Most MSI motherboards support three ways to update the BIOS:
- M-Flash – Update directly from the BIOS interface.
- BIOS Flashback – Recover or update the BIOS on a system that can’t boot.
- LiveUpdate – Update from Windows via the MSI Centre.
I’ll use our MAG B550M MORTAR and PRO B760M-E boards to demonstrate all three methods in this article.
MSI BIOS Update – Dos and Don’ts
MSI releases new BIOS versions for most of their lineup every few months. But that doesn’t mean you need to update just as often. You should have a specific reason to update, such as:
- Better hardware compatibility in the new BIOS version
- Critical security patches or bug fixes
- Improved system performance and stability
- Support for new features (e.g., Re-size BAR)
If you do need to update, keep the following things in mind before you begin:
- Make sure the BIOS update isn’t interrupted (use a power backup, don’t remove the USB mid-update, etc.).
- This is especially important on budget boards that don’t support BIOS Flashback or DualBIOS. Without these, it can be a major hassle to recover from a failed update.
- I recommend you use M-Flash or BIOS Flashback as LiveUpdate is not as reliable (explained later).
Download the BIOS Update File
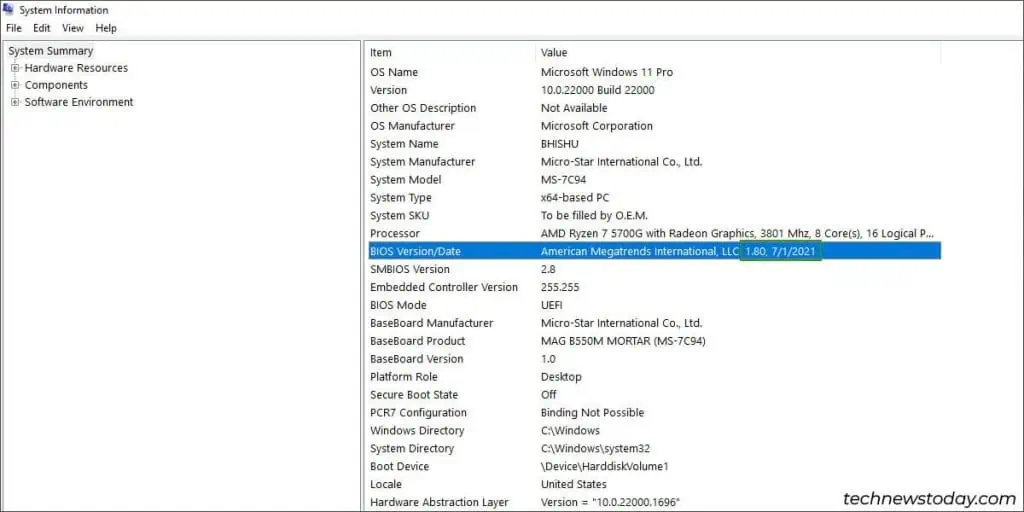
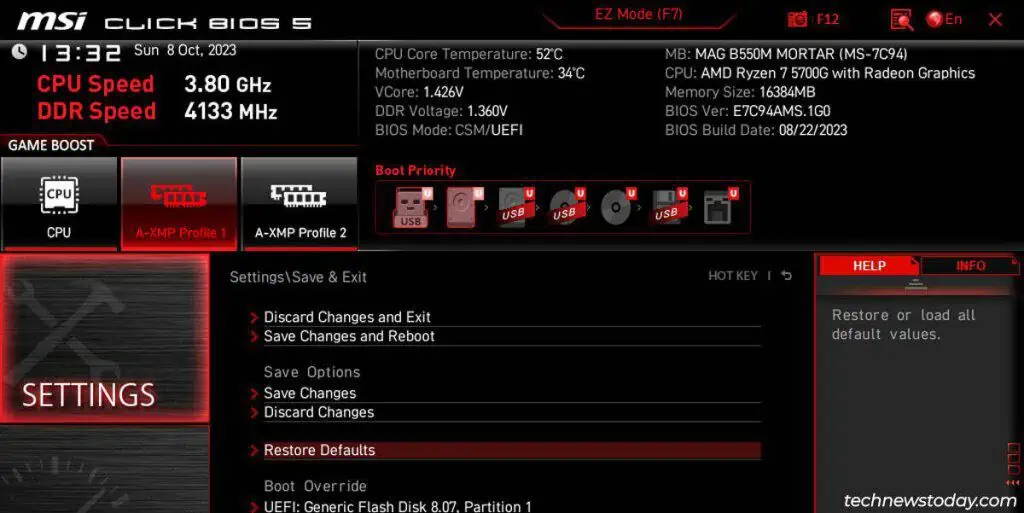
Start by identifying your motherboard model and the current BIOS version. You can boot to the BIOS to do this, or you can open the System Info applet in Windows.
Then, follow the steps shown below to obtain the correct BIOS file:
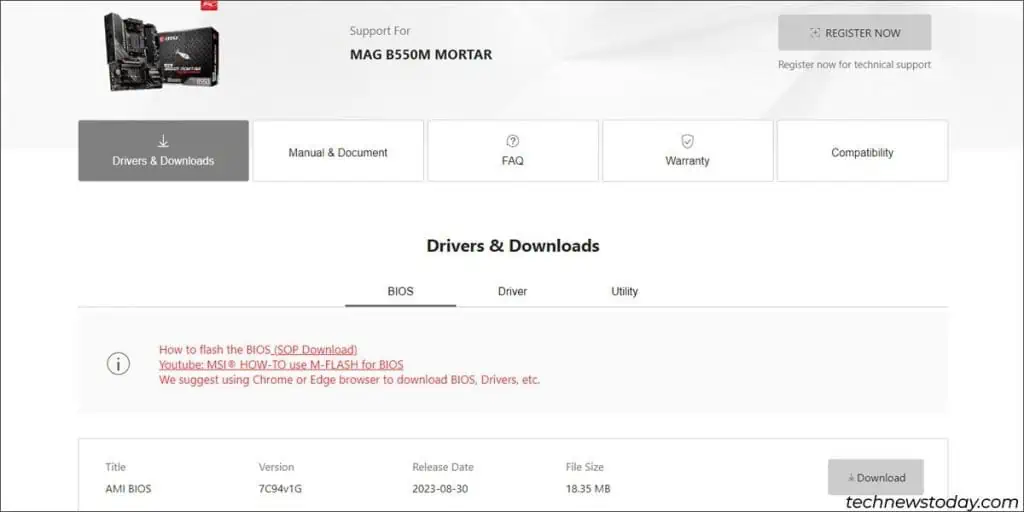
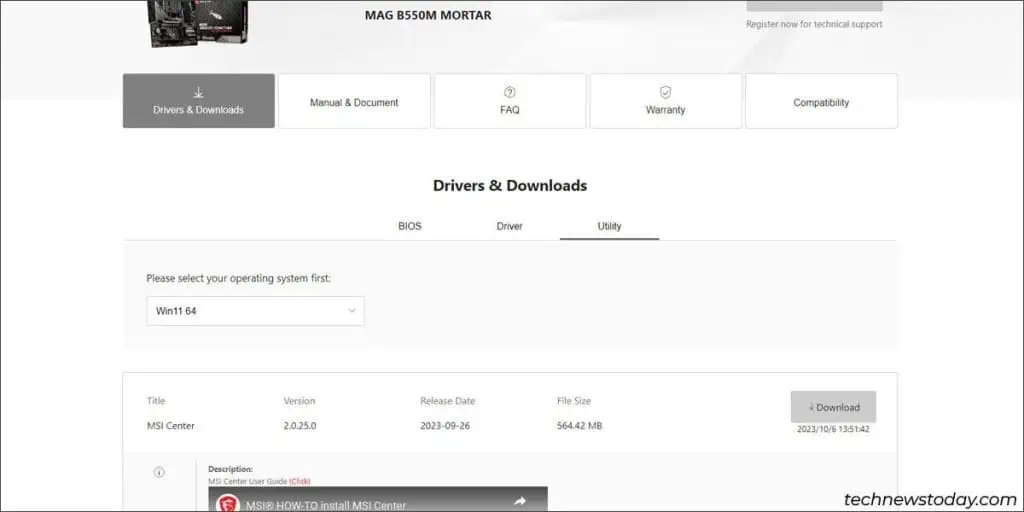
- Visit your motherboard’s support page. Ensure the board version is an exact match before proceeding (e.g., B550M Mortar vs WiFi vs Max WiFi vs Vector).
- Expand the Drivers & Downloads > BIOS section.

