Sometimes, your drives may be nearly full, but you don’t see much content inside the drives to warrant such high disk space usage. It is also possible you may only have system files on the C drive, but your computer is running on low disk space.
In the first scenario, it’s the hidden files and folders that are taking up the unexpected space. So, you need to look out for those and delete them permanently. For the second situation, you can clear up temporary and residual files or limit the storage space for certain processes to prevent the disk from filling up too fast.
Check Hidden and Protected Folders
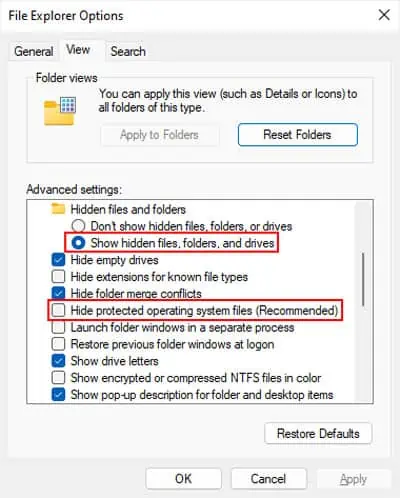
First, you need to check if you have any hidden folders taking up much of the space. You need to show these folders in your File Explorer for this purpose.
- Open Run by pressing Windows key + R.
- Type
control foldersand press Enter to open File Explorer Options. - Go to the View tab.
- Check Show hidden files, folders and drives and uncheck Hide protected operating system files.

- Confirm any prompts.
- Click Apply and OK.
Now, open File Explorer (Win + E) and check your drives. If there are any unnecessary hidden folders or files inside, you can safely delete them.
Clear Recycle Bin
Deleting a file or folder without pressing the Shift key will only temporarily delete it. Your system will transfer it to the Recycle Bin for the drive instead of erasing it completely.
This file will still be present inside the Drive but within the hidden Recycle Bin shell. So, the drive will still show the same occupied space even after you delete such files. You need to clear them from the Recycle Bin to free up the disk space.
- Open Run.
- Type
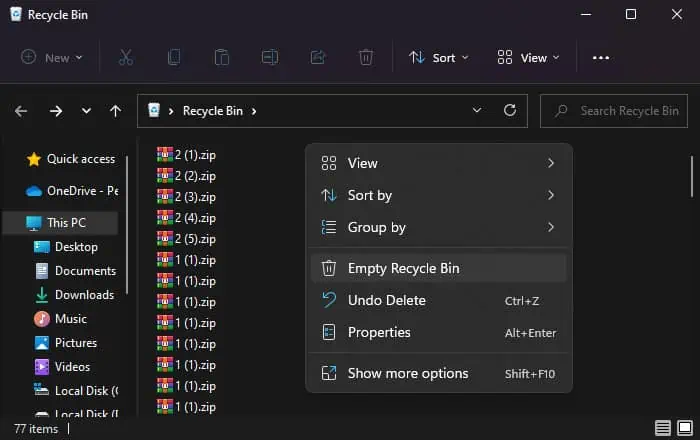
shell:recyclebinfolderand press Enter to open Recycle Bin. You can also double-click on the Recycle Bin icon on your desktop. - Right-click on all unnecessary files you don’t need and select Delete > Yes.
- If you don’t need any items inside this Shell folder, you can right-click on an empty area and select Empty Recycle Bin > Yes.

You can also lower the maximum Recycle Bin for your drives to limit it from reserving larger space in the future.
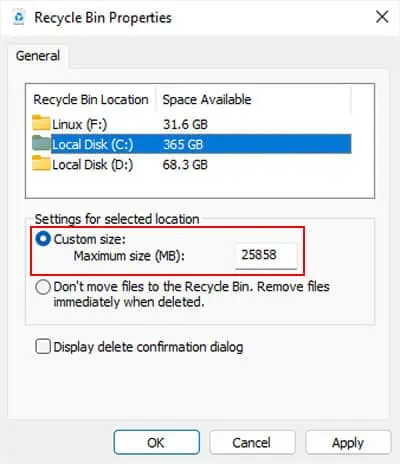
- Right-click on the Recycle bin icon on the desktop.
- Select Properties.
- Click on the drive and set the Maximum size to a lower value.

