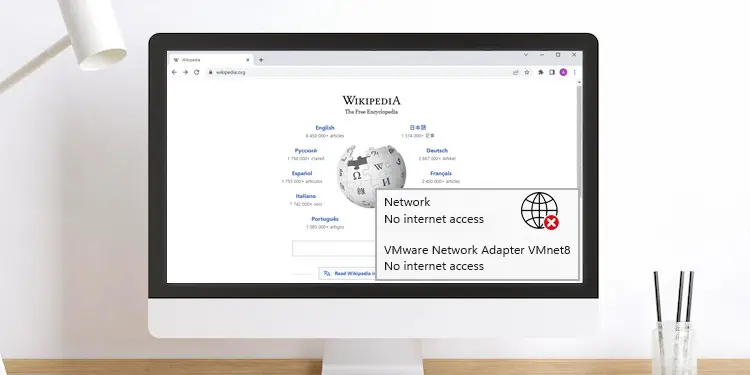
When you are not connected to the internet, you can find the “No internet access” icon on your Taskbar. However, in certain scenario, the taskbar shows this symbol instead of the Wi-Fi or Ethernet icon even when internet is working.
While most apps can access the internet in such a scenario, you may not be able to sign in to Outlook or any Microsoft 365 apps.
This issue usually happens due problems in the DNS lookup process that your system uses to determine internet connectivity. But there are also a few other reasons for the error.
In this article, we mention all such reasons, along with how you can troubleshoot them.
Why Does my Windows Show No Internet Access but Internet Works
Here are the potential causes for Windows showing “No Internet Access” even when internet is working:
- Errors on the NCSI active probe settings
- Network Driver issues
- Inaccurate hostname resolution on the Hosts file or DNS cache
- DNS servers going down frequently
How to Fix Windows Shows No Internet Access
There are a few ways to resolve the Windows shows no internet access issue depending on the nature of your issue.
First, try restarting your computer and check if you still experience this error. If yes, go through the possible solutions we have mentioned below and apply them one by one.
Run Internet Troubleshooter
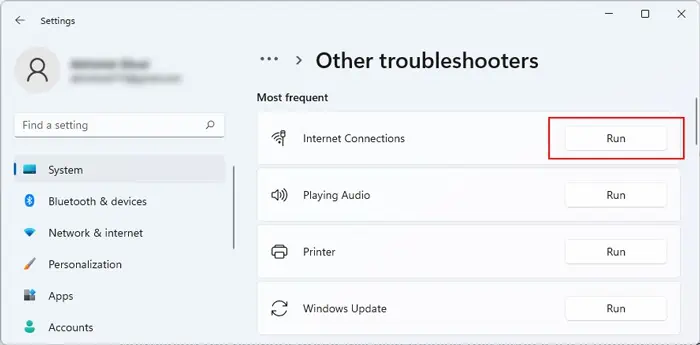
The first thing you should try in such scenario is to run the Windows troubleshooters, specifically Network Adapters and Internet Connections. Sometimes, few minor underlying issues can cause the anomaly in indication of network status, which the troubleshooters can fix easily.
To run these programs:
- Open Run (Win + R) and enter
ms-settings:troubleshoot - Select Other troubleshooters or Additional troubleshooters.
- Click on Run next to Internet Connections and Network Adapter. Or, select those options and click Run this troubleshooter.

- Follow the on-screen instructions.
Refresh Network Driver
Refreshing the network driver will also resolve this issue if it’s a temporary error. Doing so makes the system recheck whether it’s connected to the internet or not.
Here’s how you can refresh the WiFi or Ethernet network driver:
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Enter
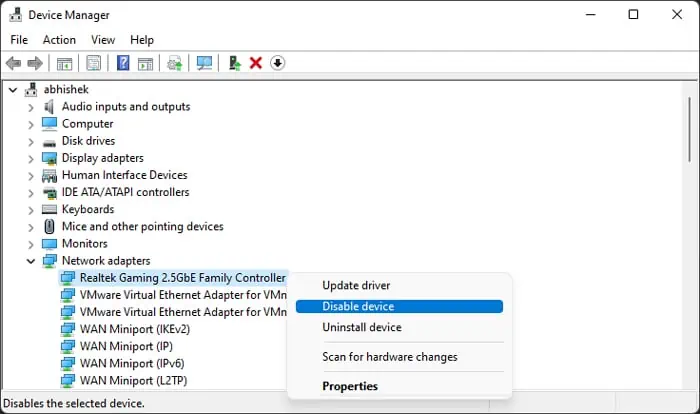
devmgmt.mscto open the Device Manager. - Expand Network Adapters.
- Right-click on your WiFi or Ethernet device and select Disable device.

