RAM frequency is a measure of the data transfer rate between the RAM and the CPU. RAM speed/frequency directly affects your system’s performance, especially if you are gaming or multitasking.
How RAM frequency works and how this number affects your system performance is a topic that even some intermediate PC users have difficulty understanding. And this is exactly what I will be explaining in this article.
Understanding RAM Frequency
When you open an application, all data required to run the application is loaded into the DRAM or Dynamic Random Access Memory. The CPU then accesses this data to run the application.
The speed at which the CPU accesses the data in the RAM is your RAM frequency/speed. RAM frequency is measured in MegaHertz or MHz.
Data on RAM are transferred in clock cycles. Older generation RAM can transfer one unit of data per clock cycle. For example, if a RAM has a speed of 400 MHz, it means it has 400,000,000 clock cycles per second and transfers 400,000,000 units of data per second, depending on the data rate of the RAM.
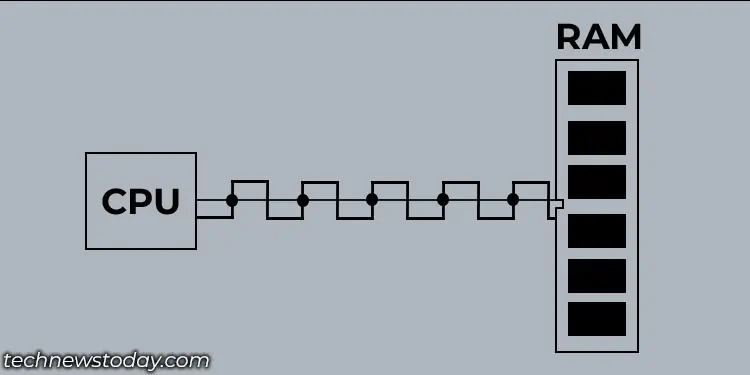
These are traditional Single Data Rate (SDR) RAM and are not so common nowadays. Today, we mostly use DDR memory.
Double Data Rate (DDR) RAM
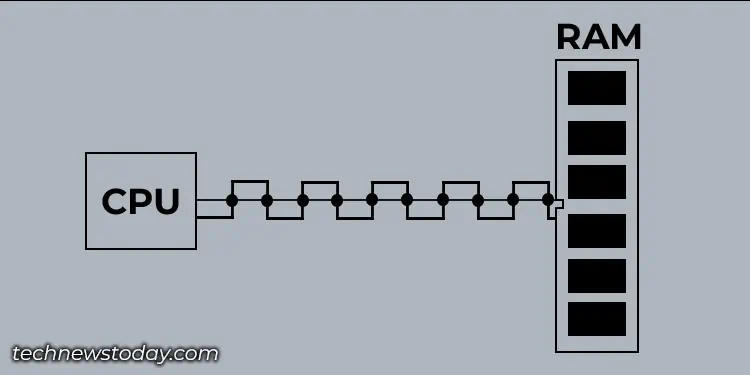
A DDR RAM transfers two unit of data per clock cycle, unlike SDR where a single data unit is transferred in one clock cycle. This means double the transfer rate, hence the name DDR.
With each generation of DDR memory, the frequency also increased significantly. Last Gen DDR4 memory supports frequencies from 1600 MHz to 5333 MHz. Currently, we are at DDR5 memory. This memory can support speeds from 3200 MHz to 6400 MHz. However, on the market, you’ll likely see DDR5 model starting from 4800Mhz
The frequency mentioned on your DDR memory is not its actual speed. A DDR memory runs at half its advertised frequency, the actual memory speed is measured at Mega-transfers per seconds.

So, if you have a DDR4-3600 RAM, it is actually running at 1800 MHz. But since the data is transferred twice in one clock cycle, the cumulative RAM speed is 3600 MT/s (MegaTransfers per second).
Most, if not all, memory modules on the market are DDR memory. However, you can achieve even higher transfer rate by pairing two identical memory modules in dual-channel mode.
Why RAM Frequency Matters
Higher RAM frequency means data transfers between the CPU and RAM is faster. So, if you have a fast CPU, it can access data from RAM, process it and give an output much faster.
So, given that you have a faster CPU that supports higher RAM speed, a RAM with higher frequency will benefit your entire system.
