Encrypting a hard drive is a good way to protect its contents from unauthorized access. It encodes the hard drive’s contents using an encryption algorithm.
This way, hackers or other random people can’t get access to your hard drive’s contents in any way unless they get the encryption key as well.
Windows allows two built-in methods to encrypt your internal as well as external drives— BitLocker and Device Encryption.
However, these methods depend on the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) hardware. Without TPM, you have to use third-party apps for the encryption.
Using BitLocker
The traditional and the most popular way of encrypting your hard drive is through the built-in feature, BitLocker. You can load this program through the Control Panel or Windows Settings.
- Log into an administrator account on Windows.
- Press Windows + I to open Settings.
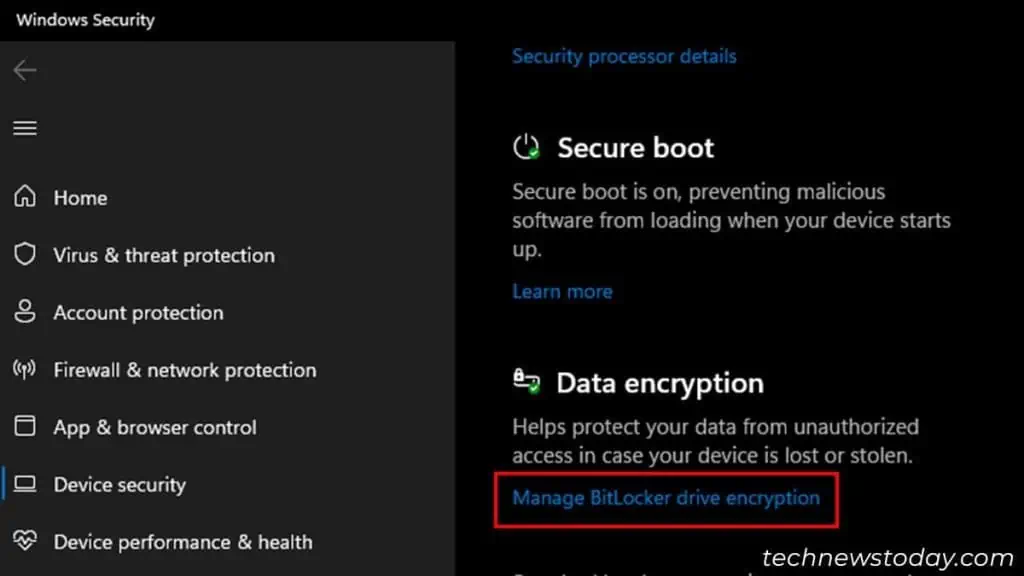
- Go to Privacy & security > Windows Security > Device security. For Windows 10, go to Update & Security > Windows Security > Device Security instead.
- Click Manage BitLocker drive encryption under Data encryption.

- If you can’t find this option, enter
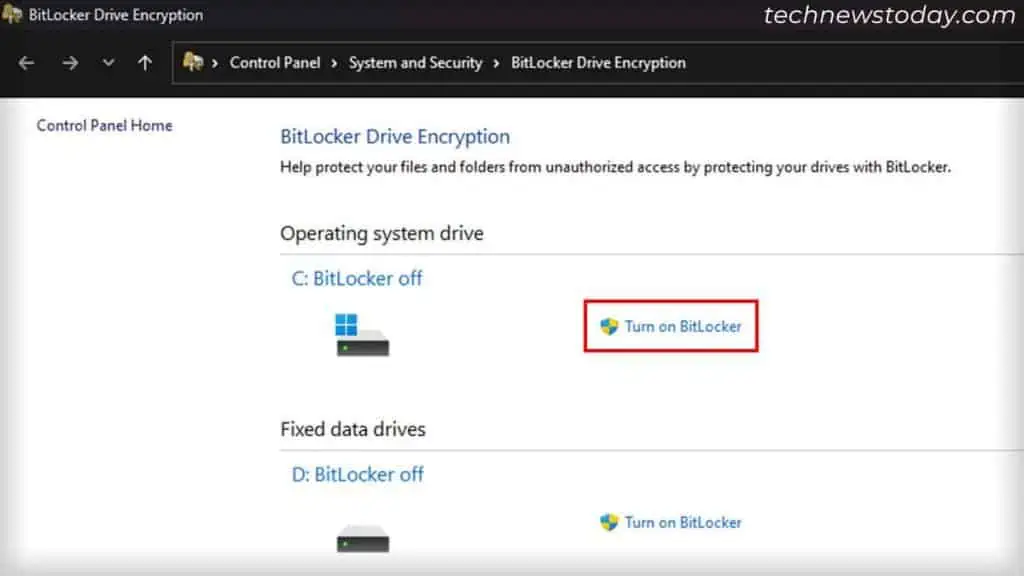
control /name Microsoft.BitLockerDriveEncryptionon Run (Win + R) to open the program. - Expand your drives by clicking on them.
- Click on Turn on BitLocker for all drives you wish to encrypt.