- First, check your current BIOS version for reference. Note the BIOS release date as well. This will be helpful as MSI’s naming scheme can be a bit confusing.

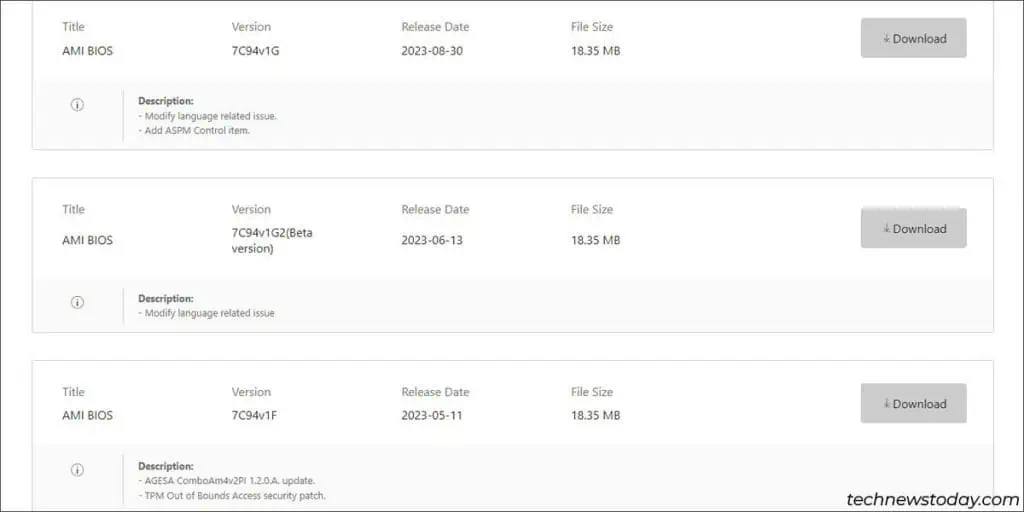
- Compare the version and date to identify your current BIOS from the list (
7C94v18in my case). - Check all the newer BIOS versions. Read the changelogs to ensure that you don’t miss any important info (e.g. if incremental updates are required).

- Once you’ve decided on the BIOS version, download it. Go for the latest stable version if you’re unsure.
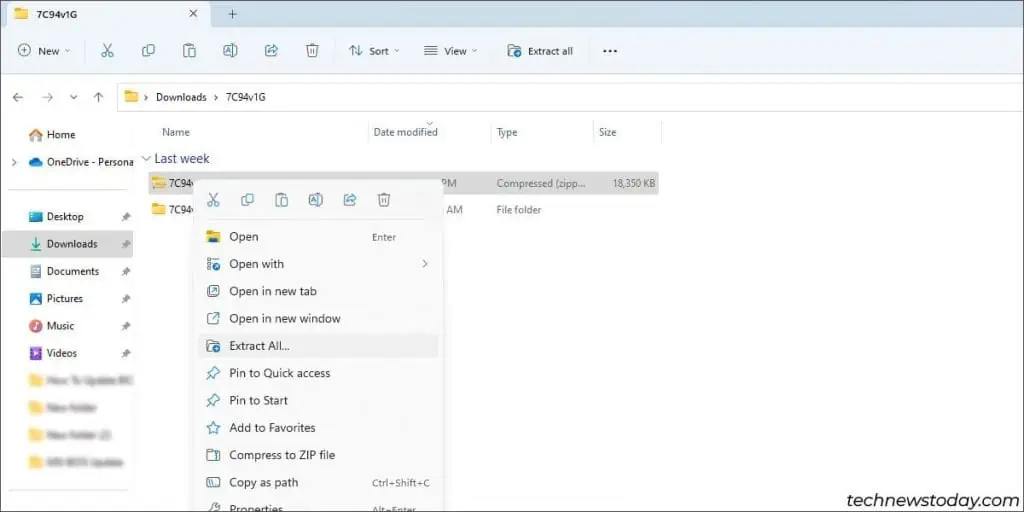
- Extract this archive and format a USB drive to FAT32.

