Whenever one device can access the internet through a router or an access point, it is obvious that other devices should be able to do so as well. However, there are some situations where all your devices except your computer can connect to the internet.
This problem usually happens because of issues with your computer’s network settings or adapter. But minor router issues, like IP assignment and DNS problems, can also cause this issue.
If you are unable to connect to the Wi-Fi network, I recommend checking out our article on My Computer Won’t Connect to Wi-Fi instead.
Power Cycle Router

If multiple devices are connected to your router, some devices may not be able to access the devices in case other devices use the internet’s entire bandwidth.
So it’s best to power cycle the router if the internet is not working on all devices connected to that network. Doing so will refresh the connections to all the connected devices and will also resolve some minor connection issues.
In order to power cycle your router, you need to turn off or unplug the router and then keep it as is for a minute. Then, turn on the router and check if you could connect to the internet.
Run Internet Troubleshooters
Windows comes with dedicated troubleshooters, including the Internet Troubleshooter to check and resolve any minor issues with its components.
The Internet Troubleshooter will check the internet connection as well as all necessary processes and then fix any problem it finds. In case it can’t, it will at least tell you the nature of the problem if it detects any.
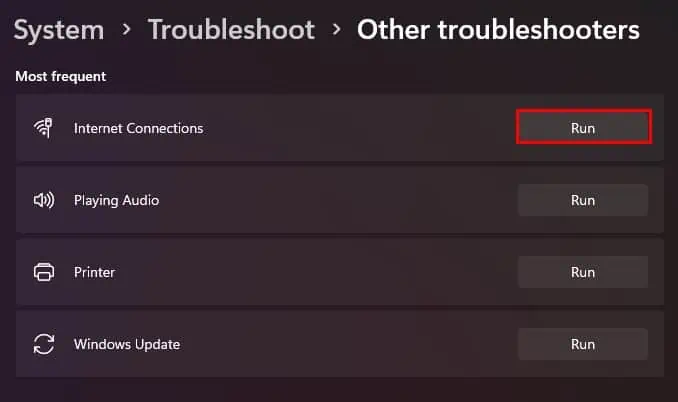
- Open Run and type
ms-settings:troubleshoot - Click OK to open Troubleshoot Settings.
- Select Other or Additional troubleshooters.
- Next to Internet Connections, click on Run. In Windows 10, you need to select Internet Connections and then click Run this troubleshooter.

- You can also run the troubleshooter for the Network Adapter.
Manually Troubleshoot Network Adapter
You should first figure out if the issue is with your network adapter device or the network settings. Start by connecting to the router through another adapter if possible, i.e., try an Ethernet connection if you were using Wi-Fi and vice versa and check if you could access the internet.
If you are still facing the issue, try to connect your device to another network. You can use a hotspot connection or public Wi-Fi.
If you also can’t establish an internet connection through other networks, there is likely something wrong with your network adapter. It may be a driver or a hardware issue.
But if you can establish an internet connection on other networks, the problem is likely with your original network’s configuration. So, you need to resolve those instead.
Verify DNS and IP Addresses
If you can’t access the internet, it is possible that the current IP assigned by your network’s DHCP is not in the proper range. In such cases, the router can’t send any internet packets to your device.
These issues can happen due to some router configuration or DNS issues. You can check if this scenario applies to you using the Command Prompt. Then, you can specify a static IP and DNS to resolve the issue.
- Open Run and type
cmd. - Type
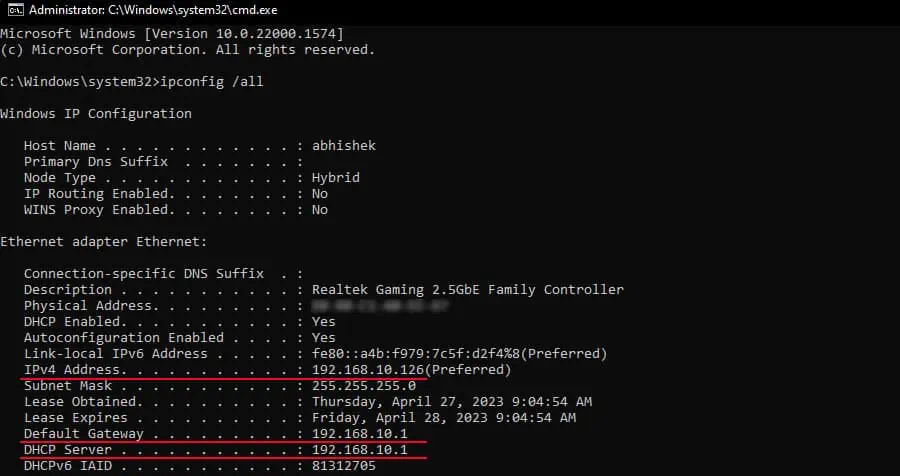
ipconfig /alland press Enter. - Go to the details of your current network adapter (WiFi or Ethernet). It is the network that has a Default Gateway.
- Check the DHCP Server, Default Gateway and the IPv4 Address.

