Overclocking your CPU increases its working speed and boosts its performance.
If you can set up a stable overclock, you’ll have a smoother computer experience and may even get FPS increase in CPU-intensive games.
However, you need to proceed with caution and work slowly when increasing the CPU frequency, voltage, or clock speed to avoid causing damage.
I will be using the following components and show how I overclock it to provide you with a practical example.
– CPU: AMD Ryzen 7 1700 Eight-Core Processor
– Motherboard: ASRock x370 Taichi
– AIO Cooler: Gamer Storm Captain 240EX White
For laptop-specific instructions, view our How To Overclock Laptop CPU guide.
Check Support for Overclocking
The CPU frequency or speed is a multiplication of the CPU core ratio or multiplier and the base clock speed (BCLK):
CPU Frequency = BCLK * MultiplierWhile overclocking a CPU, we are actually increasing this core ratio. This is only possible for CPUs that come with unlocked cores.
- Such CPUs include all available AMD CPUs and K, KF and X-series Intel processors. But there may be exceptions, so check your CPU’s official support page first.
- You should also note its Base Clock and Max Boost Clock at the same time.
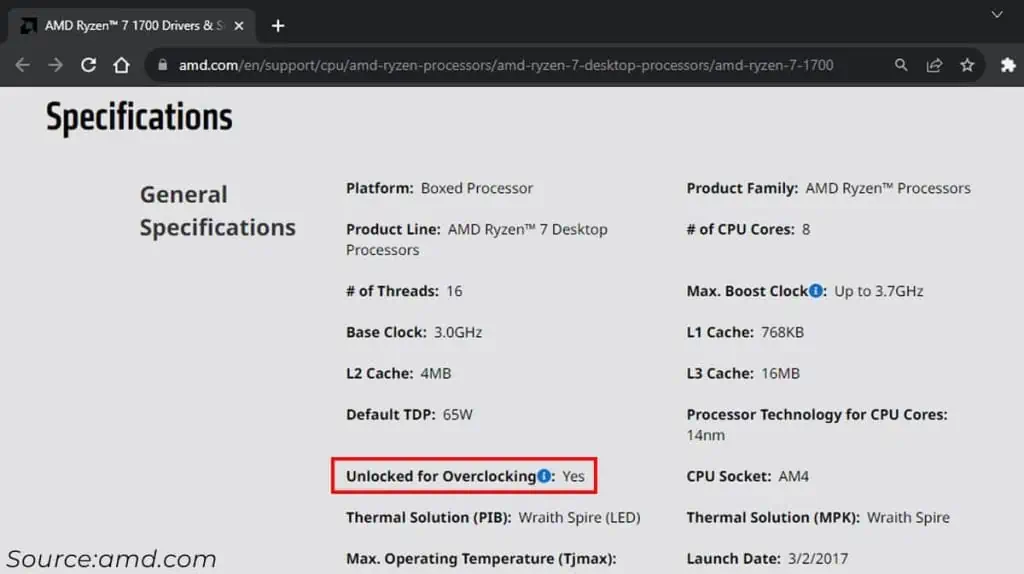
Keep in mind that Max Boost may not represent the maximum frequency you can achieve. Depending on your CPU cooler, the quality of thermal paste, motherboard design and BIOS version, the frequency may go much higher.
For Intel motherboards without unlocked cores, only some auto-OC options or BCLK (Base Clock) overclocking are available. Overclocking the base clock also increases the RAM frequency at the same time.
Establish a Baseline
Before overclocking your CPU, it’s best to run stress and benchmark tests to establish a baseline. Note down the CPU temperature, frequency, voltage and benchmark scores for future comparison.
Also, make sure to choose the program meant for your CPU like 3DMark, Cinebench, Prime95. You want to put pressure on the CPU rather than another component.
Get to BIOS
To overclock your CPU in BIOS, first get to the BIOS/UEFI Interface. After turning on your computer, press the BIOS key as soon as you see the manufacturer’s logo screen.
Alternatively, you can start pressing the keys repeatedly even before that to get the timing right.