- Right-click on the device again and select Scan for hardware changes.
- Repeat step 4 and 5 while selecting Enable device instead of Disable.
Disable IPv4 Checksum
If the Network Interface Card drivers are incompatible or IPv4 Checksum option for the device is enabled, your LAN connection may show no internet access.
In such cases, first try updating your LAN driver to the latest version. We recommend downloading it from the manufacturer’s website.
If the issue remains, use the following instructions to disable IPv4 Checksum Offload:
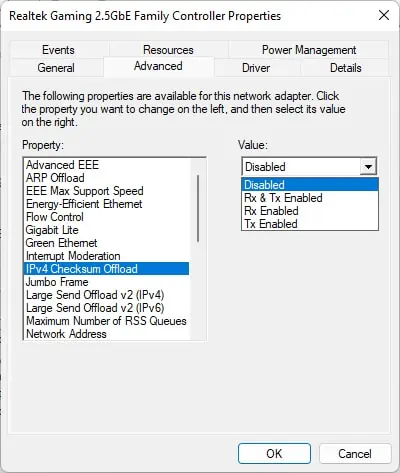
- Open the Device Manager and expand Network Adapters.
- Right-click on your LAN or Family Controller and select Properties.
- Go to the Advanced tab.
- Select IPv4 Checksum Offload and set it’s drop-down box to Disabled.

- If you find a Wait for Link option, disable it as well.
- Click OK.
Check NCSI Active Probing Settings
Windows uses Network Connection Status Indicator (NCSI) Probing feature to determine internet connectivity. Your system regularly sends a DNS and HTTP request to a certain web page (by default the Microsoft Connect Test website’s http://www.msftconnecttest.com/connecttest.txt page) for such probing.
The registry stores the information on the ip address, domain name, page name, etc., for this web page. If there’s any discrepancies with this information, the probing fails and Windows determines that there’s no internet access.
You can still use the internet through your browsers or third-party apps in such a scenario. However, some Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps like Outlook fails to connect to the internet.
An easy way to resolve this issue is to,
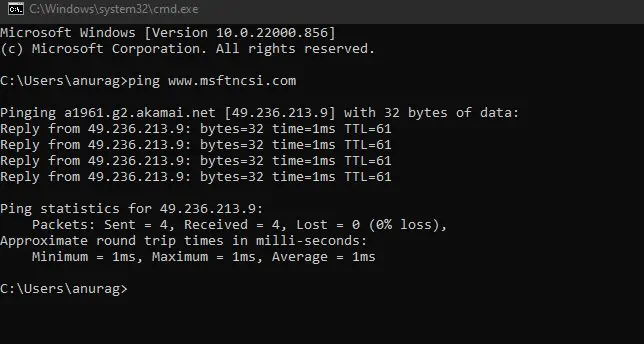
- Open Command Prompt and enter
ping www.msftncsi.comto manually ping to that website.
- You need to do so every time you disconnect and reconnect to the internet.
To permanently resolve the issue, You need to check and change the settings for both your group policy and registry to resolve this issue.
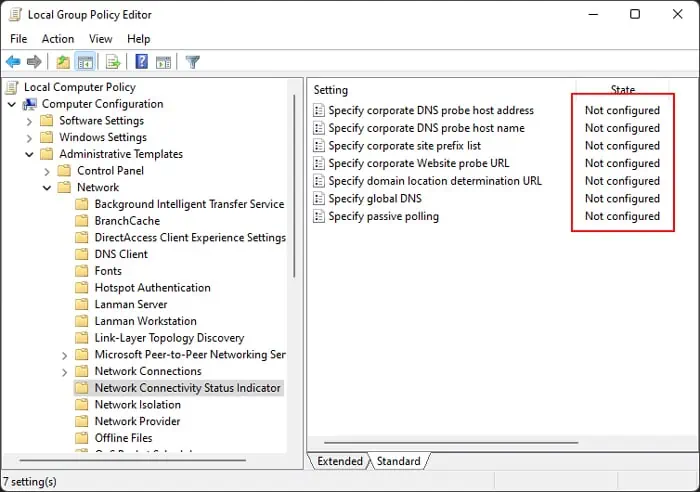
NCSI Group Policy
Your group policy settings can override the registry settings. So, it’s better to make sure to remove any configuration for the NCSI policies and let solely the registry editor handle the information.
Here’s what you need to do:
- Open Run and enter
gpedit.mscto open the Local Group Policy Editor. - Go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network > Network Connectivity Status Indicator.
- Make sure all policies show Not configured.

