A lot of users can’t find the hardware virtualization option in the BIOS interface as its name and location differs depending on the processor type and BIOS version.
In Gigabyte’s case, it’s usually called SVM (AMD) or VT-x (Intel) and can be configured from the Chipset or Advanced CPU Settings sections.
I’ll cover the steps to do this on different Gigabyte BIOS/UEFI interfaces in this article.
Access BIOS/UEFI Interface
To enable Virtualization, you’ll need to access your BIOS settings first. Press F2/Del when booting to enter the Gigabyte BIOS Setup utility.

If you’ve enabled Fast Boot and the BIOS key doesn’t work, you can use an alternate method to get to the firmware interface.
Restart your PC 3 times in a row to boot to the recovery environment. Then, select Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > UEFI Firmware Settings.
Locate Virtualization Option
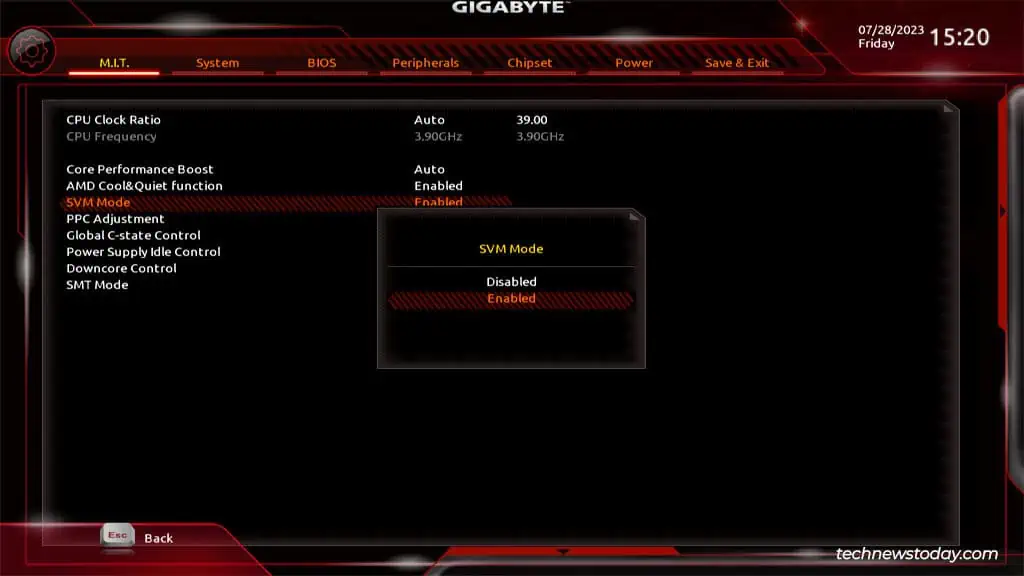
Press F2 (if required) to switch to Advanced Mode. As mentioned earlier, you’re looking for an option named SVM (AMD) or VT-x (Intel) here.
Currently, older Gigabyte boards use the classic black-and-red UI, while the latest ones come with the revamped orange/yellow UI released in 2020.
Old UI
On the old UI, you can manage the virtualization setting from the locations listed below:
- Chipset > Intel Virtualization Technology (VT-x)
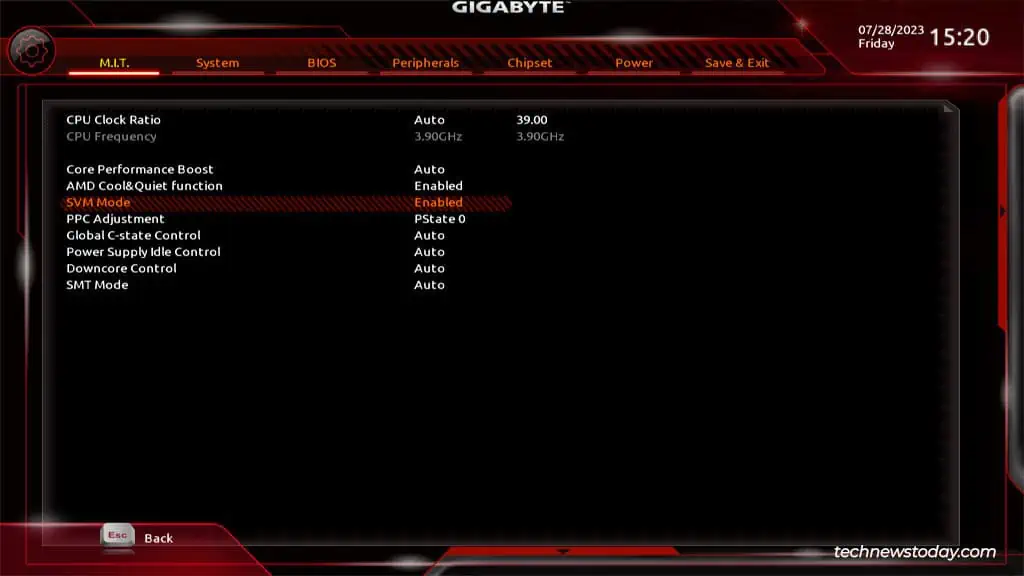
- M.I.T. > Advanced Frequency Settings > Advanced CPU Settings > SVM Mode
- M.I.T. > Advanced CPU Core Settings > SVM Mode
New UI
With the new UI, you can find the virtualization option in the following locations:
- Tweaker > Advanced CPU Settings > SVM Mode
- Tweaker > Advanced CPU Settings > Intel Virtualization Technology (VT-x)
Enable Virtualization on Gigabyte
Once you find the virtualization option, all you need to do is set it to Enabled.