The steps vary after this. So, continue from the appropriate section.
Updating with M-Flash
M-Flash is the standard BIOS update utility on MSI systems. It’s reliable and easy to use. Follow the steps shown below to update the BIOS with this method:
- Move the extracted BIOS file to the USB drive.
- Connect the USB drive to the system where you want to update the BIOS.
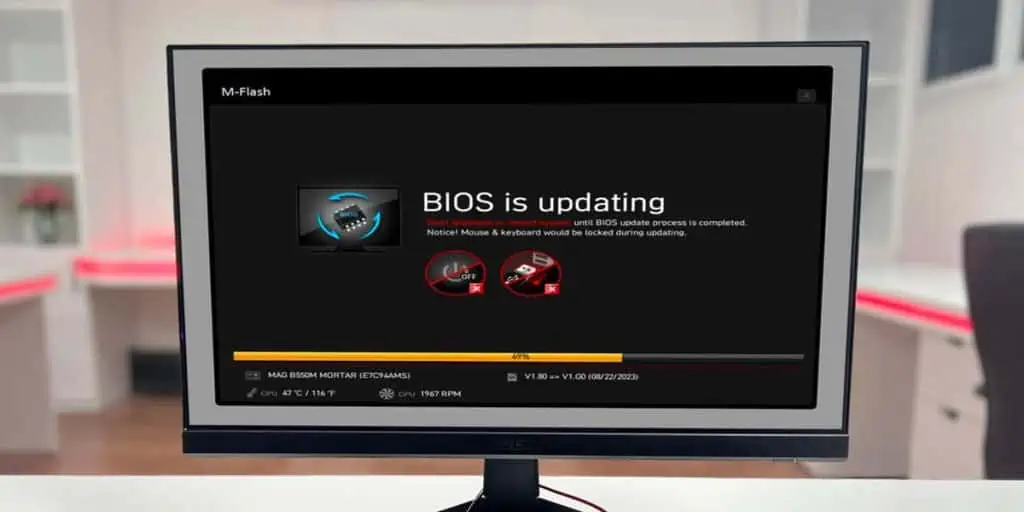
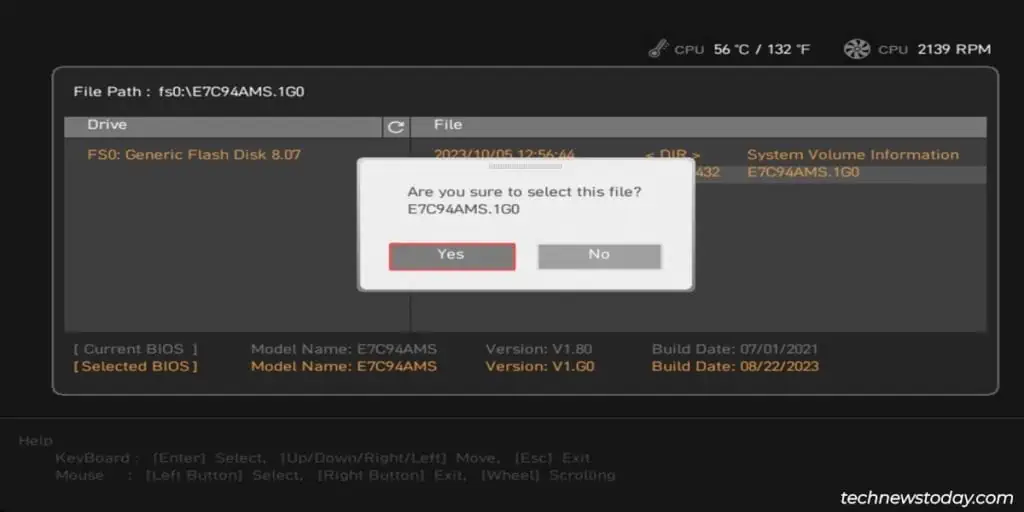
- Restart your PC and repeatedly press Ctrl + F5 to launch the M-Flash utility. You can also boot to the BIOS (press Del at startup) and launch it from there.

- Highlight the BIOS file and select Yes to start flashing the BIOS.

