As your laptop’s hard disk gradually gets filled up and used over time, storing new files in it will cause disk fragmentation. This significantly slows down the rate of retrieving data from your hard drive. In severe cases, it can cause performance drops, freezes, and even hard drive failure.
So, you should defrag your laptop’s hard disk to rearrange those fragmented data in an organized and contiguous manner. In a Windows laptop, you can use the in-built Microsoft Drive Optimizer application to automatically or manually defrag your device.
Disk Fragmentation Process
Disk fragmentation is a process in which a file or parts of a file get stored in random places across your hard drive. So, let’s see how a hard disk can gradually get fragmented over time.
The hard disk stores data on a spinning disk called a disk platter, and a thin magnetic blade called a read/write head is used to read and write data on the disk.

Now, when storing new data on your hard drive, the read/write head will store that data in the immediate free storage block it can find while the disk platter is spinning. After it hits a place where data is already stored, it will skip and start storing parts of the same data in a new free storage block it can find.
This process repeats over and over as your hard drive goes through the read and write operations, increasing disk fragmentation.
Defragging a Laptop
It is pretty easy to defrag your laptop, as the Windows operating system provides an in-built application called Microsoft Drive Optimizer to defrag the hard disks in your laptop. Here’s how you can do so:
- Press Windows + R to open the Run Utility.
- Type
dfrguiand press Enter to open Microsoft Drive Optimizer.
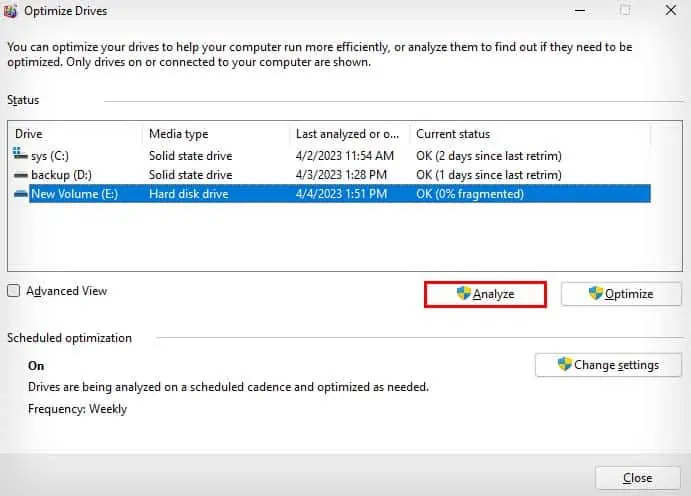
- Select the drive you want to defrag. (Defragging an SSD is not recommended or necessary.)
- Click on Analyze to make sure your hard drive needs to be defragged or not.

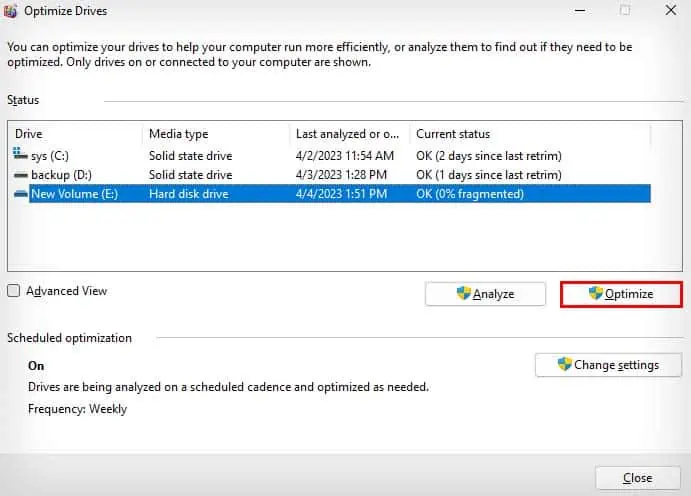
- If it says you need to defragment your hard drive, click OK, and select Optimize.