- They need to have the same initial three numbers.
If not, follow these steps.
- Open Run again.
- Type
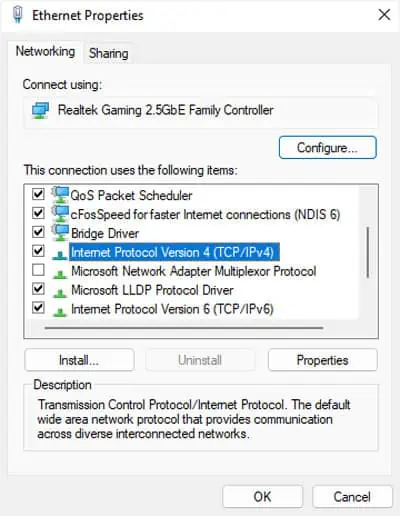
ncpa.cpland press Enter to open Network Connections. - Right-click on your network device and select Properties.
- Double-click on Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).

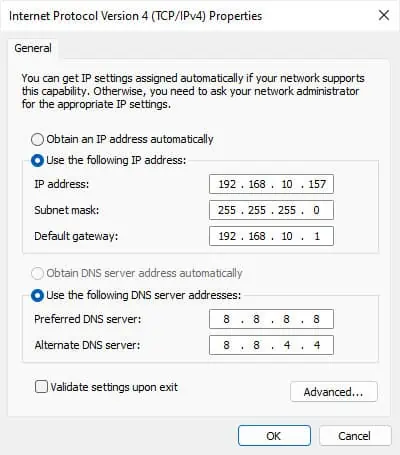
- Check Use the following IP address.
- If the Default Gateway on Command Prompt had the same three numbers as the DHCP server, enter the same value on the Default gateway here as well. Otherwise, enter the first three numbers of the DHCP server here, and on the fourth number, put
1. - Enter the three same numbers on the IP address as well. Here, on the fourth number you need to enter any value between 1 and 254.
- Click on the Subnet mask’s value box to automatically enter the necessary data.
- Then, on the DNS server addresses, you can use some public DNS servers like Google’s (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare’s (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1)

