The C drive usually contains your PC’s operating system and stores all new applications. So, it’s crucial that this drive has enough free space and delivers high performance.
If your storage space is running out or the drive is not optimized, you’ll start experiencing lags or freezes. To resolve such issues, you need to clean your C drive properly.
However, since the drive contains your OS, you can’t haphazardly delete its contents. You need to use proper methods to optimize it, which we have explained below.
How to Clean C Drive
Here are the ways with which you can clean your C Drive and optimize your PC:
Defragment C Drive
Your hard drives search for free sectors to store your files. But if there’s no sufficient free space in consecutive sectors, it can only store the files on random sectors. So accessing the fragmented files takes more time.
Defragmentation the disk doesn’t usually free up any space, but it’s still useful in improving your computer’s performance. If your computer starts lagging or opening files/running programs takes more time, you definitely want to defragment your HDD.
However, only hard drives (HDD) require defragmentation. You can not defragment SSDs as they use a separate optimal writing process. SSD comprises of a single magnetic tape and your system doesn’t scatter the data while storing on an SSD, like it does for an HDD.
It is possible to optimize SSDs. But they automatically clears data, based on frequency of usage, every 30 days or so. So, manually optimizing consumes more read/write cycles instead.
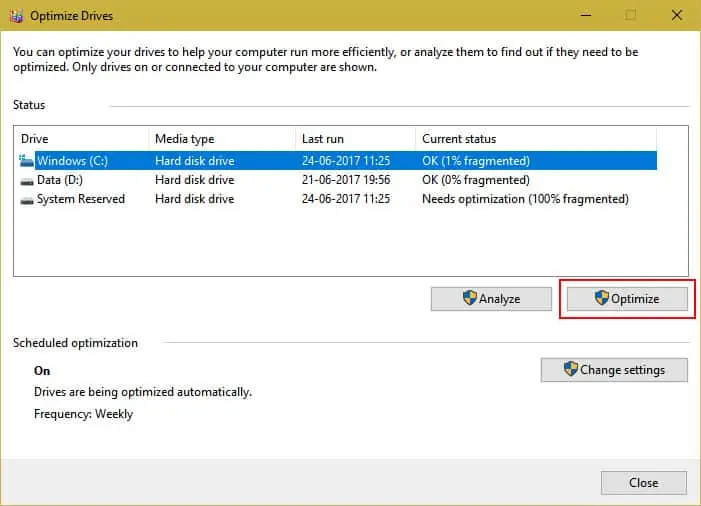
Here’s how you can defragment your C drive:
- Open Run and enter
dfrgui. - If the Media type for your C drive shows Hard disk drive, select it and click Optimize.

Use Disk Cleanup
Disk Cleanup is the traditional Windows utility to clean your drives. You can use it to delete your temporary files, thumbnails and Recycle Bin contents, and some other files the system deems unimportant.
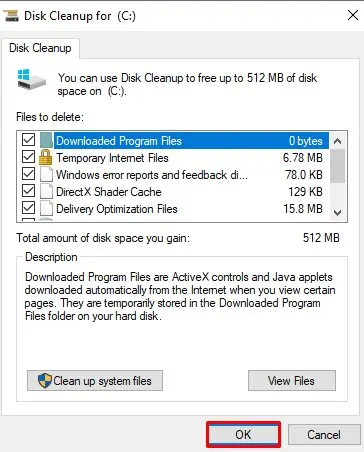
Here’s how you can use this tool to clean your C Drive:
- Open Run (Win + R) and enter
cleanmgr. - If you have more than one partitions, select the C drive and click Ok.
- Select the options you want to clear, including Recycle Bin. The files you don’t permanently delete by pressing Shift + Del stay in the Recycle bin.
- If the Cleanup shows the Previous Windows installation (s) or Windows Update / Upgrade Files, you can also delete them. However, only do so if your PC is working correctly, as you may want to revert your OS if there are any system issues.
- Click Ok, then confirm with Delete Files.