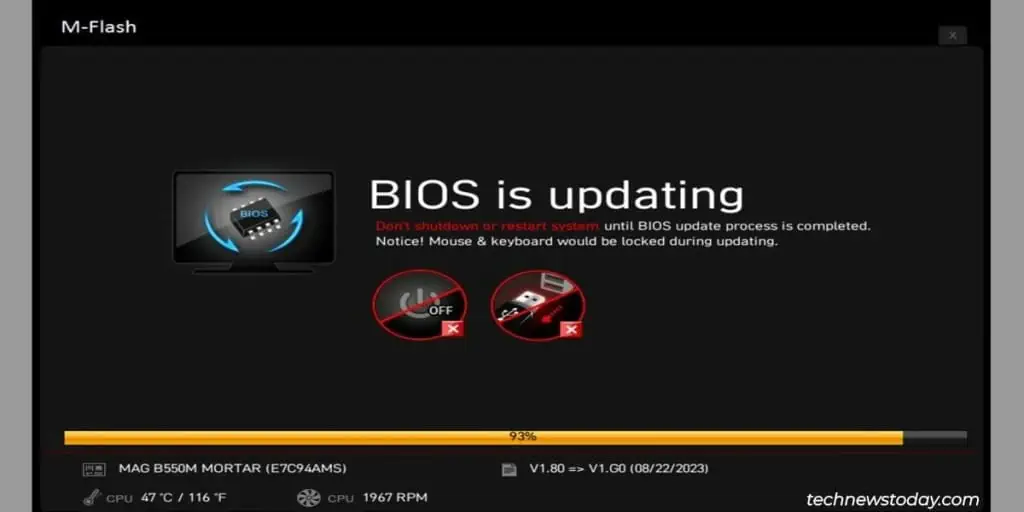
- The update should finish in 5 minutes or so. Your PC will restart afterward.

Performing a BIOS Flashback
BIOS Flashback is used to update systems without a CPU or to recover boards bricked by a failed BIOS update. But you can also use it for normal BIOS updates.
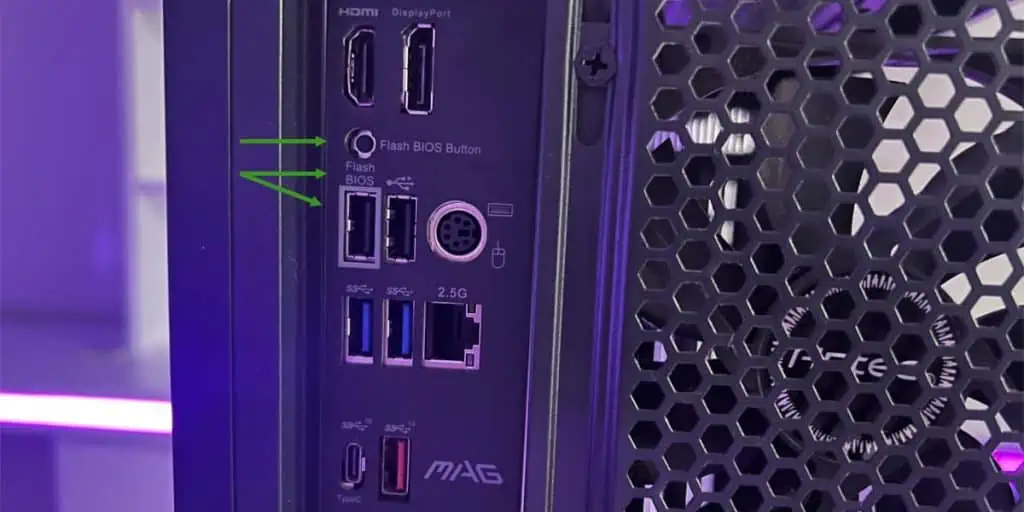
Most MSI boards support it as a fail-safe feature. To verify this on your board, look for the Flash BIOS