If you are using a fast SSD, but your system is slow, improper connections, firmware/driver issues, or high system resource usage are usually the culprits.
So, if you want to speed up your slow SSD, first check its type to understand the usual speed it should provide. If it doesn’t show the necessary speed, check connections and update firmware and drivers.
You can also lower system resource usage, scan for malware, and change power settings to boost system performance.
First, Check the SSD Type (and Health)

Different types of SSD (M.2, NVMe, SATA) offer different read/write speeds depending on the type of motherboard connection.
In general, you’ll find the following speeds for the SSD drives:
| Bus Interface | Bus Interface Generation | Common Practical Read/Write Speeds (MB/s) |
| SATA | SATA-III | 300–500 |
| M.2 NVMe | PCIe 3.0×4 | 600–3500 |
| PCIe 4.0×4 | 3000–7000 | |
| PCIe 5.0×4 | 7000–10000 |
The large range for the speeds of the same types of SSD drives is due to the difference in the quality and the cell memory level in the SSD.
You may even find a slight variance between quality and performance between the same SSD models.
So first, check the type of your SSD. If you are using an M.2 NVMe SSD, check the PCIe generation supported by your motherboard as well.
Your SSD will use the lowest possible speed among those supported by the SSD and the motherboard.
Then, use a benchmark or testing application like CrystalDiskMark, SSD-Z, and so on to test the read/write speed. Then,
- If the disk shows significantly lower speed than what it’s supposed to have, first check the SSD health. If it is going bad, you need to replace it. Otherwise, go through the solutions below.
- If the SSD model you are using itself does not provide enough speed, upgrade it or try using other performance-boosting methods. Check out our guides on How to Optimize Windows and How to Make Windows 11 Faster for more details.
- Keep in mind that other components like the RAM or the CPU may bottleneck the SSD drive and impact the system’s performance. You can also test them in a similar manner and upgrade them as necessary.
Note: If the SSD benchmark shows enough read/write speeds, but you are experiencing performance issues, it may be a result of other problems instead of the SSD.
In such cases, I recommend you check out following articles on our platform depending upon your issue:
- Why is My Computer Suddenly Slow?
- How to Fix Slow Computer Startup
- How to Fix Slow Boot Time Issues
- Why Am I Lagging So Much?
Change Connection Ports or Slots
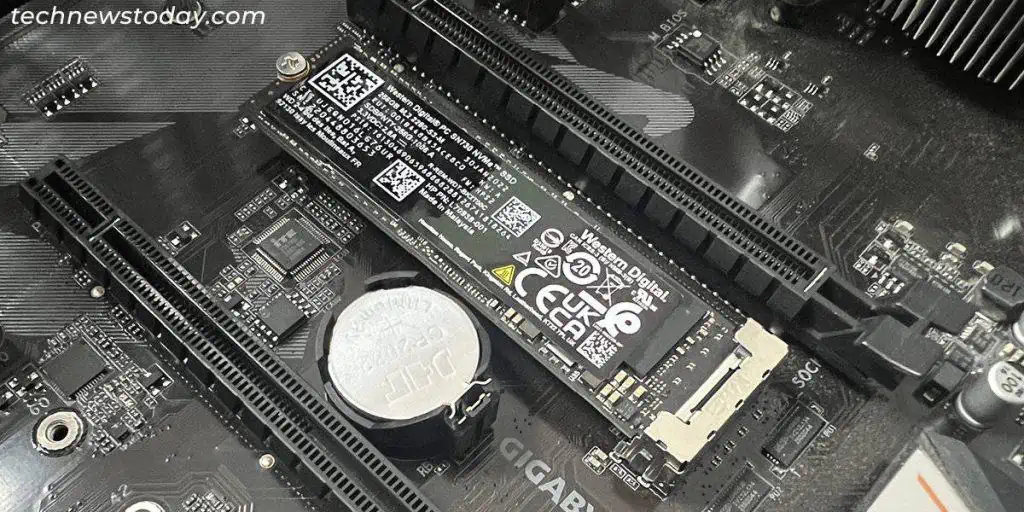

Improper connection of the SSD with its port or slot may also bring about lags. This issue usually occurs due to faults in the port or the slot, so try changing them and see if it helps.
