A lot of programs require admin privileges to function properly. Running a file as an admin can also be an easy solution to many application errors.
The most common approach is to right-click the .exe file and select the Run as administrator option. But there are numerous other ways to accomplish the same thing such as keyboard shortcuts, task manager, command prompt, and more.
So, without further ado, here are all the possible ways to run files as an administrator.
Using Contextual (Right-Click) Menu
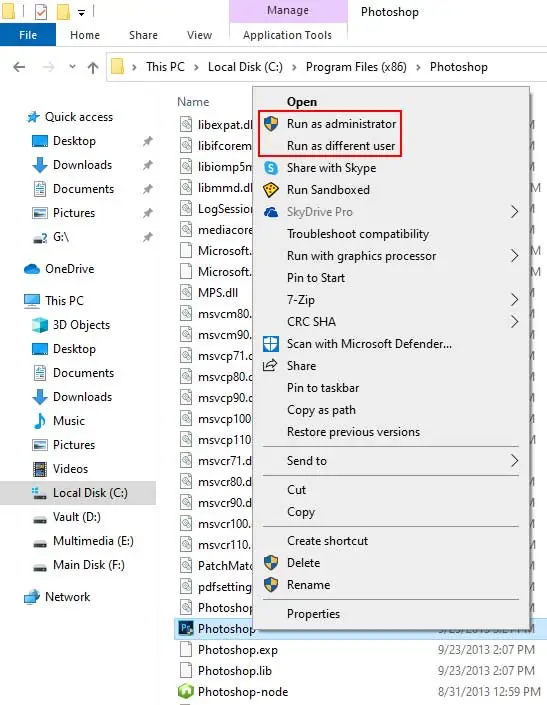
The usual way most users run a file as an administrator is by right-clicking its executable (.exe) file and selecting Run as Administrator.
Additionally, if you hold Shift and then right-click, you can select the Run as different user option. With this, you can enter the credentials for another admin account to run the file as an administrator.
You will need to confirm that you want to run the file with administrator privileges before it opens. This also applies to most other methods in this guide.
It’s possible to bypass this prompt if you want. Check the FAQ section for more on that.
Using File Explorer Ribbon
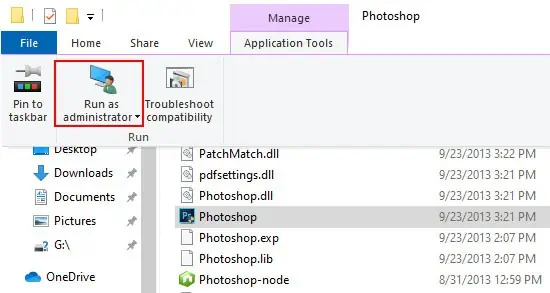
In the file explorer, select your file and open the Application tools tab. You can Run as Administrator or troubleshoot compatibility directly from here.
Search
In the search Window, you can press the option on the right or use the keyboard shortcut CTRL + Shift + Enter to run a file as an administrator.
Through Run
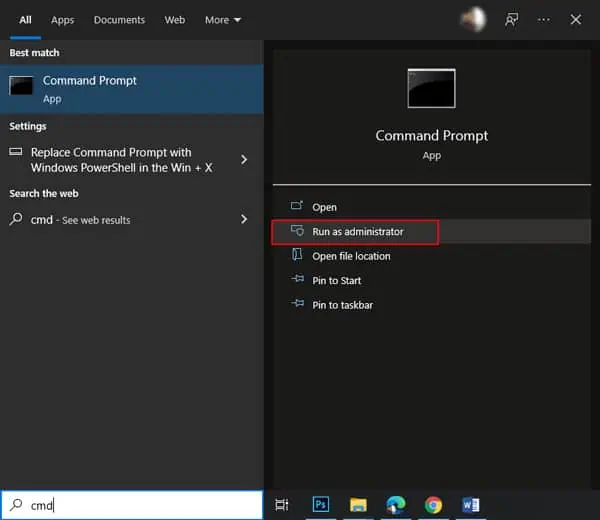
If you type a run command (cmd for instance) and press CTRL + Shift + Enter, you can directly launch it in Administrator Mode.
Using Start Menu
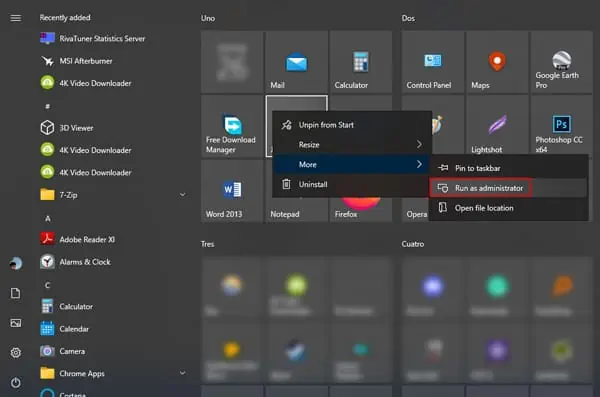
In the Start Menu, you can right-click any program and press More > Run as administrator.
Alternatively, you can also hold CTRL + Shift and left-click a program to run it as an administrator.
From Task Bar
You can hold CTRL + Shift and left-click any program to run it as an administrator directly from the taskbar.
Using Task Manager
Very few users know about this but it is actually possible to run a file as an administrator using the Task Manager. This can come in handy in certain situations, such as when the file explorer is not responding for instance.
- Press CTRL + Shift + Esc to launch the Task Manager.
- Press the More Details button to change to advanced view.
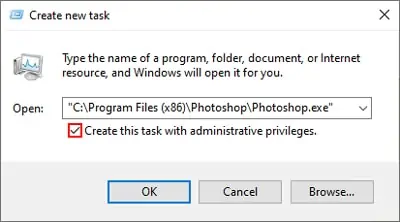
- Click on File and select Run new task.
- Use the Browse option to locate and select your file.
- Enable the Create this task with Administrative privileges option.