port and button on the rear I/O panel. Alternatively, check the user manual.
If your board supports it, use the following steps to update your MSI BIOS with BIOS Flashback:
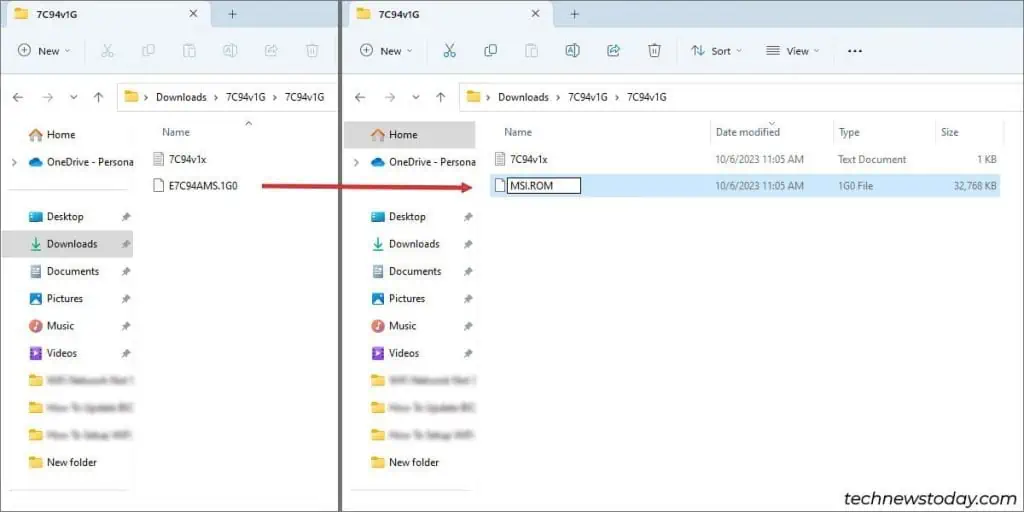
- Locate the BIOS file extracted earlier. Rename this file and it’s extension to
MSI.ROM.
- Move this renamed file to the FAT32 USB.
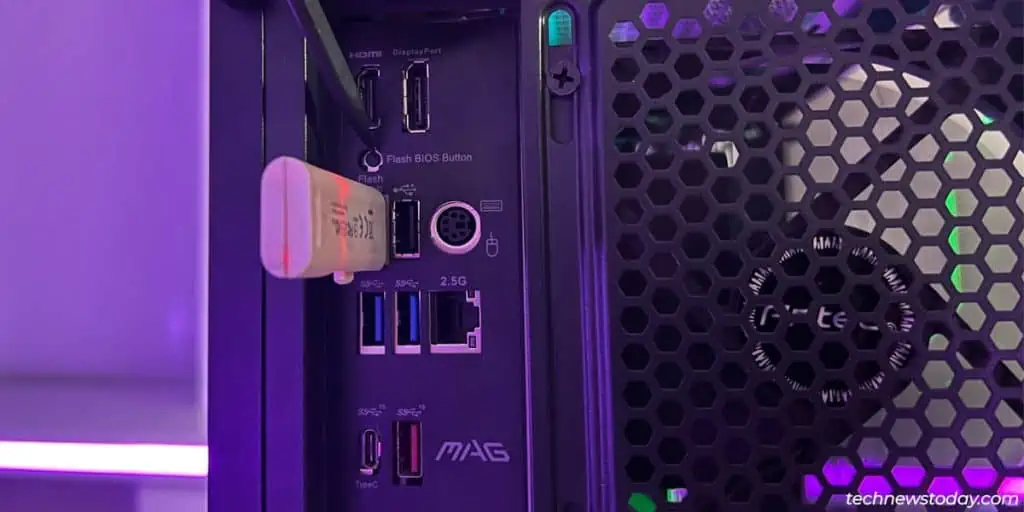
- Connect this USB to the Flash BIOS port on the motherboard.