Enable Storage Sense
Storage Sense is the modern alternative to Disk Cleanup that Microsoft created to facilitate the automatic cleanup of your drives. You can also set a schedule along with which types of files to remove during this process.
This process cleans up all your drives simultaneously. However, since drives other than C do not store any temporary files by default, Storage Sense usually just cleans the C Drive.
Here are the necessary steps for this method:
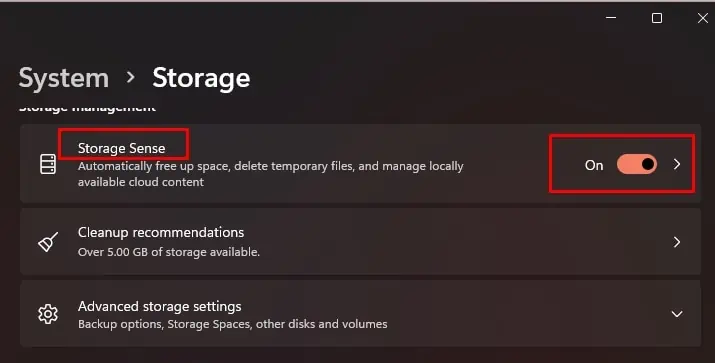
- Press Win + I to open Settings.
- Go to System > Storage.
- Toggle On Storage Sense.

- Click Storage Sense or Configure Storage Sense or run it now.
- Check the option to delete or clear temporary files.
- Set the drop-down for Run Storage Sense to the schedule you want.
- You can also set the condition to delete the contents of the Recycle Bin and the Downloads folder.
If you want to run this process now, click Clean now or Run Storage Sense now.
Delete Temp Files
While Disk Cleanup and Storage Sense remove most temporary files, your computer still keeps storing some temporary files. We recommend deleting them from their save location through the file explorer. Here’s an easy way to do so:
- Open Run and enter
temp. - Select all (Ctrl + A) and press Ctrl + Shift + Delete to permanently delete the contents.
- Confirm with Yes.
- You can’t delete the files your system is using, for which you’ll get the File in Use prompt.
- Check Do this for all current items and click Skip on the prompt.
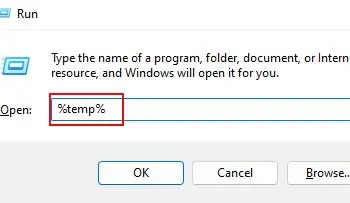
- Now, open Run again, and this time, enter
%temp%.
- Permanently delete the contents and skip all the files you can’t delete.
Clear System and Browser Cache
Your system stores many types of cache files for different purposes. Several processes like File Explorer, DNS, Windows Store, Windows Update, etc., all store cache which accumulates to a large size. Your browsers also use particular storage space to store their cache and cookies.
You can delete such files to clean your C Drive. We have a dedicated article on How to Clear Cache on Windows. Check it out to learn how to clear all cached files on Windows system as well as web browsers.
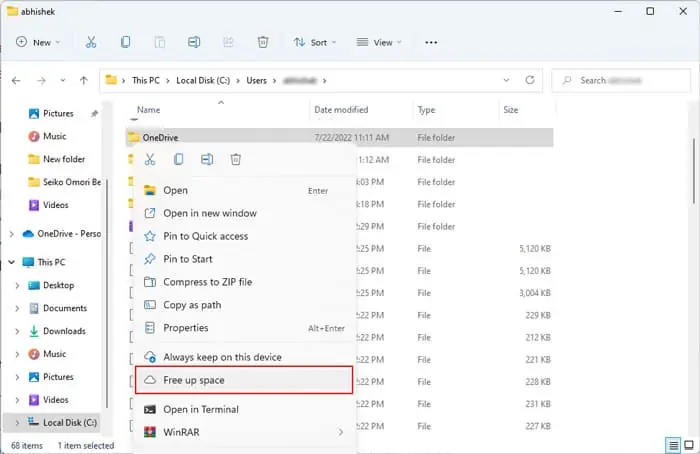
Make OneDrive Online Only
OneDrive uses 200 MB of your storage space to sync your files to the cloud. However, you can make some files and folders online-only. These files and folders only appear on the cloud, and your local drive no longer stores them.
Here are the necessary steps for this procedure:
- Navigate to your OneDrive folder on your File Explorer. It’s usually at your
%userprofile%folder. - Right-click on OneDrive and select Free up Space.

You can also make OneDrive online only from Storage Sense settings on Windows 10.
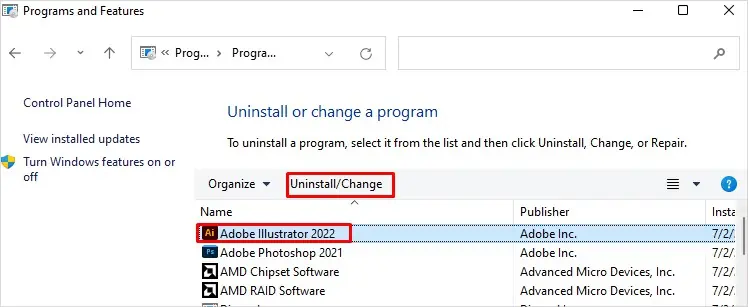
Uninstall Unnecessary Applications
Many users have a habit of installing new applications and forgetting about the apps after they stop using them. Such applications can take up considerable space on your C drive. So it’s always a good practice to periodically check for and uninstall unnecessary applications. Here’s how you can do so:
- Enter
appwiz.cplon Run. - Check all available apps.
- If you don’t need any, select it and click Uninstall or Uninstall/Change.

