Package Installer for Python (PIP) is the preferred package-management system for Python. It’s used to install third-party packages from an online repository called the Python Package Index.
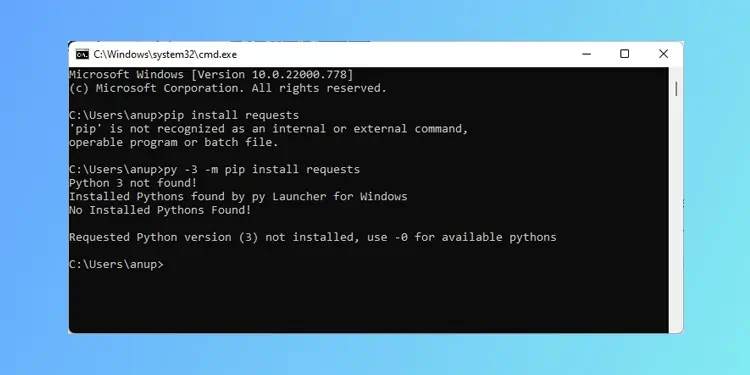
When attempting to install Python packages, you may encounter errors stating PIP is not recognized, command not found, or can’t open the file. In this article, we’ve detailed why such errors occur, as well as how you can fix them.
Why is the PIP Install Not Working?
How to Fix PIP Install Not Working?
In most cases, you won’t encounter this error if you use a Python IDE instead of CMD. However, if you don’t want to use an IDE, or you face this error despite using an IDE, you can try the fixes from the section below to resolve the issue.
Include PIP During Installation
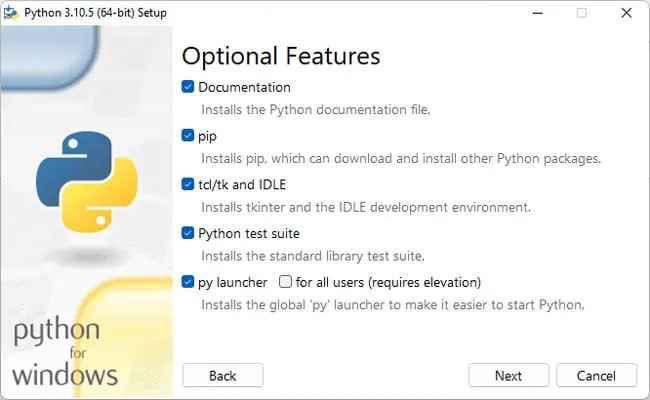
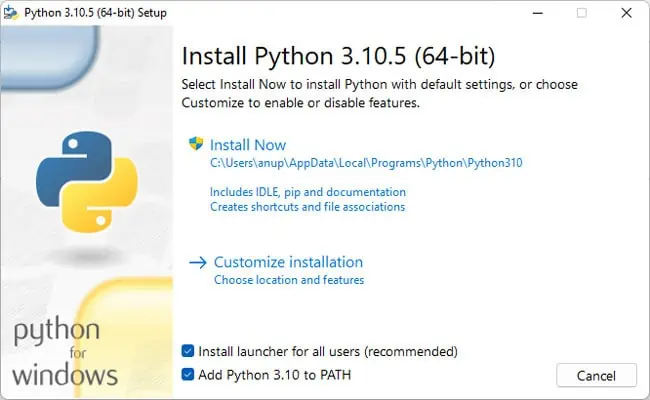
First, you should make sure that PIP was actually included during the Python installation. Here are the steps to do so:
- Press Win + R, type
appwiz.cpl, and press Enter. - Select Python from the list and press Change.
- Click on Modify. Ensure pip is selected and press Next > Install.

- After the installation completes, check if you can install the Python packages now.
