The CMOS battery supplies power to the CMOS chip so that the system can remember all your BIOS configurations even after the system turns off.
One major variable that determines the lifespan of a CMOS battery is its current voltage. The CMOS battery becomes useless once it reaches a point where the battery fails to supply the minimum required voltage for the CMOS chip.
Once the battery dies, any data saved on the CMOS chip will be set to its default value. This data includes all your BIOS settings and the system clock. So if you see that the BIOS or the system clock resets every time you turn on the system, you might need to replace the CMOS battery in your system.
How Long Does CMOS Battery Last?
The CMOS battery can last three to ten years depending on the CMOS battery charge capacity, the system’s uptime, the standby current of the motherboard, and many other factors.
The voltage on a CMOS battery decreases gradually if it is not in use. Therefore if you leave your PC turned off, the system constantly uses the CMOS battery and hence will deplete over time. In such a case, the battery may not last more than four years.
On the other hand, the system does not use the CMOS battery when you turn it on. So if you constantly use the PC, the CMOS battery may even last up to ten years.
How to Know if Your CMOS Battery is Dying?
The CMOS chip holds all your BIOS settings and Real Time Clock (RTC). All these configurations will be reset once the CMOS battery stops functioning. Some motherboards even have features that let you know when to replace the CMOS battery. Some motherboards even have features that display a message when the CMOS battery runs out.
Here are some ways you can determine if you have a dead CMOS battery.
Incorrect Date and Time
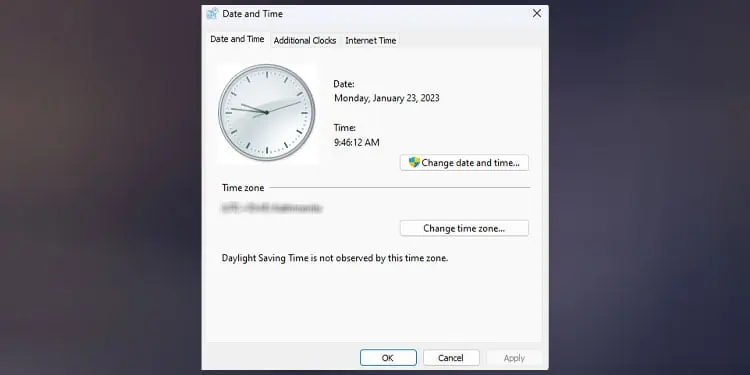
Your motherboard keeps track of time using the RTC (Real-time Clock) chip. But the RTC chip requires constant power to function. When you turn off the system, the RTC uses the CMOS battery as the power source. And if the CMOS battery is not functional, your system time will reset every time you turn off the computer.
If you have not synced your time computer to an internet time server, you will notice that your computer time is not accurate.
If you have not synced your time computer to a time server, you will notice that your computer time is not accurate.
BIOS Settings Keep Resetting
All your motherboard configurations are saved on a CMOS chip. These include RAM’s XMP, hardware frequency in which it operates, and all other configurable settings in BIOS.
Similar to the RTC chip, the CMOS chip also stores all its data as long as it has constant power to it. When you turn off the system, the CMOS chip uses the CMOS battery as the power source.
So when the CMOS battery dies, all your BIOS configurations will reset once you turn off the system. You will especially notice this if you have changed the settings in the BIOS. Besides the BIOS settings, you may also run into CMOS checksum error or System battery voltage is low error.
POST Error Message
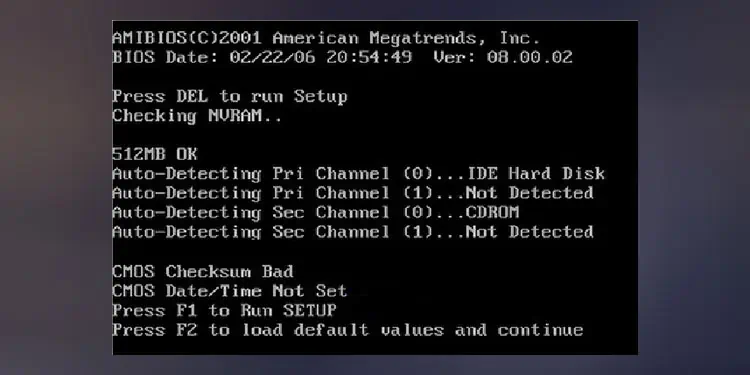
When you turn on your system, the motherboard first runs a POST. During POST the system checks crucial hardware components. POST also detects any data mismatch in the CMOS chip. These errors in the CMOS chip might be indicating a possible CMOS battery failure.
Check for Visible Damages
You can physically check your CMOS battery for damages. Your motherboard has a dedicated slot for the CMOS battery. Any visible damage to the CMOS battery might hint at a dead battery. These damages could be a swollen or corroded battery.
Check CMOS Battery Voltage
You can check the CMOS battery’s voltage using a voltmeter if you want to get accurate data.
The voltage does not need to drop to zero for it to become useless. Depending on your CMOS chip, the minimum voltage required for it to function may vary.
- Turn on your multimeter and set it to read voltage from a DC source.