- Hit OK.
Scan for Malware
Certain types of malware can create multiple copies of itself or perform other processes to fill up your disk space. So, it’s worth running an antivirus program to scan for such threats whenever your drive space suddenly gets occupied.
- Open Run.
- Type
ms-settings:windowsdefenderand press Enter to open Windows Security. - Click on Virus & threat protection and then Scan options.
- Check the Full scan and click Scan now.

Clean Unnecessary and Temporary Files
Windows also automatically creates and store many temporary files for your system and application processes. Also, updates or Windows installation can leave behind some temporary files in case you need to roll back or restore the changes.
These files can take up a lot of space. So you should try checking for these and then delete them if necessary.
- Open Run.
- Type
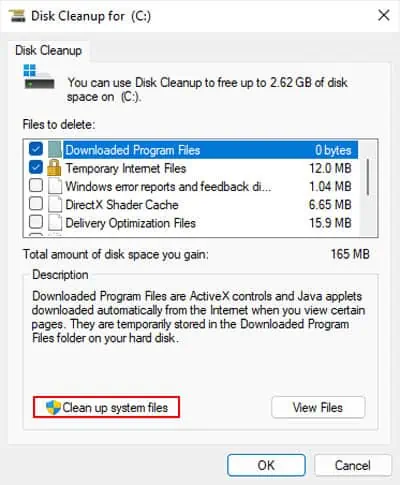
cleanmgrand press Enter to open the Disk Cleanup wizard. - Select C drive and press Enter.
- Click on Clean up system files.

- Select the drive again and click OK.
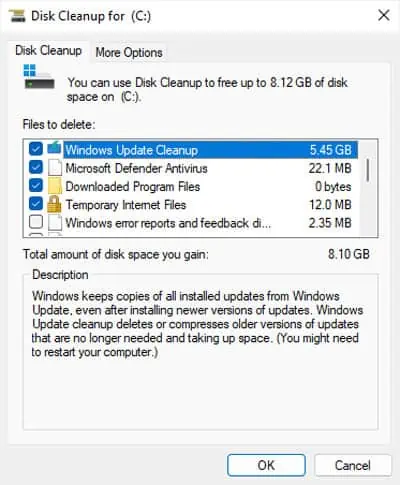
- Select all the unnecessary options, including Windows Update Cleanup, Previous Windows installation and Temporary Windows installation files (if available).

- Click OK.
- Now, perform the same task on your other drives (D or E) and clean their unnecessary files as well.
Windows also offers other minor ways to clear up space in your system drive. I recommend checking out my article on cleaning C drive for a detailed guide.
Clear Previous Restore Points
If the System Protection feature is enabled in your computer, your system will create restore points before you make major changes to the computer. You can also manually create the restore points. Both types of points will use up quite a bit of space inside your drives individually.
Your system stores these restore points in the hidden System Volume Information folder on each drive if system protection is enabled for the drives. Since usually, only the last restore point is necessary, you can clear up all previous points to free up the space.
It is not possible to enter the System Volume Information folder unless you change the permission settings, which is not recommended. You will also need to use the Disk Cleanup Wizard for this purpose.
- Open Run.
- Type
cleanmgrand press Enter to open the Disk Cleanup wizard. SelectCdrive and press Enter. - Click on Clean up system files. Select the drive again and click OK.
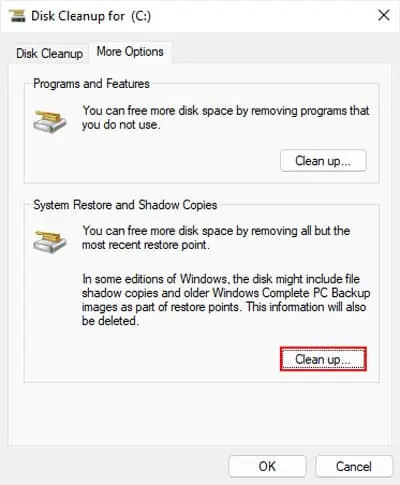
- Go to the More Options tab.
- Click Clean up under System Restore and Shadow Copies.