However, this situation only occurs when the CPU constantly requires data from RAM, or in technical terms, when the system is running CPU intensive applications. If you do not require much processing or use the PC just for casual desktop application, the difference between a higher and a lower frequency RAM might not be noticeable.
CPU performance Depending on RAM frequency
To check the performance change in CPU depending on RAM frequency, we performed two test on Geekbench 6. The system ran the DDR4 RAM first at 1300MHz and 2933 MHz on the second test.
GeekBench runs several tests and times how long it takes for the processor to complete. Faster a processor finishes a task, higher the score.
The CPU was an AMD Ryzen 5 2600, a fairly older CPU but this should not matter as we are just comparing the affect of RAM speed on the final CPU score. And here are the final score.
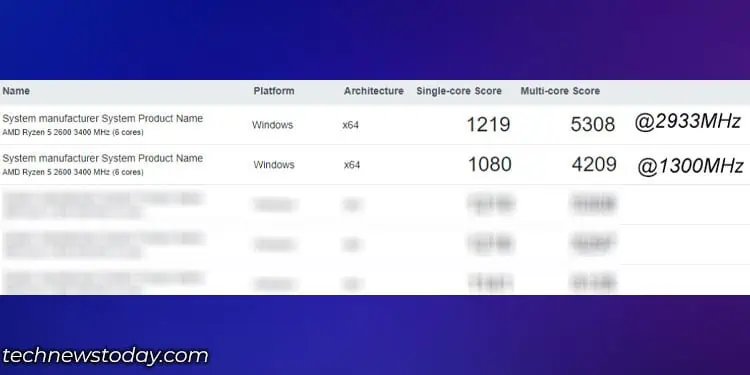
Both in single and multi-core, CPU with RAM running at higher speed finishes the GeekBench benchmark first. So, you see those higher number on RAM running at 2933 MHz.
Factors that Affects RAM Speed
First, RAM stick run at a set frequency, and no other factor changes this speed unless you chance RAM speed manually from BIOS. However, how fast a RAM can respond to a request entirely depends on memory timings.
In your memory module package you may have seen something like, DDR4 8GB 3200MHz CL 16. Here, CL means CAS Latency and it is what affects your RAMs performance the most.
CAS Latency (CL)

CAS Latency or Column Address Strobe Latency is the time your RAM takes (in clock cycle) to access specific data from its column and make it available to transfer to the CPU.
18 CAS or CL 18 means once the memory controller requests this data, the memory takes 18 clock cycles to find the data from memory chips and make the data ready to transfer.
Memory with same speed can come with different CAS Latency. In such case, RAM with lower CL performs better than the higher one. A RAM running on 3600 MT/s with CL 16 is always better than a RAM stick running on 3600 MT/s with CL 18.
Memory Stick Configurations
Memory configuration does not exactly affect your RAM frequency. However, it does change your maximum memory bandwidth.
CPU and RAM uses two 64-bit channel to transfer data. But, if the motherboard only has one stick of memory or the memory configuration does not match, it only uses one 64-bit channel.
If it uses two 64-bit channel, data transfers in higher bandwidth, effectively increasing your CPU performance. This requirement of using two 64-bit channel is met when two identical memory runs on dual channel mode.
Again, this does not increase RAM frequency. The frequency at which the data transfer remains the same. It increases the bandwidth which allows more data to flow in the same frequency.
Using Memory with Different Speed and Timings
Using memories with different speed and memory timings will also affect the actual speed of your RAM.
Say you have a system with 8GB DDR4-3600 with CL 16 and a 8GB DDR4-2666 CL 18 memory. In your system, both these RAM will run on 2600 MT/s at CL 18.
Your system will automatically use lower of the two speed and the higher timing values when you use two memory module with variable speed and latency.
