Microsoft Hyper-V is a native hypervisor that can create virtual machines on x86-64 systems running Windows. Starting with Windows 8, Hyper-V has acted as the hardware virtualization component of Windows.
Hyper-V lets you create a virtualized computing environment where you can create and manage virtual machines.
Hyper-V is available as an optional component of Windows. It is also available as Hyper-V Server, a standalone freeware, with limited Windows Server functionality and Hyper-V component.
Applications of Hyper-V
As discussed above, Hyper-V lets you create and run a software version of a computer, called a virtual machine. You might want to create and run a virtual machine for the following reasons:
- Dual boot multiple Operating Systems
- Create a sandbox environment for testing
- Run softwares which are incompatible with the OS.
- Create a private cloud environment.
Checking Hardware Compatibility to Run Hyper-V
To run Hyper-V, you will need a 64-bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT). Your CPU must also support VM Monitor Mode Extension (VT-x on Intel CPUs, and AMD-V on AMD CPUs). Make sure your system meets Hyper-V’s system requirements.
You can find out whether your system is compatible with Hyper-V. To do so, please follow the simple steps outlined below:
- Press Win + R and type in cmd.
- In the command prompt window, type in
systeminfoand press enter.
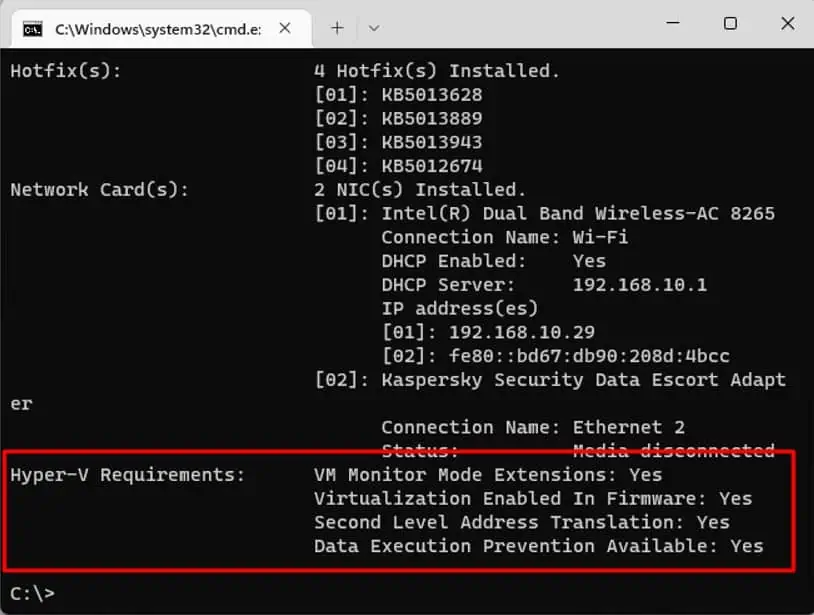
If all listed Hyper-V requirements have a value of Yes then you can run Hyper-V. However, if any of the values are No then you need to rectify the situation before you can run it.
You will also need to enable virtualization in the system BIOS. If you do not know how to turn on virtualization in BIOS, worry not because we have just the article for you.
Enabling Hyper-V in Windows 11
Now that you have ascertained you meet the system requirements for enabling Hyper-V and that virtualization is enabled in your system BIOS, we can go about enabling Hyper-V.
Below we have outlined a few different methods to enable Hyper-V in Windows 11. Please go through the methods outlined below and let us know if this worked for you.
Enabling Hyper-V Through Optional Components of Windows
Hyper-V is not installed by default in Windows clients, which is also the case for Windows 11. However, you will find the option to install Hyper-V through Optional Components. To use this feature, please follow the steps below:
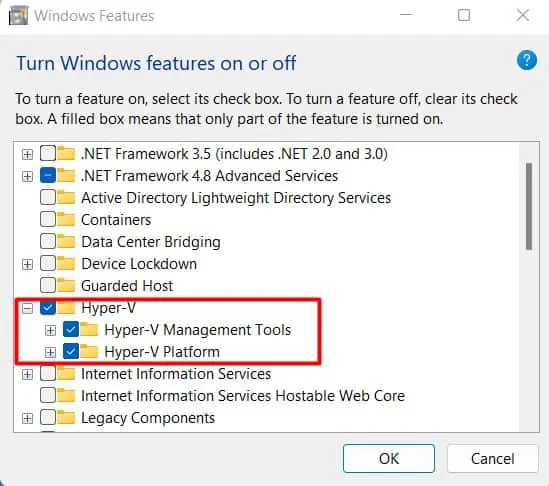
- Press Win + R and type in OptionalFeatures.