- For your OS drive, it will warn you that you won’t be able to use the Windows Recovery Environment after encrypting the drive. Click Next to process.
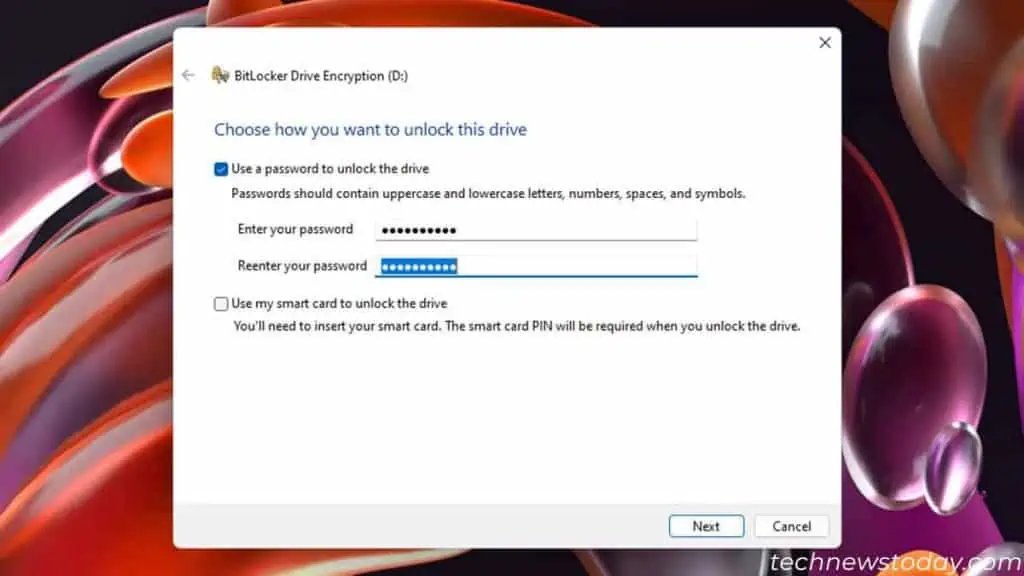
- For other drives, check Use a password to unlock the drive and specify the passwords. If you wish to use a smart card, check that option instead. Click Next.

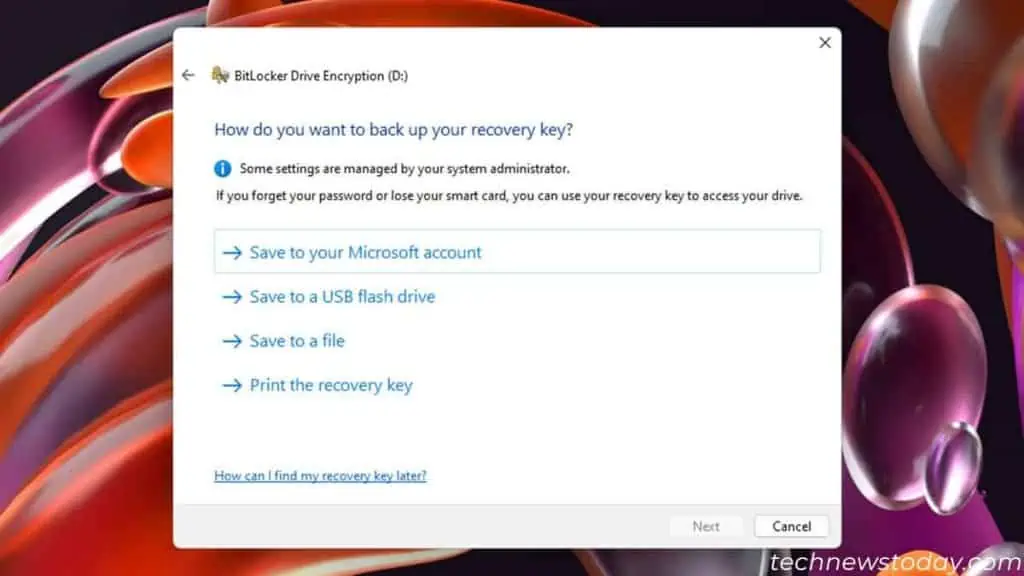
- Choose how you want to back up your recovery key and follow the instructions. I recommend saving the key (or file) to a USB flash drive. You can also save it in multiple locations.
- After that, click on Next.