If your CPU supports it, you can also enable the PCI passthrough feature. AMD calls it IOMMU while Intel calls it VT-d.
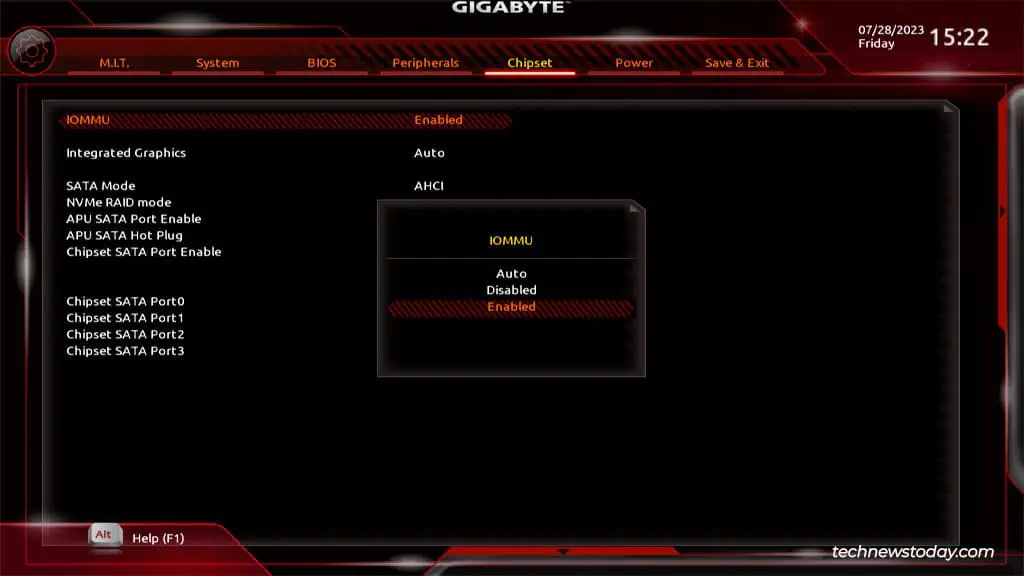
This improves performance by letting the PCI devices function as if they were directly connected to the guest machine (e.g., better GPU performance in video games).
Finally, after enabling virtualization and any additional settings, press F10 to save the changes and exit.
Verify Virtualization Status
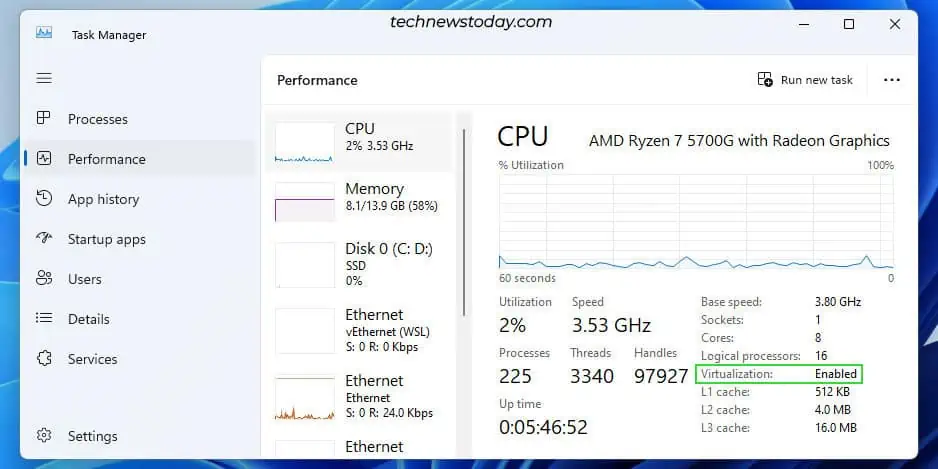
After you exit the BIOS, the system should reboot into Windows. You can easily check the virtualization status here from the Task Manager.
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open the Task Manager. In the Performance tab, check the CPU page for the Virtualization status.
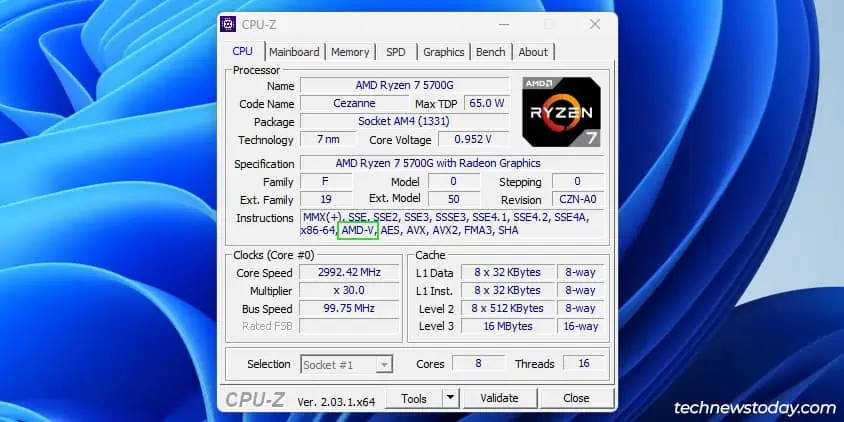
System profiling programs like CPU-Z are also popularly used for checking the Virtualization status. If it’s enabled, you should see flags like AMD-V or VT-x in the CPU Instructions section.