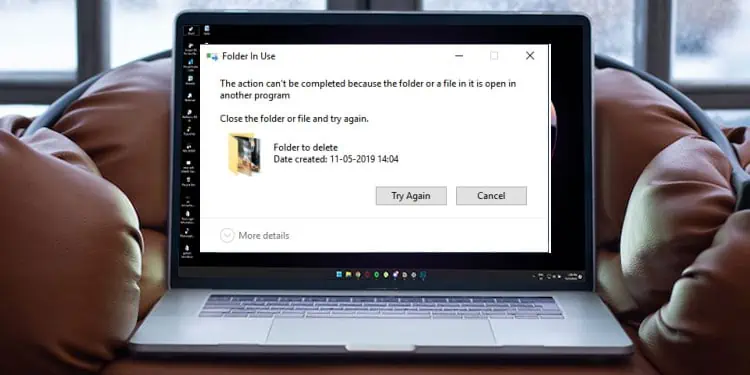
Deleting a file is a simple process as long as a program is not currently using it. You cannot delete a file if a program currently uses it. You will need to close the program or process that is using the file and then delete the file to complete the deletion process.
Although closing the program will work in most cases, it may not work if a critical windows process uses the file you want to delete. Besides this, you are also bound to get this error message when this program runs in the background. In that case, you may need to follow specific solutions to delete these files.
How to Delete a File That is Open in Another Program?
When you get this error message while deleting a file, first close all the applications that are running. Also, make sure that you exit any unnecessary application from the tray icon. If you have a lot of applications/programs running, it may be hard to determine which one is using the file you want to delete.
Check Resource Monitor
You need to know the application/process that is using the file. however, this is not possible without Resource Monitor. Resource Monitor allows you to know the process that is currently using the file that you want to delete.
Once you figure this out, stop this process/application and delete the file. To find the process that is using the file using Resource monitor,
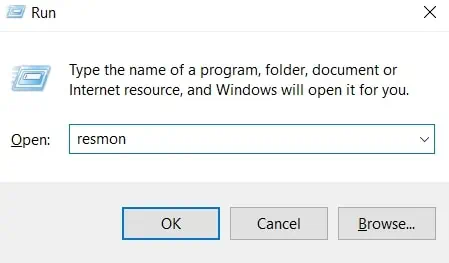
- Press the Windows + R key to open Run.
- Type
resmonand press Enter.
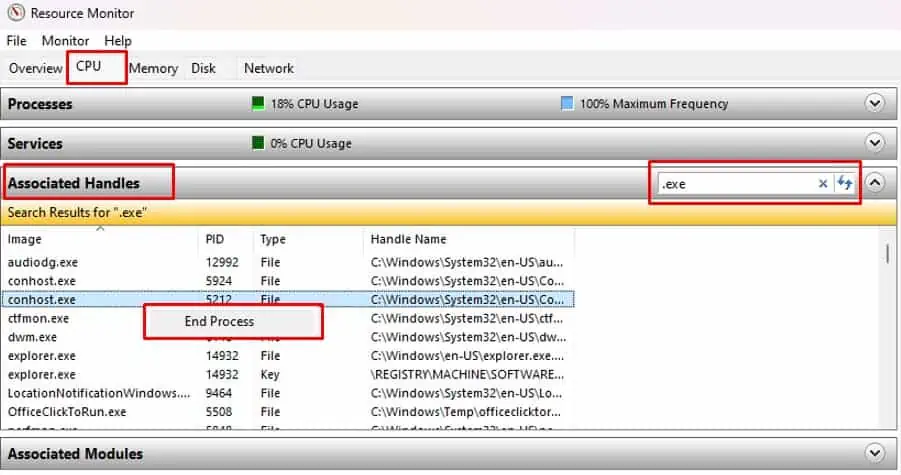
- Click on the CPU tab and expand Associated Handles.
- In Search Handles input bar, type in the filename that you want to delete.
- Now, you will see any application/process that is currently using the file.
- Right-click on this process/application and select End process.

