When you run an application, all the files required to run the application, load into the primary memory or the RAM. More RAM means it can load multiple application files and run multiple applications simultaneously. Therefore, most users increase their RAM capacity to make their PC faster.
However, your PC has a maximum RAM capacity. This depends on the OS, the CPU chip, and the motherboard itself.
In this article, we are here to give you a detailed guide to checking the maximum RAM you can add on your PC.
What Does Maximum RAM Capacity Depend on?
The total RAM you can add to your PC depends on the maximum RAM capacity of three different components in your PC.
- Operating System’s architecture (32-bit/64-bit)
- The motherboard
- The CPU
For example, if your OS and CPUs maximum RAM capacity is 2TB and 128GB, but the total DIMM slot on the motherboard only supports the total of 16 GB RAM, your PC’s maximum RAM capacity will be no more than 16 GB.
In this case, you need to upgrade your motherboard that supports more RAM before adding more RAM to the PC.
How to Check Maximum RAM Capacity on Your PC?
The maximum RAM capacity of the CPU and the OS is generally high compared to what your motherboard supports. Depending on the number of DIMM slots and their capacity, the motherboard will have certain restrictions when upgrading RAM.
There are multiple ways you can get the details about the maximum RAM capacity but using Command Prompt is one of the simplest methods.
- Press the Windows + R key to open Run.
- Type cmd and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to run Command Prompt as an administrator.
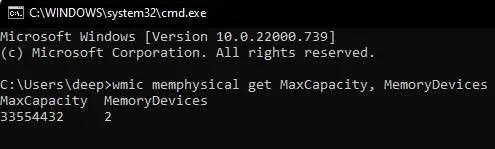
- Type
wmic memphysical get MaxCapacity, MemoryDevicesand press Enter.
Max capacity displays the maximum RAM capacity for your PC in kilobytes. Convert the value from Kb to Gb and get the maximum RAM capacity in Gigabyte.
MemoryDevices represent the total number of memory sticks present on your computer.
Below we have mentioned a few ways you can get details about the PC so that you can determine its maximum RAM capacity.
Maximum RAM Capacity for the CPU, Motherboard, and the OS
CPU models, Motherboard, and OS will each have multiple maximum RAM capacities. If you want to check the individual maximum RAM capacity for the CPU, OS, or the motherboard itself, you first need to get their details.
Once you have the details, you can determine its maximum RAM capacity using the internet. Follow the steps mentioned below to get details about the CPU, motherboard, and OS.
- Press the Windows + R key to open Run.
- Type
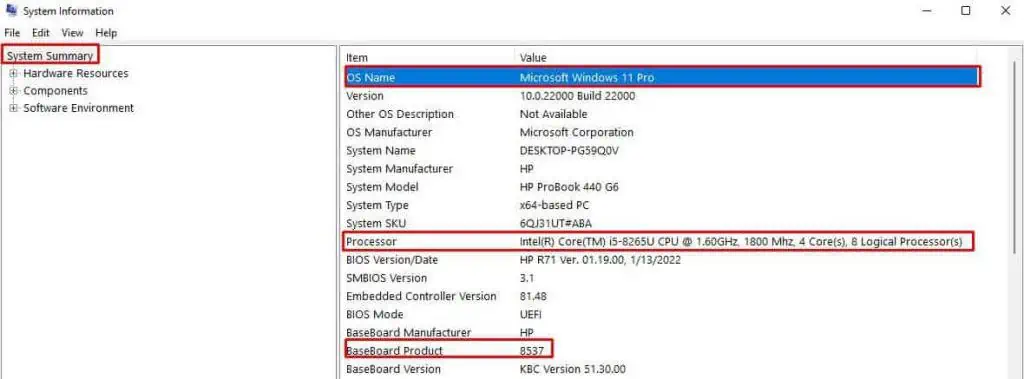
msinfo32.exeand press Enter. - Click on System summary on the left panel.
- On the right panel, you can see the OS name, system type, processor model, and the BaseBoard Product.