- Follow the on-screen instructions.
Some users also copy applications from another system and use them without installation. This process is not possible for many applications, but running some programs without properly installing them is possible. If this is the case for you, don’t forget to navigate to their location using the file explorer and delete such apps if you don’t need them any longer.
Delete Unnecessary Files
You may have many unnecessary files on your system apart from the applications. Some applications leave behind their user files even if you uninstall them. So you need to manually search for these files and delete them to clean your C drive.
The remnants of the old programs are usually present in the AppData folders. You would want to check our article on opening and using AppData to learn how to search for and delete such files.
You should also go through your Desktop, Documents, Downloads, Music, Pictures, and Videos folders and delete unneeded files and folders.
Third-party cleaners available on the internet are also of great use in automatically determining unnecessary and duplicate files and removing them. So, you can also use one if you want.
Disable Hibernation
While disabling hibernation may not seem like it does anything to clean your C drive, the process reserves some storage space. With hibernation enabled, your system stores all active files, folders, and some RAM contents on a hiberfil.sys file while hibernating the PC to restore them the next time you boot.
This file reserves a storage space equal to 20-40% of your RAM if hibernation is enabled. So, if you have 16 GB RAM, this file uses about 4-7 GB of space. If you don’t actually use hibernation, you can disable it to free up this space. Doing so has no impact on the normal shut down and powering up process, except maybe slightly increasing startup time.
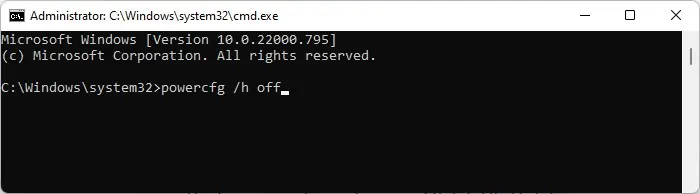
To disable hibernation mode,
- Open Run.
- Type
cmdand press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open Command Prompt as administrator. - Here, type
powercfg /h offand press Enter.
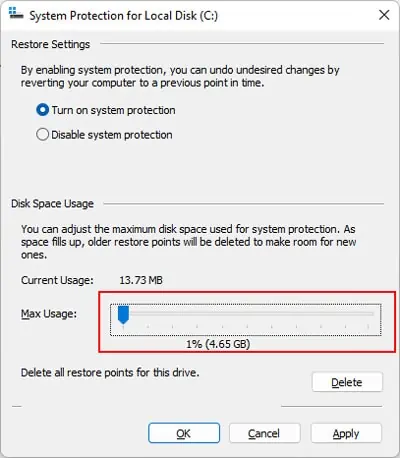
Reduce Space For Restore Points
System Restore is a protection feature that allows creating restore points or snapshots, which your system can revert to if you encounter any issues. Your system allocates a maximum of specific storage space to store the restore points.
If any of this space is free, System Restore uses the free space to create new restore points. And if none is available, it deletes the oldest restore point to free up space.
It is possible to change the maximum allocation to make more space available for other purposes. Here’s how you can do so:
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type
systempropertiesprotectionand press Enter. - Click on Configure and set the slider next to Max Usage to the lowest value.

- Click Ok and confirm if you get any prompts.
- Create a new restore point as your system may remove previous ones if you lower the Max Usage. Click Create, type a name for the restore point and hit Create to do so.
You can also disable System Restore completely from Configure > Disable system protection. However, we don’t recommend doing so you may need this process in case of any system issues.
Related Question
Can I Use DiskPart Clean Command to Clean C Drive?
The clean command on the DiskPart CLI actually erases all the contents of a partition. You can’t run this command as this drive contains your OS. However, it is possible to do so from a Windows installation media’s WinRE.
But cleaning the drive removes all OS files as well, so you need to reinstall windows to actually use a PC.
If you find it tedious to use all the methods we have mentioned above, you can reinstall windows to clean your C drive. However, remember to backup your necessary files before doing so. After the reinstall, install all necessary applications and restore the backed up files.