Add PIP to PATH Variable
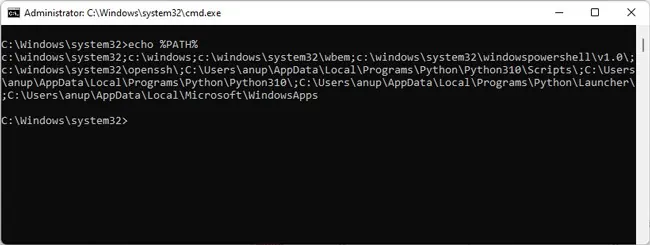
As stated, the PIP Install path needs to be added to the PATH system variable for it to work. Otherwise, CMD won’t recognize the command and you’ll encounter the not recognized error. First, you should check if this is the issue with the following steps:
- Press Win + R, type
cmd, and press CTRL + Shift + Enter. - Type
echo %PATH%and press Enter.
Depending on your Python version and install location, you may see a path like C:\Python36\Scripts. This means the PIP path is already added to the PATH variable. If you don’t see it, you can add it via the command line with the following steps:
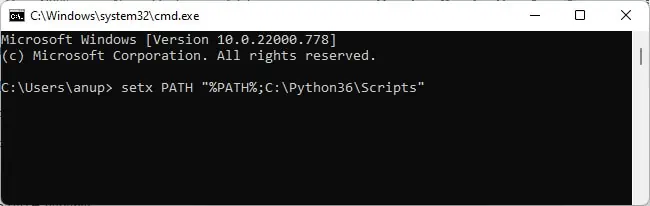
- Execute the following command:
setx PATH "%PATH%;<PIP Path>"
As stated, the PIP path will differ according to your Python version. We’ve usedC:\Python36\Scriptsas an example but in your case, the PIP path maybe different. If you aren’t sure what the PIP path is, check the GUI method below. - Start a new instance of command prompt and check if you can install any packages.
The command-line interface method returns a lot of paths at once, which can get confusing. Instead, you can also check the paths via the GUI. Here are the steps to do so:
- Press Win + R, type
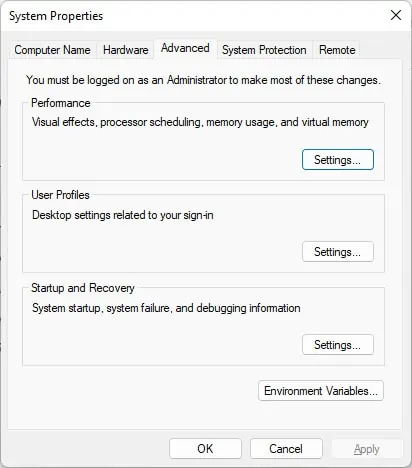
sysdm.cpl, and press Enter. - Switch to the Advanced tab and click on Environment Variables.

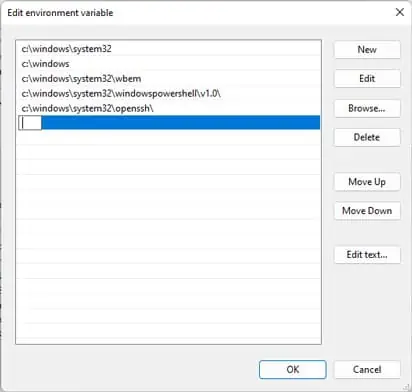
- In the System variables section, select Path and press Edit.
- Click on New and add the pip installation path. This differs depending on your Python version but for the current latest version (3.10), the path is:
C:\Users\Username\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\Scripts.
- Check if you can install a pip package now.
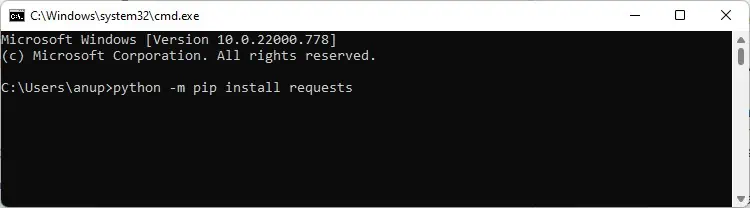
Use Correct PIP and Python Version
The pip install packagename command is generally used to install Python packages. If this command doesn’t work, you can try the commands shown below instead. Don’t forget to replace packagename with the actual package you’re trying to install.