- Touch the red lead to one side of the CMOS battery. And touch the black lead to the other side of the CMOS battery. The voltmeter should display the reading on the display panel.

What to Do if the CMOS Battery is Dead?
Once you are certain that the CMOS battery is dead, the first thing to do is replace it.
Since the CMOS battery slot is embedded into the motherboard, you will need to access the motherboard first in order to remove the CMOS battery.
Remove PC Side Panel
- Turn off your computer and unplug the PSU from any wall outlet.

- Press the power button for a few seconds to discharge the residual charge on the capacitors.

- Unscrew all the screws on one side of the CPU case to remove the side panel.

Locate CMOS Battery
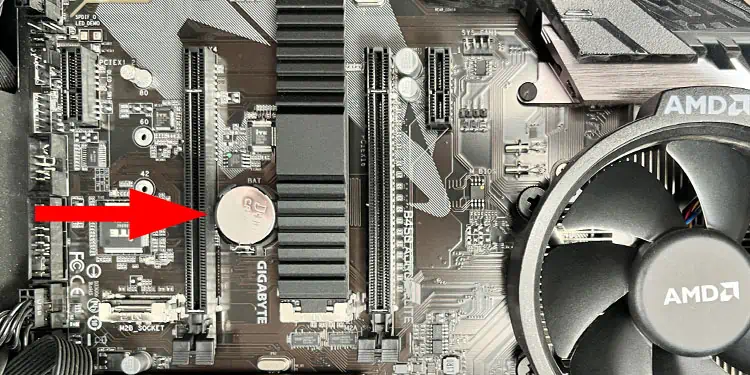
The CMOS battery connects to the motherboard. For desktop PCs, you will find a separate circular slot in the motherboard that holds the CMOS battery. As for laptops, they may have a separate slot on the motherboard, just like the motherboards on desktop PCs.
If the laptop’s motherboard does not have a separate slot, CMOS should be connected to one of the ports on the laptop motherboard with a short cable. In that case, the CMOS battery will be wrapped with electrical tape.
Replace CMOS Battery
- Press the lock that holds the CMOS battery in place to pop the battery out of the socket.

- Take the fresh CMOS battery and insert it into the CMOS battery slot on your motherboard. Ensure that you insert the battery such that the + sign faces up.

- Insert the side panel and connect all the screws that you previously removed.
- Once you put everything together, turn on your system.
How to Increase CMOS Battery Lifespan?
The CMOS battery loses the charge stored inside it if not in use for a long time. When this happens, the battery fails to deliver the minimum voltage required for the CMOS chip.
When you constantly turn on the system, it does not use the CMOS battery. Therefore, if you want to increase the life span of a CMOS battery, we recommend that you use your computer regularly.