Once you know the CPU, motherboard, and OS details, the following topic will help you know each component’s maximum RAM capacity.
Maximum RAM Capacity for an OS
A 32-Bit OS will only support a maximum of 4GB of RAM. However, 64-Bit can support maximum RAM ranging from 128GB to 6TB, depending on the edition of the OS.
For example, Windows 10 Home 64-Bit supports up to 128GB of memory while Windows 10 Pro for Workstation 64-Bit supports up to 6TB of RAM.
Maximum RAM Capacity for a Motherboard

Once you get the motherboard details, you can access the internet to learn about its memory types and the number of memory slots it has.
Using a motherboard that supports DDR3 memory can only support up to 16GB of memory per DIMM slot. A motherboard that supports DDR4 memory has a maximum RAM capacity of 64GB per DIMM slot.
Therefore, the number of DIMM slots and the type of memory play a vital role in determining a motherboard’s maximum RAM support.
Maximum RAM Capacity for a CPU
As with the 32-bit OS, a 32-bit processor will also support a maximum RAM of 4GB. However, a 64-bit processor will have a variety of maximum RAM depending on the type of processor. Search the processor’s maximum RAM size on the internet to determine the maximum RAM size for your CPU.
Related Question
Is VRAM and Virtual Memory the same?
VRAM and Virtual Memory are two entirely different topics. VRAM (Video Random Access Memory) is the memory that the OS uses to perform graphics-intensive tasks.
On the other hand, virtual memory is the memory taken from a storage device that acts as Random Access Memory.
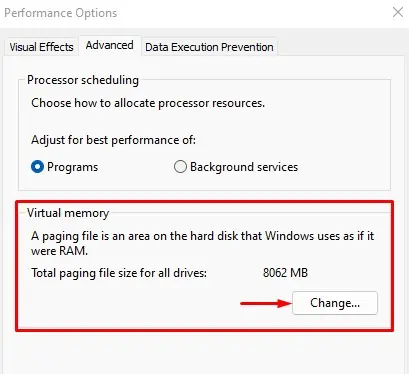
How to increase virtual RAM?
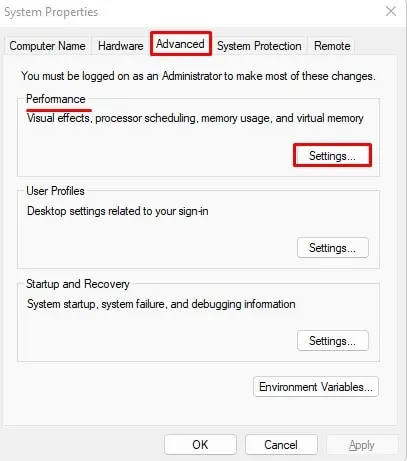
You can adjust the amount of virtual RAM from Advanced System Setting.
- Press the Windows + R key to open Run.
- Type
sysdm.cpland press Enter. - Go to the Advanced tab.
- Under Performance, select Settings.

- Go to Advanced.
- Under Virtual memory, you can see the actual size of the virtual memory.
- Click on Change.

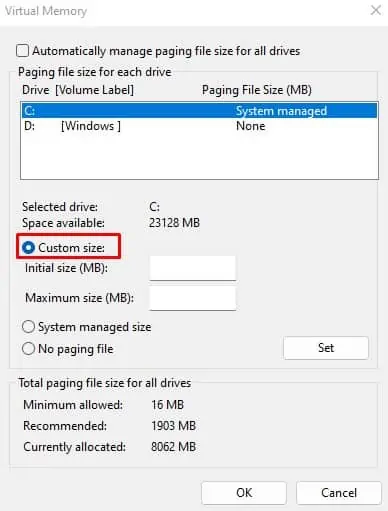
- Here, check the Custom size and set the amount of virtual memory you want to use.

- Click on Set and then OK.