python -m pip install packagename
py -m pip install packagename
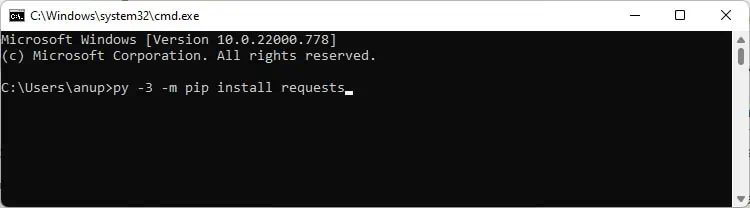
If you have multiple python versions, specify the version number as shown below:
py -3 -m pip install packagename
Manually Install PIP
Due to failed upgrades and similar issues, your PIP file can get corrupted which can also lead to various problems such as PIP Install Not Working. One easy way to fix this is by removing Python and reinstalling it. You can find the steps to do so in the next section.
Alternatively, you can also manually install PIP with the following steps:
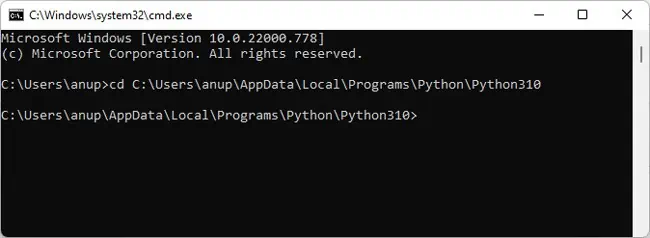
- Download get-pip.py and store it in Python’s installation directory.
- Enter
cd <above directory>to switch to the installation directory in CMD.
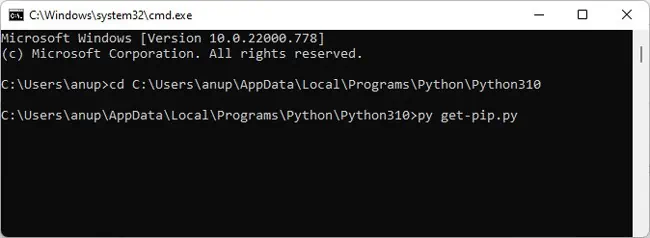
- Type
py get-pip.pyand press Enter.
- Once pip is installed, check if you can install any packages.
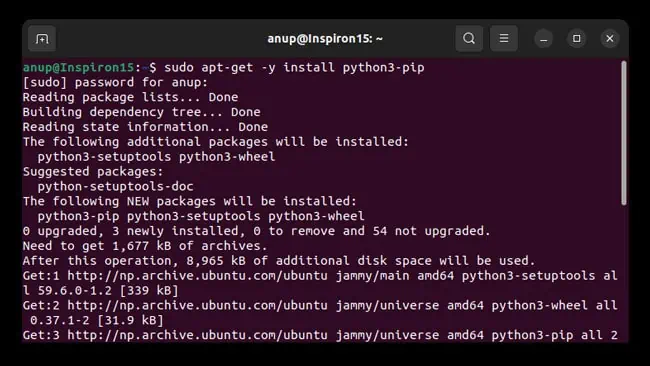
In case of Linux, pip doesn’t come bundled with Python. You have to manually install it first. You can do so by executing the following command in the terminal:
sudo apt-get -y install python3-pip
Reinstall Python
The final option is to remove Python entirely and then reinstall it. Any problematic files will be replaced during the process, which should ultimately resolve the issue. Here are the steps to do so:
- Press Win + R, type appwiz.cpl, and press Enter.
- Select Python from the list, click on Uninstall and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Restart your PC and reinstall Python.
- Enable the Add Python to Path option and select Customize installation. Also, make sure that PIP is included during the installation.

- After the installation completes, restart your PC once more, then check if you can install any Python packages.