Have you ever tried running old games on your desktop or laptop? If yes, you may have faced weird video glitches or have a pixelated, blurry, stretched display, or screen flickering. Scaling is what solves them. But what is scaling?
Today in this article, we are here to discuss exactly that. So, without further delay, let’s get right into it.
What is Scaling?
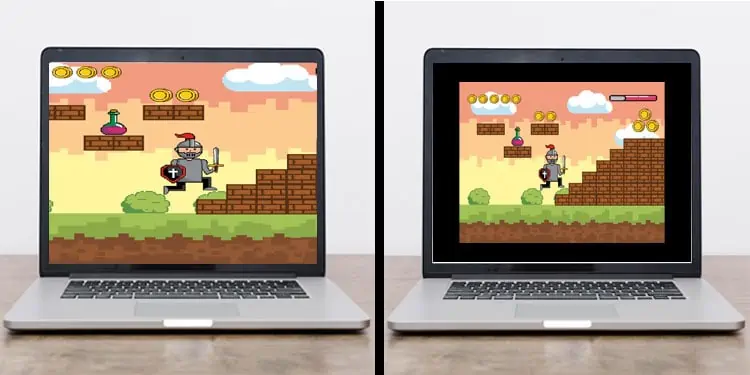
Scaling means adjusting an image or video with a certain aspect ratio to fit into a screen with a different aspect ratio. However, this definition is not only restricted to images and videos, but also games.
If you have an older game that runs at a lower aspect ratio, such as 5:4 or 4:3, running them on newer monitors can stretch and the game can look blurry. So, scaling adjusts the lower aspect ratio so that it fits on displays with different aspect ratios without having pixelated, stretched, or screen flickering issues.
There are two ways you can perform scaling, named GPU Scaling and Display Scaling.
What is GPU Scaling?
GPU scaling is a feature that upscales or downscales an image or a frame output so that it fits on the monitor’s native aspect ratio.
When you run a game, the GPU handles all its graphics-intensive tasks, including displaying it on a monitor. With GPU scaling off, as discussed above, you will see pixelated (blurry image) or stretched versions of the game. This is where GPU scaling, especially down-scaling, comes in.
Enabling GPU scaling changes the default aspect ratio of the game to the monitor’s native resolution. GPU scaling works best when you want to run a game with a lower aspect ratio on a monitor with a higher aspect ratio.
Besides this, GPU scaling can also increase your monitor resolution. If you want more out of your graphics card, you can perform an upscale that increases the size of your display.
However, using GPU to scale means that it takes on more load than usual. This, in turn, causes FPS drops and input lag,
Now, let us look at some of the pros and cons of GPU scaling.
- Scale older games with default resolution.
- It can display a higher resolution than supported by the monitor.
- Provides proper scaling compared to display scaling, making your image a lot sharper.
- The GPU is already doing extra work scaling. Therefore, it can cause a decrease in FPS (Frames Per Second) to some extent.
- GPU scaling in older GPUs is known to cause input lag.
- Can occasionally display blurry frames.
What is Display Scaling?
Like GPU scaling, display scaling downscale or upscale a frame that is displayed on the monitor. When down-scaled, your PC may also have a little performance boost as it reduces the number of pixels that the CPU processes.
Display Scaling scales to a lower resolution by the monitor itself rather than using the GPU. Using Extended Display Identification Data (EDID) the monitor automatically adjusts the default resolution to its native resolution.
Gamers use display scaling when playing games at a lower resolution than the monitor’s default resolution.
Now, let us discuss some pros and cons of Display Scaling.
- Using display scaling, you will get little to no input lag compared to GPU scaling.
- Down-scaling using display scaling can increase your FPS.
- Cost-efficient, as no dedicated high-end GPUs are required.
- Some monitors may not support display scaling.
- You can only downscale from the monitor’s default resolution.
- Display quality will seldom be as desired.
Should I Perform Scaling on GPU or Display?
Both GPU and display scaling increase or decrease the number of pixels displayed on the screen. One particular difference is that GPU scaling, before sending data to the monitor, scales video data to the preferred resolution using a graphics card. Whereas, using display scaling, your monitor automatically performs scaling using EDID.