The BIOS key for my ASRock motherboard was Del or F2. The key you need for some other popular motherboard are as follows:
If the BIOS key doesn’t work, you may have enabled Fast Boot or similar settings. In such cases, access UEFI Firmware Settings through the Advanced Startup options.
Use Automatic Overclock
If you are just getting into overclocking the CPU, I recommend starting with automatic overclocking options. They actually provide a significant improvement in CPU frequency and performance.
- You may find different options such as Intel Turbo Boost Technology, AMD Precision Boost Overdrive, Base Frequency Boost, depending on your motherboard.
- Look inside Advanced CPU Configuration or simialr options in the Overclocking (OC) tabs to find them.
- Some motherboards like ASUS also come with automatic tuning features that enable different levels of overclocking depending on your need. For ASUS, these are EZ System Tuning and EZ Tuning Wizard.
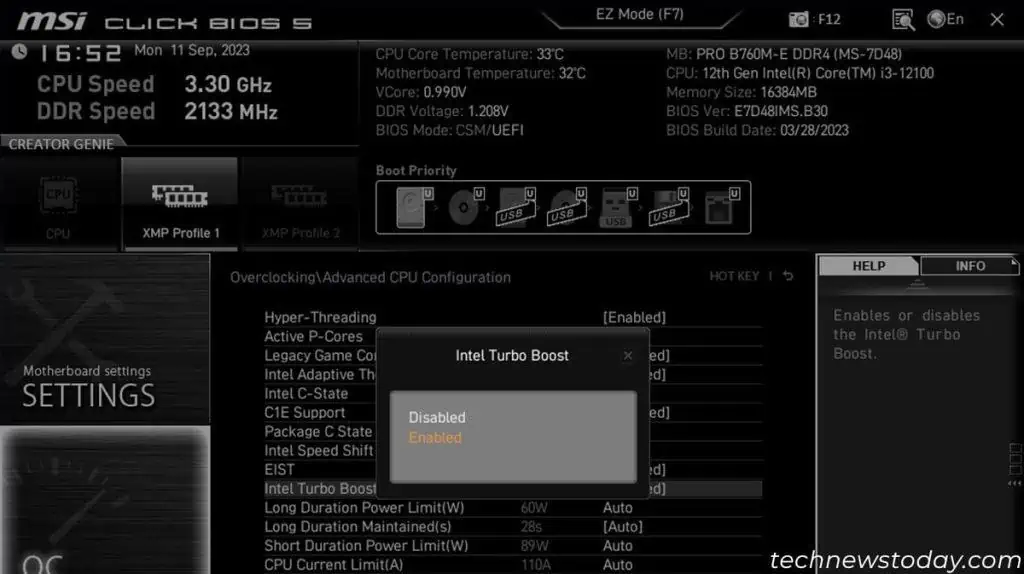
After enabling such options, save the changes and restart your PC. Then run stress and benchmarks tests to analyze the stability and performance improvement.
Manually Overclock CPU
Auto-OC options are generally not the most optimal settings. If you want to get the best overclocking results, manually change the overclock settings instead.
However, keep in mind that you can’t rely on others to get the necessary OC values. Even for same models, separate CPUs have different tolerances due to manufacturing differences.
You have to experiment with the values and slowly work your way up to get the optimal configuration.