Once you find the process/application you can close the program using the Task Manager.
Close the program Via Task Manager
Some programs will keep running in the background even when you close the entire application. Since the application still uses the file in the background, you cannot remove this file. To delete these files, you need to kill the background process via the Task Manager.
- Press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
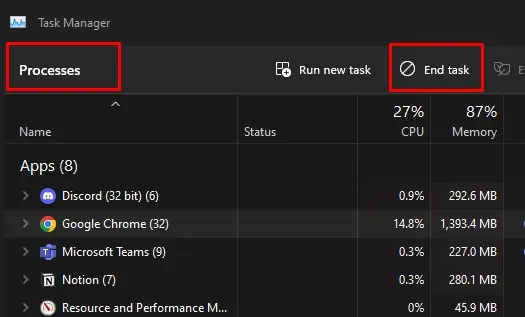
- Go to the Processes tab.
- Select the application that is using the file.
- Select End task.

- Try deleting the file.
If you cannot find the correct application, close any unnecessary application/process running in the background.
Close the Process using Process Explorer
Sometimes, you may be unable to determine which process is using the file. In this case, we recommend that you use an application developed by Microsoft called Process Explorer. You can use this application to determine the process that is using a specific file.
- Download Process Explorer from the official Microsoft website.

- Extract and open the folder.
- Run
procexp.exe.
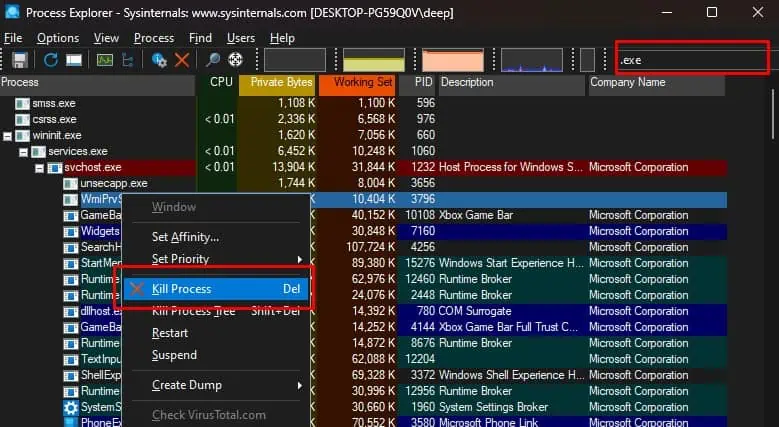
- Press Ctrl + F and type the filename you want to delete.
- The application will display any process that is currently using the file.
- Once you find the process, right-click on it and select Kill process.

- Try deleting the file from your PC.
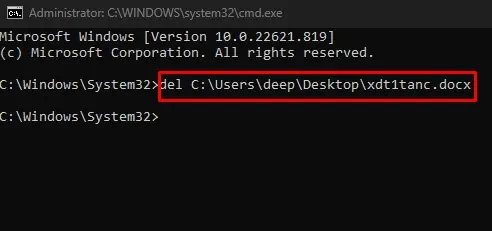
Delete from Command Prompt
Running Command Prompt as Administrator gives you admin privileges. This means that you will have access to features that are normally restricted. And you can run commands that are not available in normal user mode.
If the file you want to run is in use by an application that is invoked by normal user, you may be able to delete the file using Command Prompt as administrator. However, if the application is running as admin, you cannot delete this file using this method.
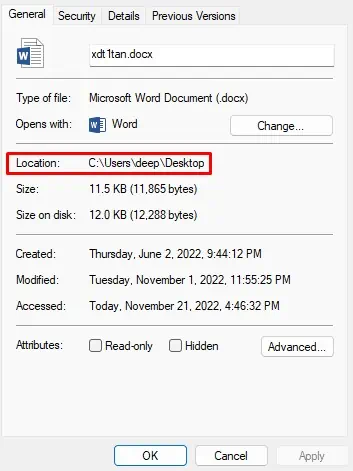
- Right-click on the file you want to delete.
- Copy the Location.

- Press the Windows + R key to open Run.
- Type
cmdand press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open Command Prompt as Administrator. - Now type
del *Location*\*filename*(replace *location* and *filename* with the location you copied from step 2 and the filename, respectively) and press Enter to delete the file.
Restart the PC and Delete
When you restart the PC, any process that is halting the deletion process stops as well. And if this process/program is not enabled in the startup, deleting this file will work once you restart your PC.
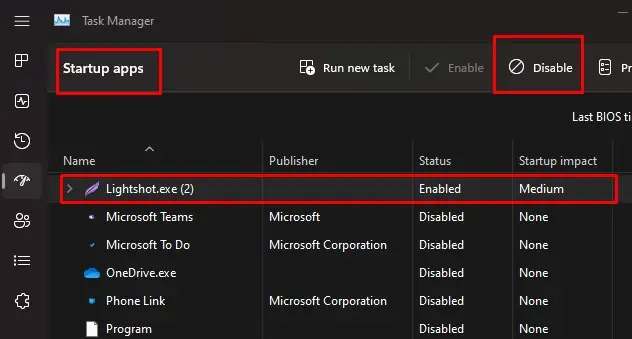
However, if this process starts during boot, you will need to disable the application during startup. To do this,
- Press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open the Task Manager.
- Go to the Startup tab.
- Click on any application and select Disable.