- First, open your computer’s case.
- For a SATA SSD, unplug the data cable from the motherboard and plug it into another port.
- For the NVMe SSD, unscrew the heatsink and the SSD, take it out and insert it to another slot and screw it along with the heatsink.
You can also check out our How to Install SSD guide for the detailed steps.
Update Firmware and Driver
An SSD with outdated firmware or driver may not be fully compatible with the latest motherboard or operating system.
So, it’s best to update the firmware and drivers to the latest available versions as soon as possible.
You can do so through the manual Windows update, as it also provides driver and firmware updates.
For that,
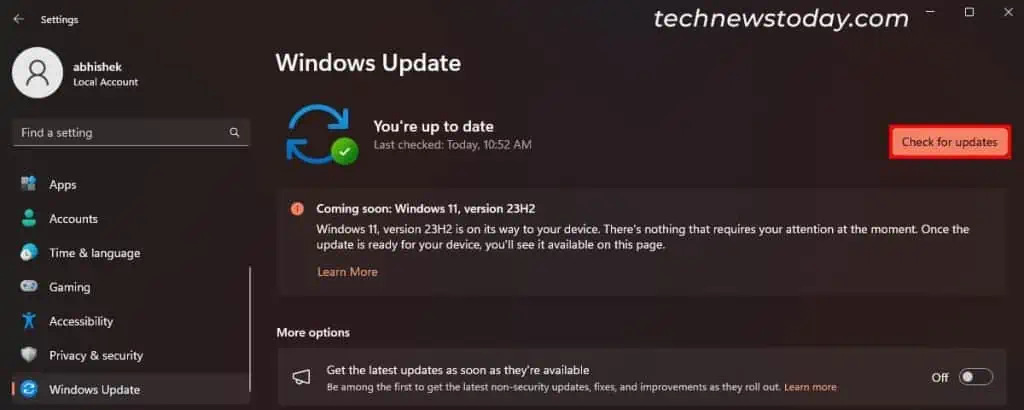
- Open Windows Settings by pressing the Windows key + I.
- Go to Windows Update and click Check for Updates.
- If you see a Firmware or Driver update for your SSD, install it.
You can check the official website of your SSD for firmware/driver updates or any update application.
Lower CPU, RAM, and Disk Usage
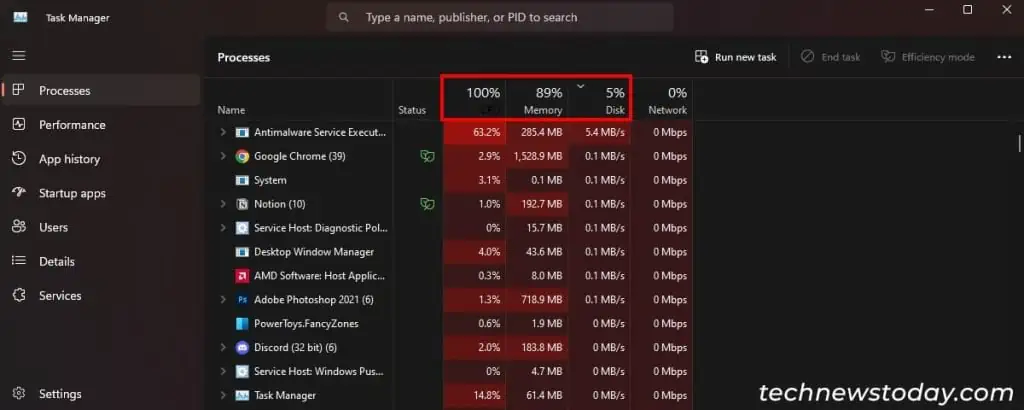
If the SSD needs to perform a lot of read-write operations during the same period, it will run into performance issues. You can check the current disk usage on the Task Manager’s Processes tab.
If it is high, lower the usage by disabling background processes that are consuming the most disk resources.
Also, if your CPU Usage or RAM usage is high, these components may be bottlenecking your SSD.
In such cases, you need to free up memory and CPU resources by closing unnecessary programs in a similar manner.