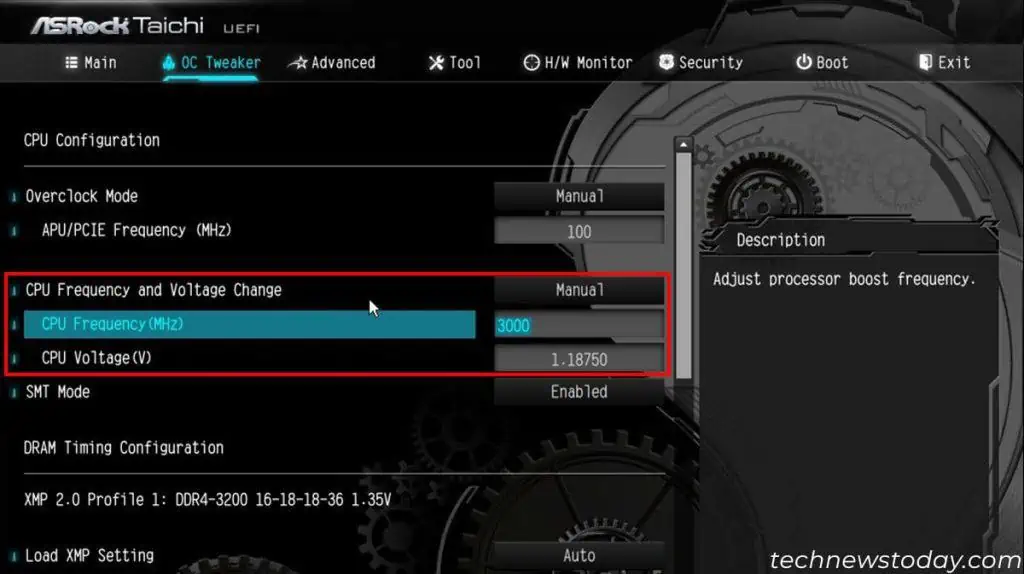
The goal is to have the highest possible CPU frequency with the lowest supporting CPU Voltage. The voltage also can’t be so high that it overheats the CPU.
In general, it involves the following steps:
Increase CPU Frequency
- First, enable Manual Overclock mode. As you can see above, I’ve set CPU Frequency and Voltage Change inside OC Tweaker > CPU Configuration to Manual.
- Slightly increase the CPU Multiplier. Only adjust the multiplier by 1 at a time.
- If you directly see the CPU Frequency, increase it by 100 MHz.
- Save and exit the BIOS, then restart your computer.
Test for Stability and Adjust CPU Voltage
- If the computer doesn’t restart correctly, there isn’t enough power on the chip to perform at that level.
- Increase the CPU voltage on the BIOS to see whether an increased power flow fixes the problem. Only use increments of 0.05 V and don’t let the CPU voltage cross the safe limit (usually 1.4-1.5V).
- Save your settings and get inside your OS.
- If the PC starts properly, stress test the CPU to see how it performs under heavy load.
- When the system runs stably, increase the CPU Multiplier again and continue testing.
- If you experience crashes or glitches, go back into your BIOS and increase the voltage.
Monitor CPU Temperature
- You should also monitor the CPU temperature when running the stress test.
- Don’t let the temperature cross 100°C. Also, make sure the temperature does not go beyond 85°C on normal use (without stress test).
- If temperature remains excessively high, decrease the overclock settings to the last stable values. You need more efficient cooling options like custom water loops for higher overclocking.
Test and Repeat
Continue changing the settings and tweaking them as needed until you find a stable overclock. With Manual Overclock, I could raise my AMD Ryzen 7 1700 processor’s frequency from 3.0 up to 3.7 GHz. If I had a better cooler, I could probably raise it beyond 4GHz.
You can then run benchmark tests and record the improvements in the CPU performance.
Note: Since the exact steps for changing the CPU Frequency and Voltage vary for different motherboards, I recommend checking our dedicated guides if you need additional help.
Extra Tips
After enabling CPU overclock, you can also enable XMP for your RAMs in the BIOS to boost your system performance even further.
If you also want to overclock your GPU, you need to use specific OEM or third-party applications such as MSI Afterburner.
Also, any type of overclocking will affect your CPU health. So after overclocking, it’s best to do the following things to prolong CPU lifespan as much as possible.
- Add enough case fans both as exhaust and intake to maintain higher airflow inside the PC case.
- If applicable, upgrade your CPU cooler. If you are using an air cooler, move to liquid cooling options, such as AIO coolers.
- Clean your CPU cooler every six months or whenever your CPU temperature shows abnormal increase.
- It’s also better to clean and reapply the thermal paste at the same time. Make sure to apply a suitable amount using a good pattern.
If you want to disable manual overclocking, rather than manually reverting the settings, it’s best to reset your BIOS altogether.
Also, updating BIOS while enabling overclock may bring about system instabilities. So make sure to disable the overclock beforehand.