- To change a policy, double-click on it, check Not configured and click OK.
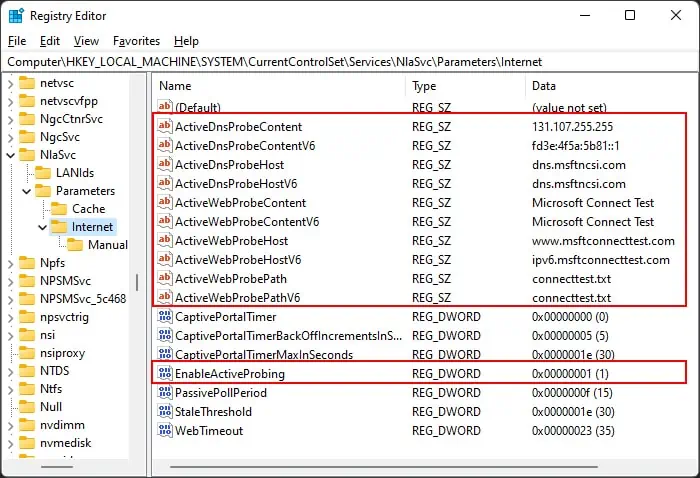
NCSI Registry Entries
After setting the policies to Not Configured, you need to make sure your registry stores the standard information. To do so,
- Open Run.
- Enter
regeditto open the Registry Editor. - Navigate to
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NlaSvc\Parameters\Internet - Make sure the values are the same as those from the image below.

- If you need to change a value, double-click on it, change the Value data and click OK.
- Then, Go to
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\NetworkConnectivityStatusIndicator - If you have a NoActiveProbe entry, make sure it’s value is 0.
Make sure to backup your registry before making any changes to it.
Check Outage at Microsoft’s Connect Test Page
As we mentioned earlier, your Windows system checks for internet connectivity by probing on the Microsoft’s Connect Test Page. If this website’s server or the DNS probe server is down, you’ll temporary encounter the “No Internet Access” error.
You can check for the server outages or issues (dns.msftncsi.com and www.msftconnecttest.com) on the down server detecting websites. This issue should resolve itself after some time, so the only thing you need to do is wait.
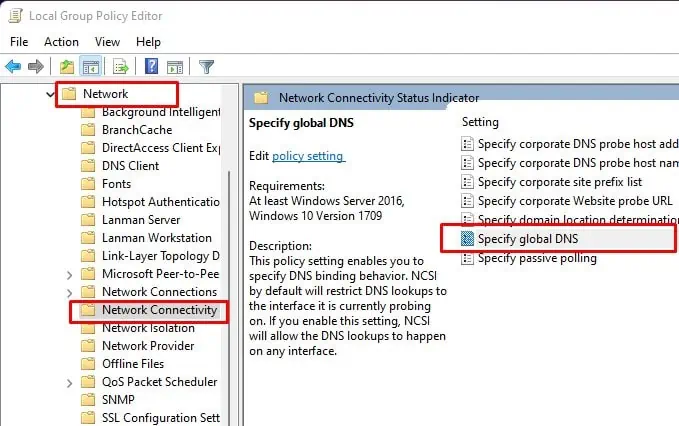
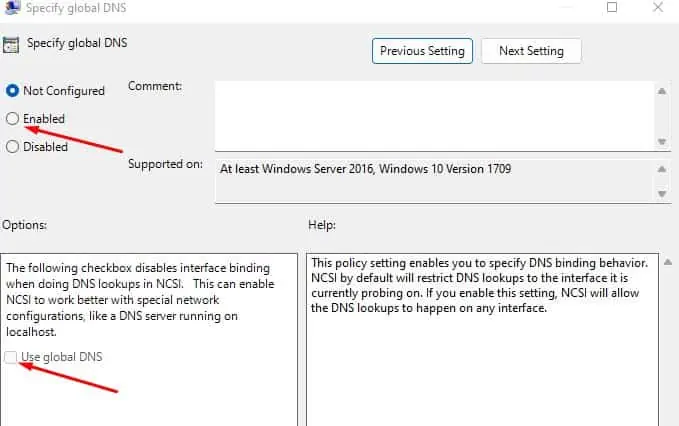
Specify Global DNS
By default, NCSI only allows DNS lookups to the interface it is currently probing on. However, if you use DNS protection agents or forwarders on an endpoint, the interface changes.
You need to enable the use of global DNS for this lookup to allow the DNS lookup on any interface. To do so,
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor.
- Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network > Network Connectivity Status Indicator.
- Double-click on Specify global DNS.