- Confirm with Delete.
You can also reduce the reserved space for restore points to lower the limit on how much it can fill up your disk.
- Open Run
- Type
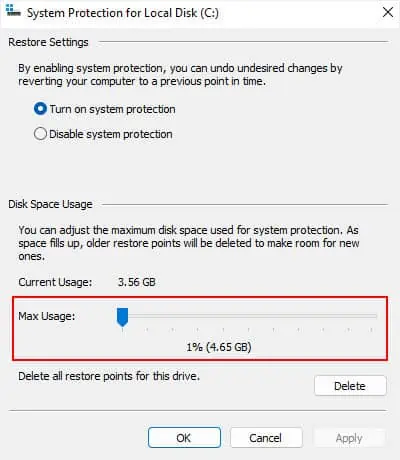
systempropertiesprotectionand press Enter to open the System Protection tab of System Properties. - Select a drive where Protection says On and click Configure.
- Change the Max Usage to a lower value by moving the slider and click OK.

- Since this process will delete all previous restore points, I recommend creating another one as soon as possible. Click on Create and follow the on-screen instructions to do so.
Disable Hibernation
Windows comes with a hibernation feature that allows saving the necessary contents on the RAM inside a hidden hiberfil.sys file in your system drive. So, if you hibernate your computer, it can load all the necessary contents into the RAM on wakeup and you can continue with your work.
Unlike sleep, hibernate does not use as much power, so it’s better if you won’t be using the computer for a longer time. On the other hand, this process reserves a lot of space even when your computer is not hibernating.
So if you don’t hibernate your computer, you can disable this feature and free up that space automatically.
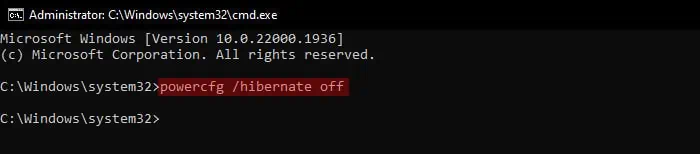
- Open Run.
- Type
cmdand press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open the Elevated Command Prompt. - Type the command
powercfg /hibernate offorpowercfg /h offand press Enter to disable this feature.
Delete Previous User Profile Folders
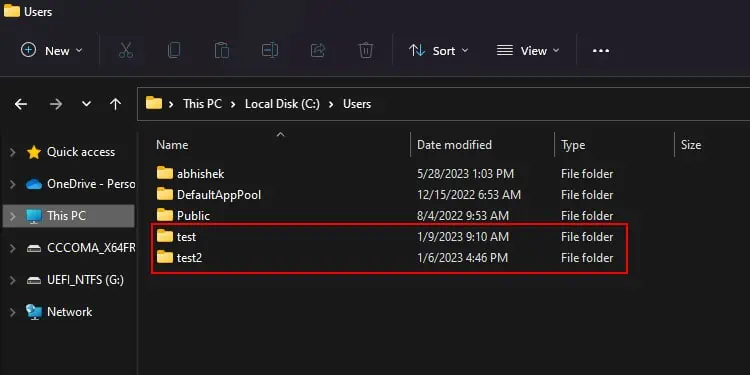
Another reason your C drive space is unexpectedly full or nearly full might be because of residual user account profile folders. Whenever you create a user account, it also creates a user profile folder for the account. This folder remains even if you delete the user account, and takes up unnecessary space.
You need to identify the folders based on their names and delete them in such scenarios. You will find the folders inside C:\Users
Upgrade Storage Device or Expand Partition
If there’s no way to free up space in your drive or disk, your only remaining option is to add more space. You can expand the partitions showing the low disk space if your storage device contains other partitions with a lot of free space.
If your whole disk does not have much space available, you need to add more storage to your computer.