- Click OK > OK.
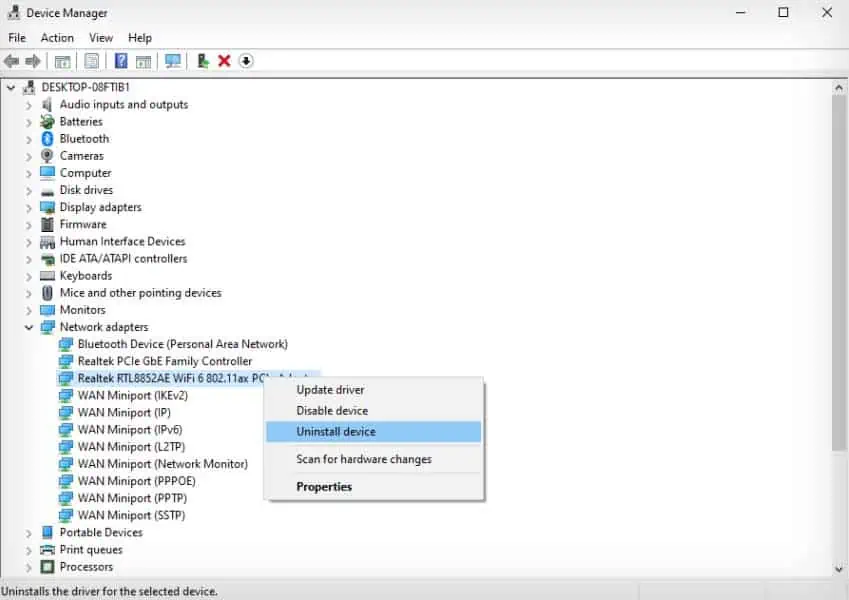
Check Device Manager
You may not be able to access the internet if your network adapter is not working properly. Since its driver is the software that lets your computer use the device, you need to check the driver and make sure there are no issues.
- Press Windows key + X and select Device Manager.
- Expand Network Adapters.
- If your network adapter shows an exclamation mark, it is not working due to some driver issue. Right-click on the problematic driver and select Uninstall device > Uninstall.

- Then, select Action on menu bar and click Scan for hardware changes.
Reset Network Settings
You can also try resetting the network settings altogether to reset the internet connection and re-configure all settings. Doing so will resolve any improper setting that was causing the connection issue.
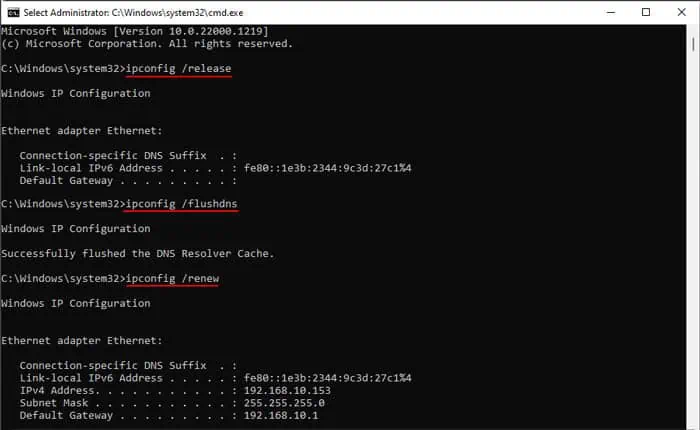
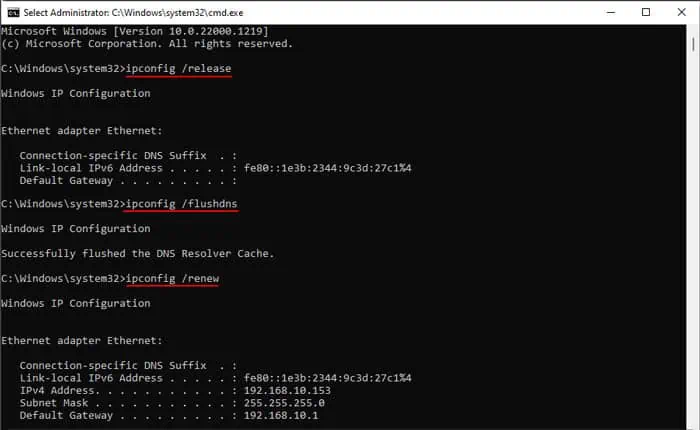
- Open Run and type
cmdand press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open the Elevated Command Prompt. - Type the following commands and press Enter after each:
ipconfig /releaseipconfig /renewipconfig /flushdns
netsh winsock resetnetsh int ip reset
- Restart your computer when required to complete the reset.
Disable VPN or Proxy
If the VPN or Proxy server you are using is suffering a network outage or high traffic overloads, you may not be able to connect to the internet through the VPN/Proxy.
If so, switch to another server and try to enable the VPN again. You can keep the VPN or Proxy connection disabled for the time being if it doesn’t work.