- Defragging your drive can take anywhere from a couple of minutes to several hours depending on your drive storage capacity and the data fragmentation percentage.
Alternatively, you can also perform manual defragmentation from the Command Prompt. To do so, you simply need to open Command Prompt with admin access and enter the command: defrag <drive letter> -w.
For example, defrag c: -w
Also, you can schedule automatic defragmentation of your hard drive from Microsoft Drive Optimizer. You can either set the scheduled defragmentation to be performed daily, weekly, or monthly.
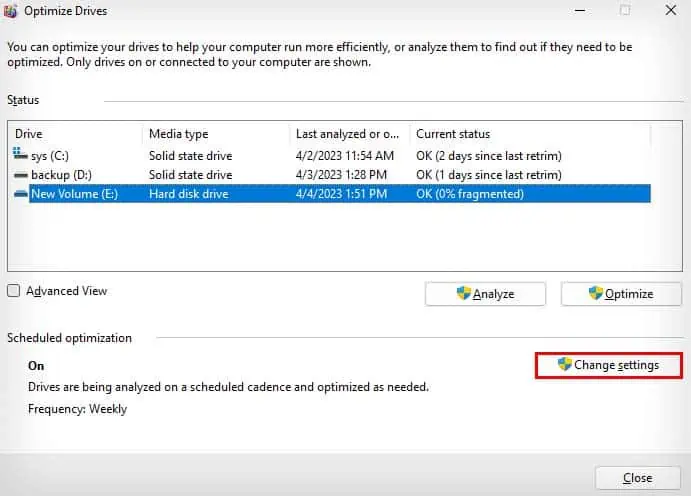
- Open Microsoft Drive Optimizer.
- Under Scheduled optimization, select Change settings.

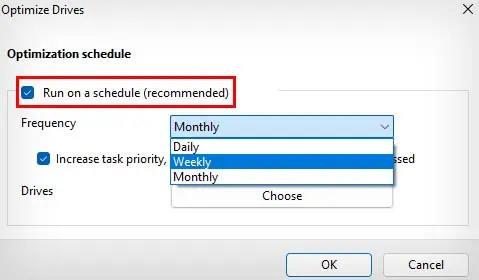
- Make sure the Run on a schedule option is selected.
- Besides Frequency, select the schedule time from the drop-down menu.

- Make sure to checkmark the Increase task priority, if three consecutive scheduled runs are missed option.
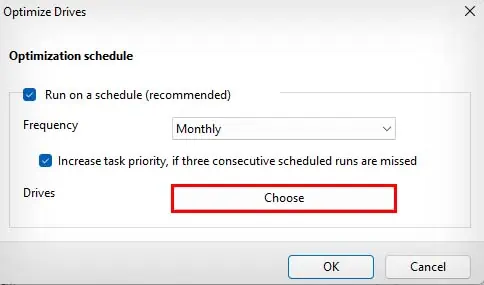
- Next to Drive, select Choose.

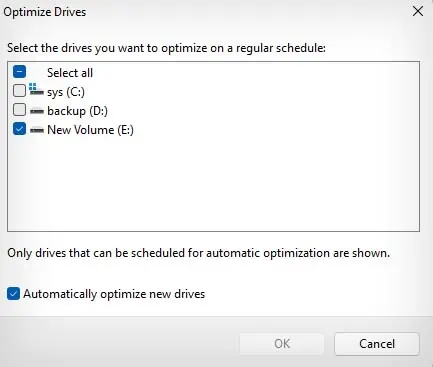
- Choose the drives you want to defragment automatically.

- Click OK and OK again to close the dialog boxes.
- Exit Microsoft Drive Optimizer.
Should I Also Defrag My SSD?
Defragging an SSD is not recommended, as it does more harm than good to your SSD. While SSDs also suffer from file fragmentation due to how Windows stores data on a storage media, it doesn’t have the constraints of a hard drive.
When a file is fragmented in a hard drive, the read/write head has to physically move across the disk platter to access all the parts of one file. This limits the rate of retrieving data from a hard drive to the physical speed of the read/write head, which massively slows down the process.
On the other hand, SSDs do not suffer from this issue, as they store data on flash memory with no moving parts. The rate of retrieving data from an SSD is the same, whether it is fragmented or not.
Furthermore, as the memory cells in SSDs can only perform a limited number of write operations, defragging an SSD can actually shorten its lifespan.