XMP And Overclocking
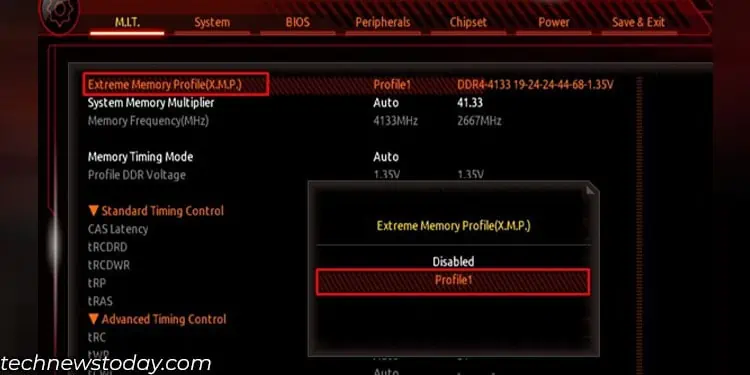
By default, your memory stick will not run at the advertised speed. The memory stick will only be able to achieve this speed when you enable XMP, or eXtreme Memory Profiles.
Enabling XMP allows users to switch between RAM frequency. You can do this via BIOS. However, this does not mean you can set the XMP profile to the maximum value. You first need to determine the maximum RAM speed supported by the CPU and the motherboard.
If you set a XMP profile with RAM speed higher than the one supported by CPU or the motherboard, the system will run into issues when booting. So, you need to know the maximum RAM speed for CPU and motherboard before you set an XMP profile.
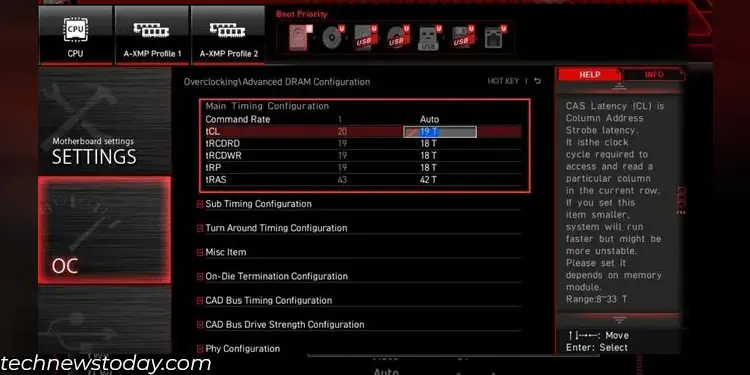
Once you use the recommended RAM frequency, you can overclock it to further improve RAM performance. In case of memory, you need to lower RAM’s memory timings to overclock it.
Overclocking a RAM is a complex topic, especially if you are performing it for the first time. So, we recommend that you follow our extensive guide on overclocking a RAM before you overclock it.
How RAM Frequency Affects System Performance?
One reason the CPU slot and the memory slot are placed so close together is to minimize the bus length between them. This in-turn lowers CAS Latency.
Your system becomes more responsive and smooth when it can transfer data to and from the RAM faster. So, there is no doubt that the RAM frequency affects the system’s performance.
The important question is would you feel any difference using a system with a lower RAM frequency compared to a system with a higher RAM frequency? Well, it depends on the type of workload you perform on your system.

For Normal Usage: Its highly unlikely that you will feel any difference if you are just using the PC for casual desktop application usage. The system will perform fine on frequency like 2400 Mhz even if you are doing some light multi-tasking.
If you are a casual computer user, you would actually benefit from a higher capacity RAM rather than a faster RAM. Having a higher capacity RAM allows you to store multiple active programs, allowing you to simultaneously run several desktop applications.
For Gaming: In terms of gaming, where frames are constantly being generated using data stored in the memory, a RAM with higher frequency benefits and provides you with a smooth gaming experience and low latency.
Considering you have a fast CPU, gaming with a higher frequency RAM means the CPU can access data loaded into the RAM much more quickly and process them. This highly makes a difference as slower RAM means the CPU has to wait to fetch the data from the memory. And this affects the FPS.
If you are gaming, RAM frequency of 2900 – 3600 Mhz should provide you a smooth experience.
For CPU Intensive Task: If you are streaming, rendering videos, or performing CPU-intensive tasks in general, having a memory with higher frequency makes a difference of night and day.
As we saw with the Geekbench benchmark, our CPU performed exceptionally well when using the memory with higher frequency. This translates to CPU intensive task as well.
For these task, its best that you use RAM that supports speeds more than 3600 MHz. Your CPU will perform better with higher RAM speed, given that the CPU supports it.
Your CPU is designed to support up to a certain RAM frequency. When your memory module matches this RAM frequency, your CPU will be able to maximize its performance, which is absolutely necessary if you are performing a CPU-intensive task.