- Disable all the applications that run on startup.
- Restart your PC and try deleting the file.
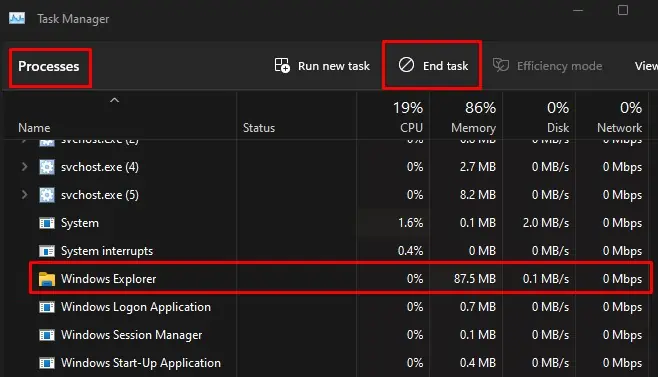
Restart Windows Explorer
Windows Explorer handles basic desktop functionalities such as icons, the taskbar, the start menu, or processes related to transferring or deleting files. If you have issues related to these components, restart Windows Explorer to fix the issue.
- Open the Task Manager.
- Select the Process tab
- Under Windows Processes, select Windows Explorer.

- Select Restart.
- Now, Try deleting the file.
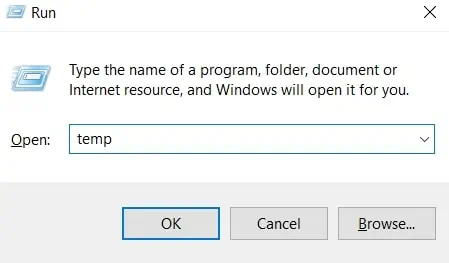
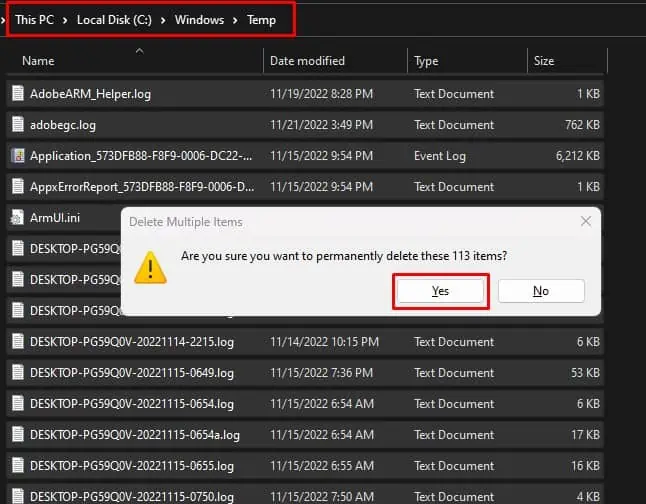
Delete Temporary Files
Windows creates temporary files to store information when a file is modified or created. After the process is complete, the system may or may not delete these temporary files depending on whether an application uses them.
If these temp files are currently in use and are linked with the file you want to delete, you may not be able to delete such files. To fix this, first try deleting temporary files.
- Press the Windows + R key to open Run.
- Type
tempand press Enter.
- Select All and permanently delete these files.