- Press OK to run the file as an administrator.
With Task Scheduler
If you want to set a program to launch at a specified time, Task Scheduler is the perfect Windows tool for this. To run the program as an administrator in such cases, follow the steps below:
- Press Windows + S to bring up the search window.
- Type task scheduler and press Enter.
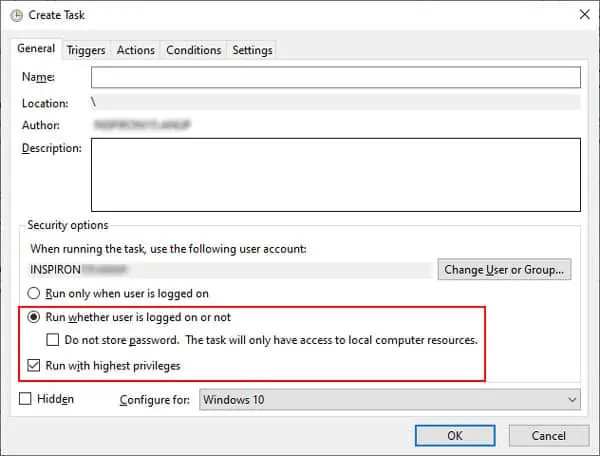
- From the top-left, select Action > Create Task.
- Once you create your task, select Run whether user is logged in or not.
- Enable Run with highest privileges and press OK to apply the changes.

Using Command Prompt
For users who prefer the command-line approach, the runas command can be used to run a file as an administrator. To do so:
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
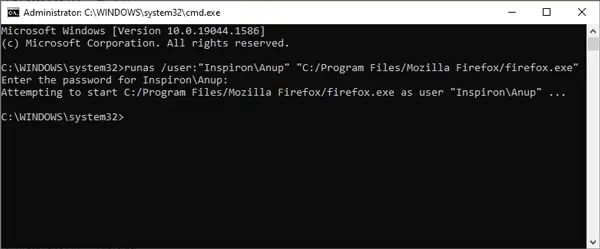
- Type cmd and press CTRL + Shift + Enter to launch Elevated Command Prompt.
- Type the following command, replace ComputerName, AdminName, and FilePath with the appropriate values as shown in the picture below, and press Enter:
runas /user:“ComputerName\AdminName” “FilePath”
If you get a system cannot find the file specified error, the file path is incorrect. Make sure you got the spaces correct as well.
When prompted to enter the admin password, type it and press Enter. The password won’t be shown on the screen, so you needn’t worry.
How to Run Files as Administrator by Default?
If you want to open any file or app as an administrator every time, you can do so from Properties.
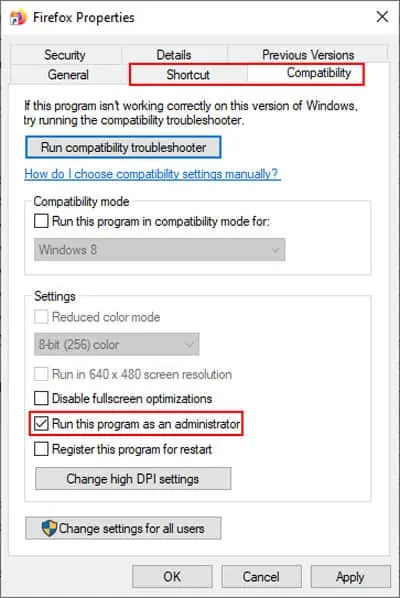
- Select the file and press CTRL + Alt + Enter to open properties. Alternatively, simply right-click and select properties.
- In the compatibility tab, enable Run this program as an administrator.

- In the case of shortcuts, enable it from Shortcut > Advanced > Run as administrator instead.