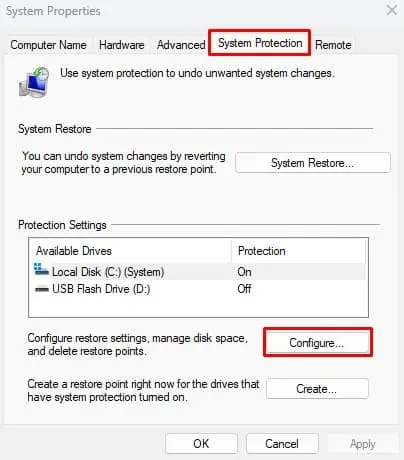
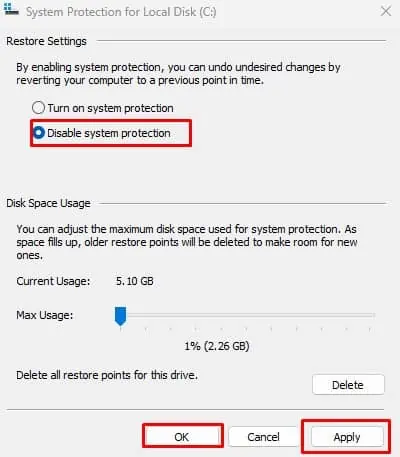
- Go to the System Protection tab.
- Click on Configure.

- Under Disk Space Usage, set a Max Usage value between 1-3 GB.

- Here, you can also delete all your system restore points by clicking on Delete. However, if you do this, you will not be able to revert the system back to its previous state.
- Click on Apply, then OK. If you do not want to save any restore points, you can disable System Protection entirely.

Scan for Virus
Deleting all temporary files and unnecessary files from the download location or uninstalling unused heavy applications should free up a considerable amount of hard disk space. If that does not even work, it could be that a virus or malware is taking the system’s storage.
To ensure this is not the case, you can try scanning the drive.
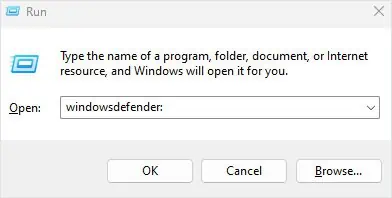
- Open Run.
- Type
windowsdefender:and then press Enter.
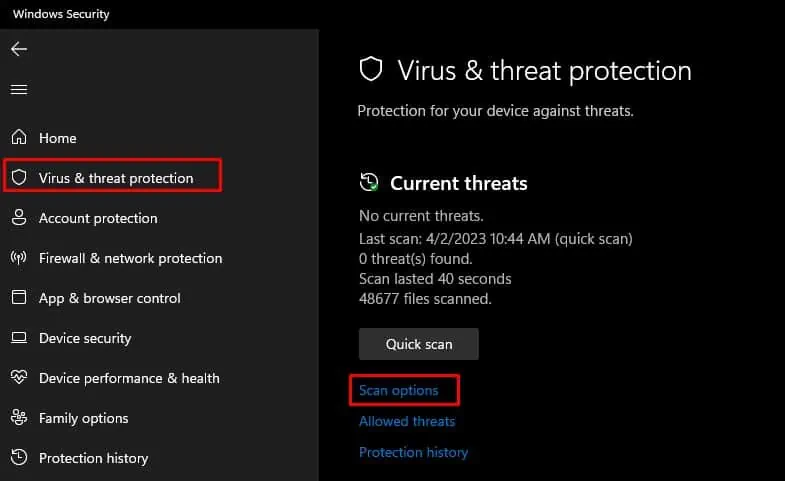
- Go to Virus and Threat Protection.
- Click on Scan options.

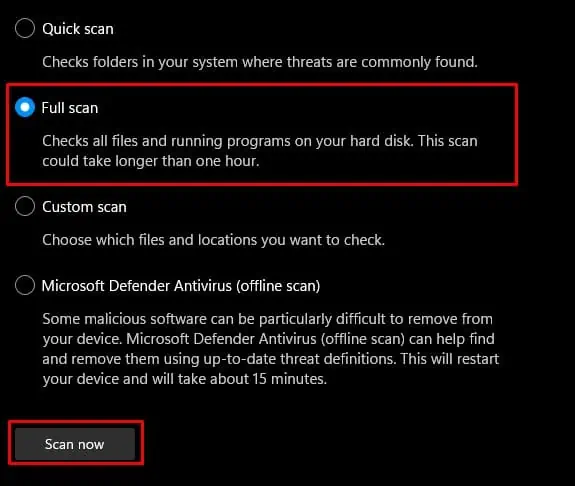
- Check Full Scan and click on Scan now.

- Wait for the system to scan your hard drives.
- Once done, it will give you a report about the scan.
Add Storage

Finally, if none of the solutions frees up the hard drive, there is a chance that the hard drive is full due to applications or personal files. In that case, you can move personal files and folders to an external storage device.
If a full hard drive is stopping you from installing new applications or some application does not run due to low hard disk space, you will need to extend your storage capacity. When upgrading the storage, we recommend that you install an SSD instead of an HDD.
Alternatively, you can also get cloud storage options available on multiple platforms. MEGA offers 20GB, Google Drive offers 15GB, and pCloud offers 10GB of cloud storage space. But besides this, you can also find several cloud storage providers.