If such background processes result from many startup apps, disable all unneeded apps from the startup.
You can also go through your app list and uninstall those you no longer need.
Also, your SSD will show latency and other performance issues if it is nearly full.
So, I recommend you have 20-25% storage space free for optimal performance. But if you have larger drives (1-2TB), you can lower this number to 10-15%.
Scan for Malware
A malware infection can also severely affect SSD performance. Some malware may use up a lot of the system resources, including the Disk read/write cycles.
Conduct a full scan of your system to prevent such issues. You can do so using Windows Settings through the steps below:
- Open Windows Settings.
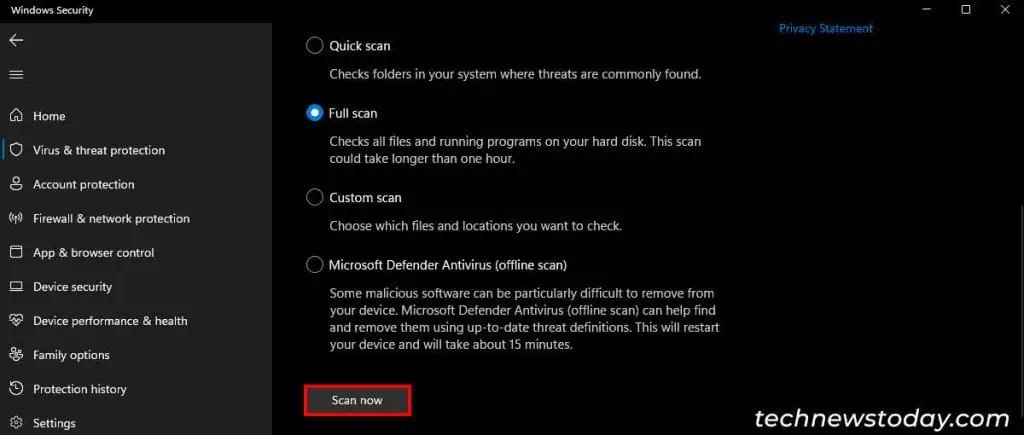
- Go to Privacy & security > Windows Security > Virus & Threat Protection.
- Click on Scan options, check Full scan, and hit Scan now.
Change Power Settings
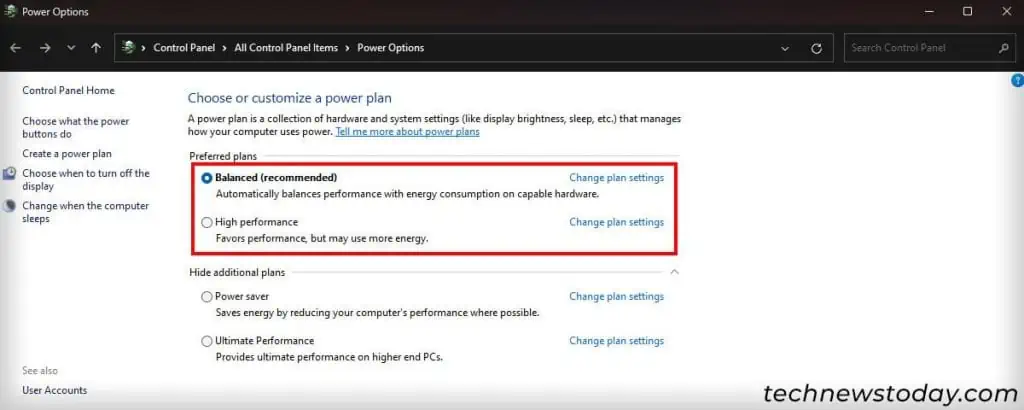
The power saving mode on Windows limits your SSD and CPU performance to lower the power consumption.
If you want a faster system, setting the mode to High Performance or Balanced is best.
To do so,
- Open Run by pressing the Windows key + R.
- Type
powercfg.cpland press Enter to open Power Options. - Change the power plan to Balanced or High performance instead of Power saver.
Some computers may have additional power settings that work separately from the Windows power settings.
For instance, my Lenovo Legion 5 laptop allows setting the power mode to Performance, Balanced and Quiet modes. So, change those settings as well.