- Scroll down to Hyper-V and enable it, including all features.

- Click OK and wait for Windows to finish installing Hyper-V.
- Click on Restart now when prompted.
Enabling Hyper-V by Using DISM tool
Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) is a command-line tool that can be used to service and prepare Windows images. You can use the DISM tool to turn on Hyper-V. Please follow these steps to find out how:
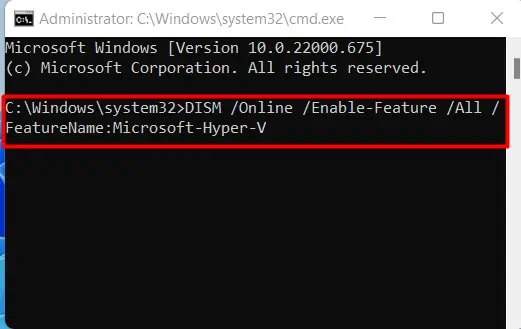
- Launch the elevated command prompt. (Press Win + R, type in cmd and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter.)
- Click Yes.
- Type in
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /All /FeatureName:Microsoft-Hyper-Vand press enter.
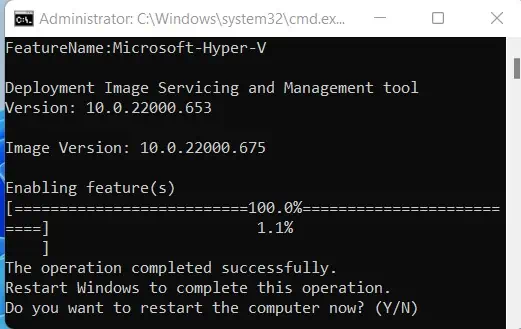
- Wait for DISM tool to finish preparing Hyper-V. Then press Y when prompted to restart the computer.

Enabling Hyper-V by Using the Terminal
You can also use the Terminal (Windows Powershell) to enable Hyper-V. Please follow the steps below:
- Press Win + R and type in powershell. Press Ctrl + Shift + Enter. (Alternatively, right-click on the Start button and choose Windows Terminal (Admin).
- Type in
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -All. - Wait for Windows Powershell to finish preparing Hyper-V. Then press Y when prompted to restart the computer.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Check Virtualization Enabled in Windows 11
To check whether you have virtualization enabled or not, follow these steps:
- Press Win + R and type in msinfo32
- In System Summary, scroll down to find Virtualization-based security
- Check the value. If it says Running, it’s enabled.
How Do I Disable Hyper-v in Windows 11?
To disable Hyper-V in your Windows 11 machine, please follow the steps below:
- Launch either the elevated command prompt or powershell with administrator privilege.
- Type in
DISM /Online /Disable-Feature /All /FeatureName:Microsoft-Hyper-V-All
Why Can’t I Enable Virtualization?
If you are having trouble enabling Hyper-V in windows, then check if one of the following is the problem:
- Virtualization is disabled in BIOS.
- Your version of windows in Windows 11 Home.
- You have less than 4GB of RAM installed.
- Your CPU does not support VM Monitor Mode Extension.
How to Enable Hyper-V in Windows 11 Home?
Officially, Hyper-V is not available in Windows 11 Home edition. However, with a little tweak, you can get around that restriction.
- Press Win + R and type in notepad.
- Copy and paste the following script into your new notepad file.
pushd "%~dp0"dir /b %SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\*Hyper-V*.mum >hyper-v.txt for /f %%i in ('findstr /i . hyper-v.txt 2^>nul') do dism /online /norestart /add-package:"%SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\%%i"del hyper-v.txt
Dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Hyper-V -All /LimitAccess /ALLpause - Save the notepad file somewhere accessible, like C:
- Change the extension of the file to
.bat(batch file). - Right-click on the batch file you just created and click on Run as administrator
- Wait for the process to be complete and restart your computer when prompted. Make sure that you are connected to the internet for the entire process.
Once your computer has booted back up, you can follow one of the three procedures outlined above to install Hyper-V on your Windows 11 Home machine.