So, which one is better, GPU scaling or Display Scaling? Well, it depends. If your monitor does not support display scaling, there is nothing you can do except enable GPU scaling.
If you want a crispier-looking image, it is recommended that you enable GPU scaling. However, it can decrease FPS and increase input lag if you are using an older generation graphics card.
Display Scaling can increase fps and give you a smooth gaming experience, but unlike GPU scaling, it also cannot display a higher resolution than the monitor’s default.
Regarding which scaling to choose, it is recommended that you try both scaling options and analyze fps, input lag, and resolution. However, if you cannot tell the difference between the two, use display scaling.
If your monitor has a poor scaler, using GPU scaling would be a better choice
How to Adjust Scaling Mode?
Depending on the graphics card you use, AMD or NVIDIA, here are steps to enable GPU Scaling.
NVIDIA Graphics Card
Before we start, remember that you can only access these settings if you have an external monitor connected. You cannot see scaling settings if you are on a laptop.
Follow these steps to enable GPU scaling on NVIDIA graphics cards.
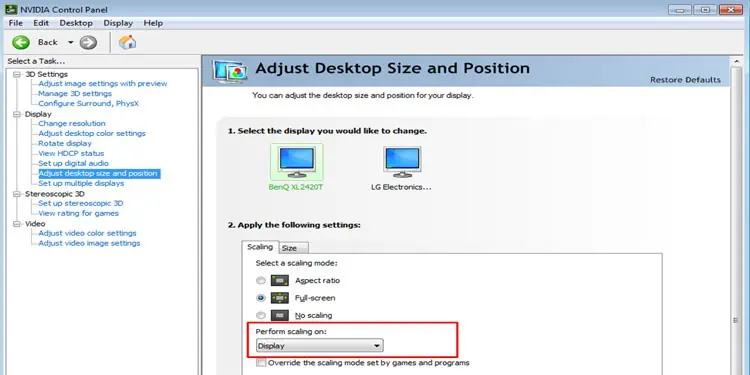
- Open NVIDIA Control Panel.
- On the left panel, expand Display and click on Adjust Desktop Size and Position.
- Select the monitor that you want to scale.
- Under Apply the following settings, and select a Scaling Mode.
- Under Perform scaling on, choose Display or GPU scaling.

AMD Graphics Card
If you have an AMD graphics card, you are either using AMD Radeon Software or AMD Catalyst Control Center.
For AMD Radeon Software
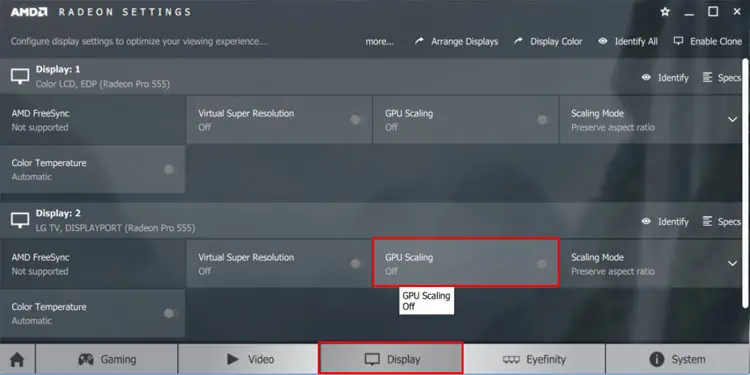
- Open AMD Radeon Software.
- Click on the Settings icon on the top right of the window.
- Open the Display tab.
- Here, under Display Options, enable GPU scaling and set your Scaling Mode.

For AMD Catalyst Control Center
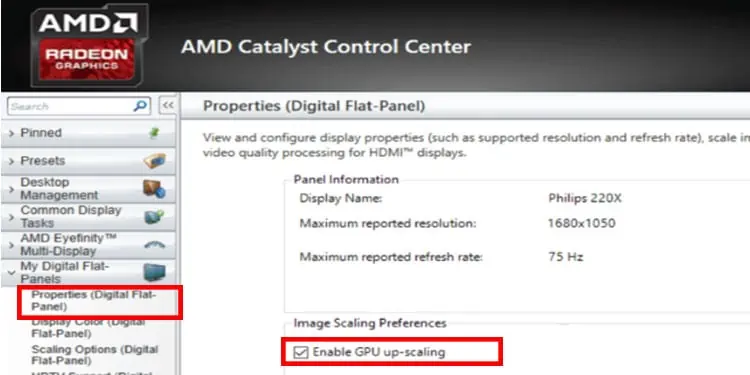
- Open AMD Catalyst Control Center.