- Pick between the encryption used disk space or the entire drive and click Next.
- Check the New encryption mode or Compatible mode depending on your need. Read the descriptions on the tab to learn their differences.
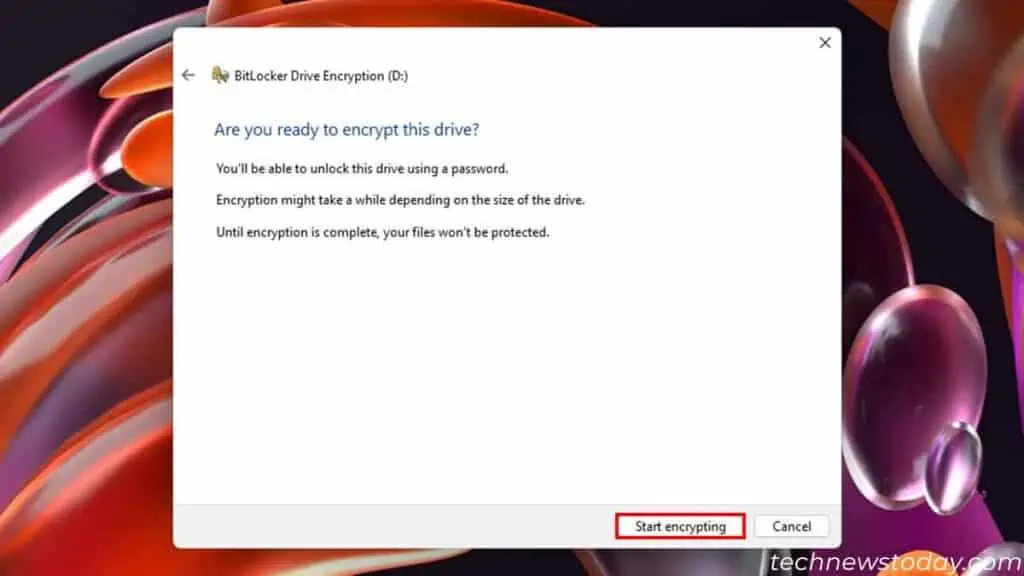
- Click on Start Encrypting to begin the process.

- Hit Close after the process completes.
Using Device Encryption
You can also use Device Encryption in some computers to encrypt your hard drives. It also uses the TPM like the BitLocker. But while BitLocker allows you to choose which drive to encrypt, this feature encrypts all connected drives.
Apart from the TPM, Device Encryption also has some more prerequisites:
- Your PC should support UEFI firmware.
- Your firmware should support modern standby (S0 state). (You can check by running
powercfg /aon Run)
If your computer supports Device Encryption,
- Log in to a Microsoft account with admin privileges. If you don’t have such an account, create it or change to one.
- Open Windows Settings by pressing the Windows key + I.
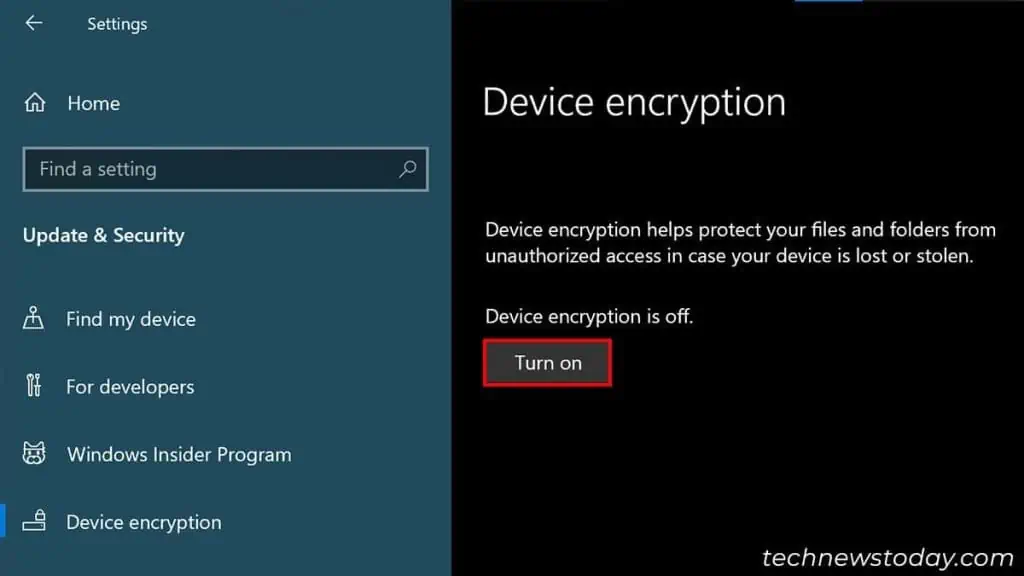
- Go to Privacy & security > Device Encryption or Update & Security > Device Encryption.
- Click on Turn on and wait until the process completes.
msinfo32 on Run) to see why automatic device encryption failed.Using Third-Party Software
You can also use other third-party encryption software to encrypt and protect your drives.
Most of these programs don’t use the TPM, so there’s no hardware limitation. Many open-source and free apps like VeraCrypt, AxCrypt, DiskCryptor, etc., are also available for this purpose.
If you want to encrypt your external hard drives, you may even find an OEM encryption application.