- Press Skip if any of these files are currently in use by another program.
- Again, open Run.
- Type
%temp%and press enter. - Select all the files and delete them permanently.
Turn off Caching of Thumbnails
Windows stores a cache database for thumbnails for your files and documents. Windows uses this database to display a glimpse of the file/folder before you open it. If the thumbnail of the file you are trying to delete is currently in use, the PC may have issues deleting this file.
To fix this, you can try turning off caching of thumbnails from the Group Policy Editor.
- Press Windows + R to open Run.
- Type
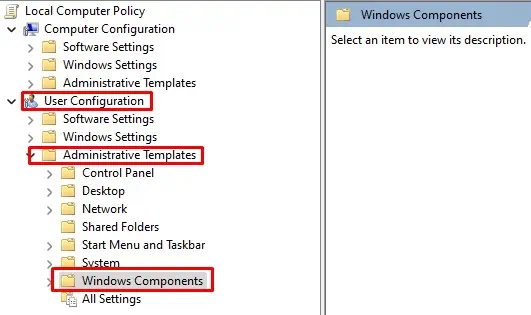
gpedit.mscand then press Enter to open Group Policy Editor. - Navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Component > File Explorer.

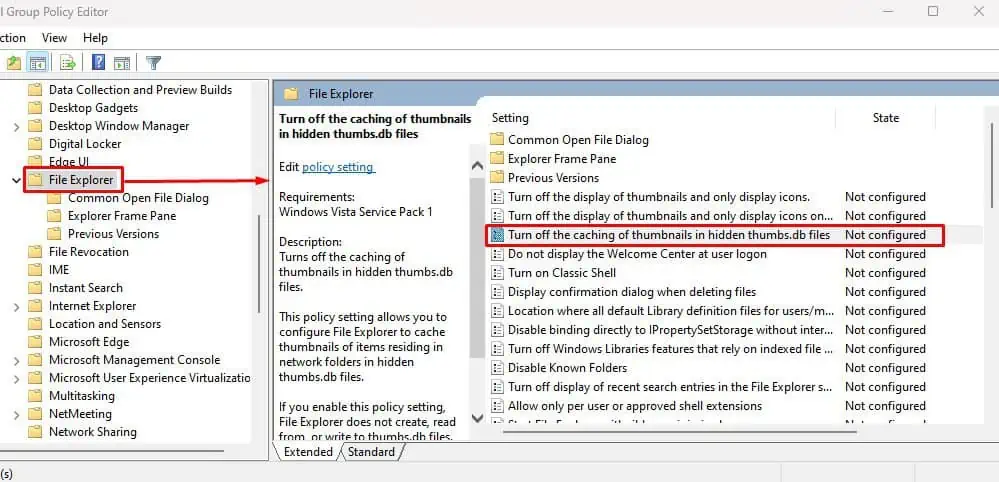
- On the right panel, double-click on Turn off the caching of thumbnails in hidden thumb.DB files.

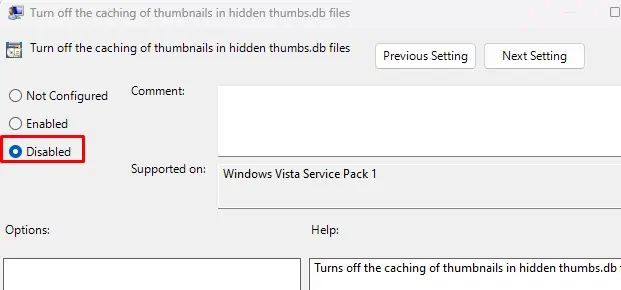
- Select Disabled and press Apply.

Change File Explorer Settings
When you launch several File Explorer, the OS runs all its windows in one single process, i.e., explorer.exe. However, if the file explorer runs as two separate processes, the PC might run into conflicts between resources.
To make sure that this does not happen, you need to launch file explorer as a single process.
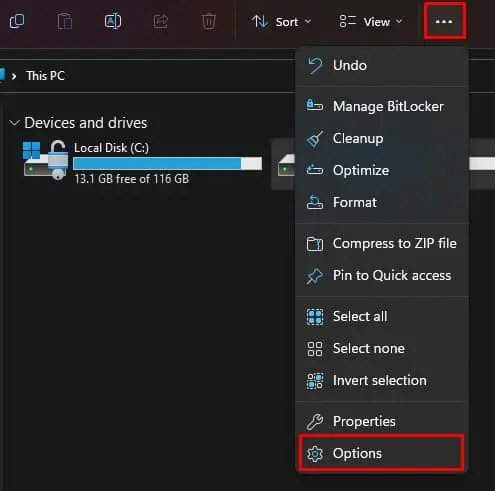
- Press the Windows + E to open File Explorer.
- Click on the three-dotted horizontal icons and select Options.