- On the left panel, expand My Digital Flat-Panels.
- Select Properties (Digital Flat-Panels).
- Now, on the right panel, under Image Scaling Preference, Check Enable GPU up-scaling

- Finally, select a mode under Preferred Scaling Mode.
Which GPU Scaling Mode Should I Use?
There are three GPU Scaling modes depending on the graphics card you use. Both AMD and NVIDIA have different GPU modes that adjust the aspect ratio.
When you enable GPU scaling, it performs necessary algorithms so that the monitor displays the game’s default aspect ratio to the monitor’s native resolution. It does this by either reserving the aspect ratio, scaling the image to full size, or center trimming (GPU scaling mode for AMD).
GPU Scaling Mode for NVIDIA Graphics Card
You can see these three scaling modes if you use an NVIDIA graphics card.
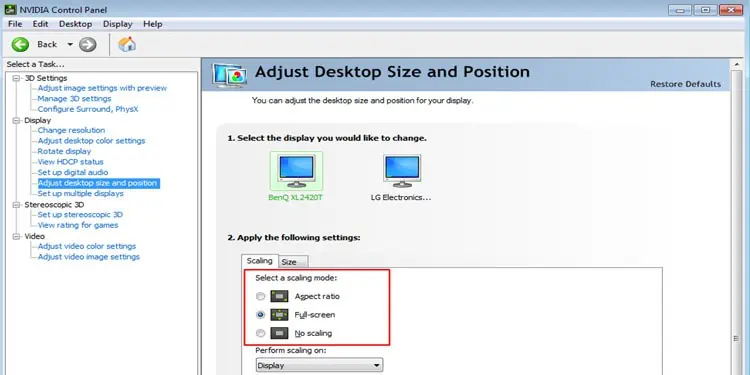
Aspect Ratio Mode
This mode allows you to run a game with its default aspect ratio by adding black bars on all four sides.
Full-Screen Mode
This setting will allow the game to run on the monitor’s resolution. This, in turn, will cause the game to get blurry or stretched.
No Scaling
This mode will turn off GPU scaling.
GPU Scaling Mode for AMD Graphics Card
Here are the settings that are available on AMD graphics cards.
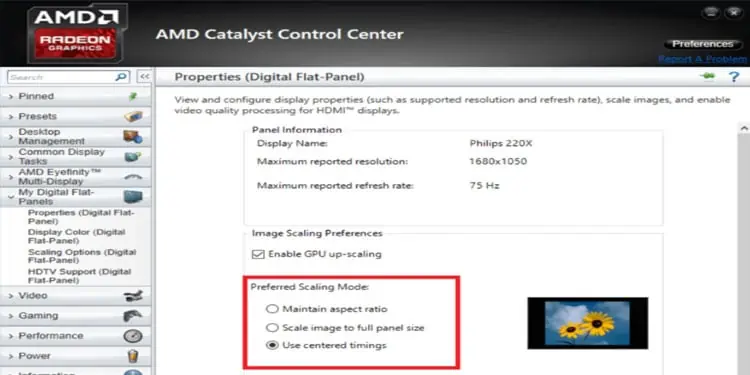
Maintain Aspect Ratio Mode
Similar to NVIDIA’s Aspect Ratio Mode, Maintain Aspect Ratio adds black bars on either side of the screen when running games with the default aspect ratio.
Full Panel Mode
This setting stretches the game to fill your monitor’s native resolution. Unfortunately, this may cause blurry frames and an overall poor gaming experience.
Center Mode
Center mode allows the game to maintain its original aspect ratio. Using this setting, you can expect to see black bars on all four sides of the screen.
Conclusion
So, the definitive answer to should you perform GPU or display scaling is that it depends. If you want crispier images, it is recommended that you use GPU scaling. However, if you need more performance and take a load off the GPU, it is ideal that you downscale using display scaling.