- Check Enabled and then, Use global DNS.

- Click Apply and OK.
- Open Command Prompt and
run gpupdate /force
Restart your PC and check if the issue resolves.
Reset Network Components
If your DNS or IP cache contains wrong information on the host name resolution for Microsoft Connection Test website, your system can’t send or receive requests to this website. The NCSI active probing fails in such cases and you’ll get the No Internet Access error even though internet works.
You need to flush the DNS cache to resolve the issue. But it’s better to reset your network components altogether to resolve any other potential connection issues. Here’s how you can do so:
- Open Run.
- Type
cmdand press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open the Elevated Command Prompt. - Enter the following commands:
netsh winsock resetnetsh int ip resetipconfig/releaseipconfig/flushdnsipconfig/renew
Change DNS Servers
If your ISP’s DNS goes down frequently, you’ll still be able to browse the internet but your system can’t send the NCSI DNS request, resulting in this issue. You can change the DNS servers to a public one to resolve such issues.
It’s better to change the DNS server on your router’s portal and then refresh your DHCP using the ipconfig /renew command. But you can also change the DNS on your device. To do so on Windows:
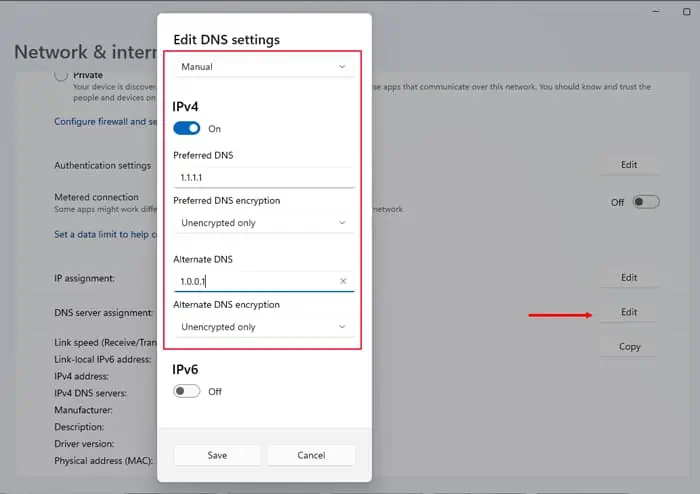
- Press Win + I to open Settings.
- Go to Network & internet and select your WiFi or Ethernet connection.
- Click Edit under DNS server assignment.
- Set the drop-down box to Manual.
- Enable IPv4 and enter the Preferred and Alternate DNS.

- You can also set the DNS servers for IPv6 if you use such connections.
There are many public DNS server you can use, such as:
Cloudflare
If you want to compare these two, Cloudflare is more secure but Google is faster. So, pick one according to your preference.
Edit Hosts File
Another thing you should do is to check your hosts file. Your system looks at the hosts file for domain name resolution even before the DNS cache. So if you have somehow entered wrong mapping information for the Microsoft Connect Test DNS probe or websites, the probe fails.
Here’s how you can resolve the issue:
- Open Run.
- Type
notepad %WinDir%\System32\drivers\etc\hostsand press Ctrl + Shift + Enter. This opens the hosts file as admin in notepad and allows you to make changes. - Look through the file and comment out or remove any lines where you find “msftncsi” or “msftconnecttest”.