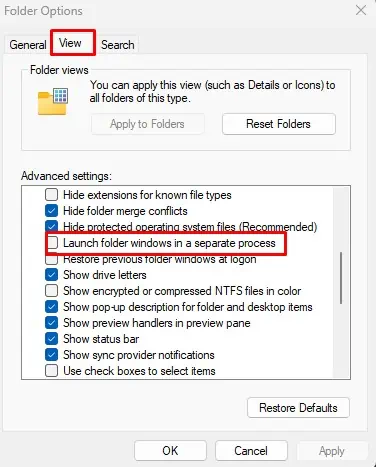
- Go to the View tab.
- Here make sure that Launch folder windows in a separate process are disabled.

- Click Apply and then OK.
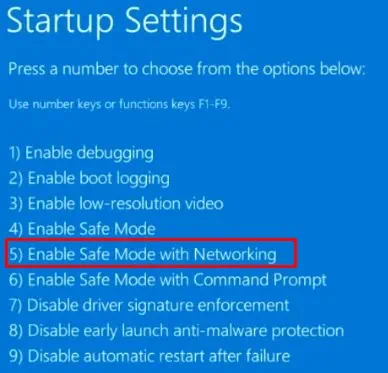
Delete Files in Safe Mode
You can try deleting the file in Safe Mode if none of the solutions work. In Safe Mode, the system only uses essential drivers and applications to run the Operating system. The OS does not run unnecessary processes, applications, or processes, and therefore you can delete the file in safe mode.
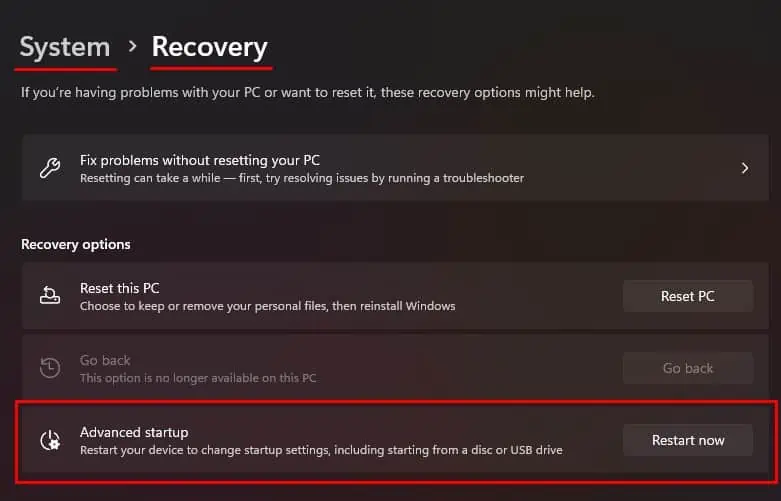
- Press Windows + I key to open Settings.
- Go to System > Recovery.
- Click on Restart now to boot into the advanced startup menu.

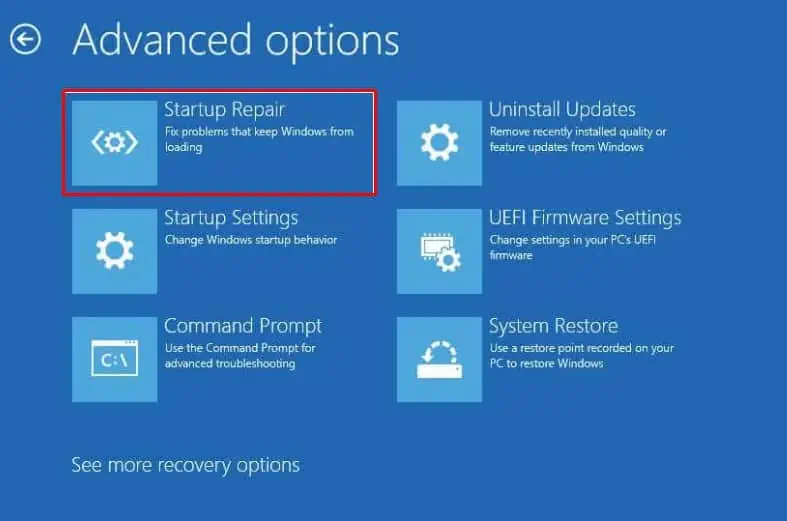
- Once the PC restarts, navigate to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup options.

- Click on Restart.
- Again after the restart, press F5 to boot the PC in Safe Mode with Networking.