- Besides this, you only need to connect the 24-pin ATX connector and 8-pin CPU connector to the motherboard. All other components (CPU, RAM, etc.) are optional and make no difference for BIOS Flashback.
- Turn off the system but keep the power cables connected.
- Without turning it on, press the Flash BIOS button for around 5 seconds.

- The Flash BIOS LED should start blinking. Your USB’s LED will start blinking too if it has one.
- After 5-10 minutes, the LEDs will stop blinking. This indicates that the BIOS update is complete.
- Power on your PC afterward. If prompted, boot to the BIOS and Restore Defaults. Then, press F10 to save the changes and reboot.

Using MSI LiveUpdate
MSI LiveUpdate automates the BIOS update process via utilities like MSI Center and MSI Dragon Center. While this is slightly more convenient, I do not recommend using this.
It involves the Windows environment for the first half of the update process (more variables involved, meaning a higher chance of problems).
This is proven through user feedback too. A lot of users have reported problems during and after the update with this method.
But if you prefer LiveUpdate despite its added risk, here’s how you can use it:
- On your motherboard support page, expand the Drivers & Downloads > Utility section.

- Download MSI Center or MSI Dragon Center from here.
- Install and launch the downloaded app.
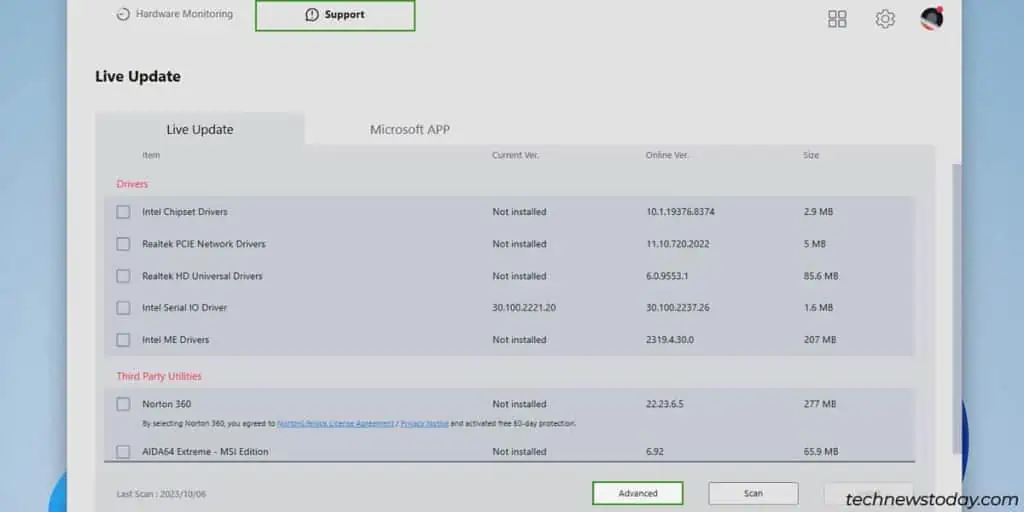
- Click on Support > Live Update > Advanced.

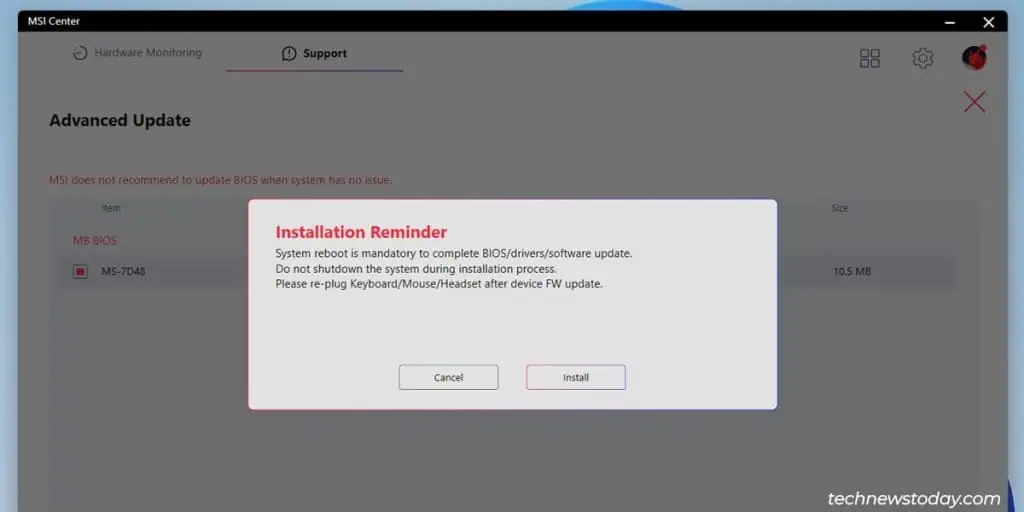
- Select the listed BIOS version and click on Install. Press Install again to confirm and proceed.

- The system will reboot and start updating the BIOS. The process will complete in 5 minutes or so, and your PC will reboot afterward.
What If the BIOS Update Fails
If you use the recommended methods (M-Flash or BIOS Flashback) and follow the steps properly, the BIOS update should complete without a hitch.
If the BIOS update does fail somehow, you have a few ways to recover your board. First, use BIOS Flashback and try the following things:
- Clear the CMOS.
- Flash another BIOS version.
- Use another USB stick.
- USB 2.0 sticks have the best compatibility but the key detail is to use a drive of a different USB version than before.
- Convert the drive to MBR. Then, repeat the steps to flash the BIOS.
Some MSI boards also support DualBIOS (meaning your board has 2 BIOS chips). In this case, you can switch to the backup BIOS to get your board working again. The main BIOS chip should automatically recover thanks to the backup image.
If none of these steps helped, refer to our in-depth MSI BIOS Recovery guide. It covers other technical methods like using a BIOS Reprogrammer and replacing the BIOS ROM.