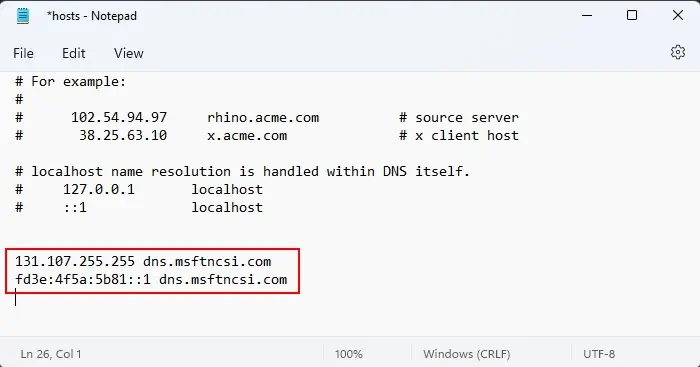
- You can also add the lines below. However, as long as you have checked the NCSI active probe setting on the registry, you don’t need to do so.
131.107.255.255 dns.msftncsi.comfd3e:4f5a:5b81::1 dns.msftncsi.com
- Press Ctrl + S to save the file and then close it.
Restart your PC and check if the issue resolves.
Disable NCSI Active and Enable Passive Probing
While NCSI uses active DNS probing to validate internet connectivity, it can also use passive probing when active probe is turned off. Such passive probing use your application’s network activity to determine internet connectivity.
So, you can completely bypass the issues with the NCSI active probing process by disabling it and enabling passive polling.
First, disable active probing on both group policy and registry using the following instructions:
On Group Policy
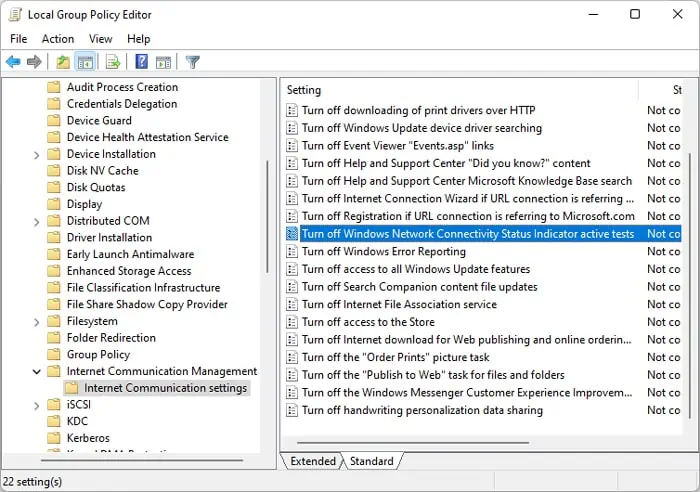
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor
- Go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Internet Communication Management > Internet Communication settings
- Double-click on Turn off Windows Network Connectivity Status Indicator active tests.

- Set it’s value to Enabled.
On Registry
- Open the Registry Editor.
- Go to
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NlaSvc\Parameters\Internet\ - Double-click on EnableActiveProbing.
- Set the Value data to 0 and click OK.
- Now, go to
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\NetworkConnectivityStatusIndicator - Change the value of NoActiveProbe to 1. If it doesn’t exist, you don’t need to do anything.
Then, enable passive probing on both group policy and registry settings using the steps below:
On Group Policy
- Open the Local Group Policy Editor
- Go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network > Network Connectivity Status Indicator.
- Double-click on Specify passive polling
- Set it’s value to Not Configured or Disabled.
On Registry
- Open the Registry Editor.
- Go to
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\NetworkConnectivityStatusIndicator\ - Double-click DisablePassivePolling, change its Value data to 0 and click OK.
- If it doesn’t exist, right-click on an empty area on the right and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value. Set it’s name to
DisablePassivePollingand make sure its value is 0.