File compression is mostly used by software and applications to compress all of their files into a single file. RAR and ZIP are extensions that represent these types of files.
On one hand, RAR is a proprietary compression extension owned by win.rar GmbH. Meanwhile, ZIP is an open-source program whose compression technology is free for all. This means anyone can create new software that creates a ZIP file without having to pay any licensing fees.
If you want to make an archive and don’t know which one to choose between RAR and ZIP, you’ve come to the correct place. In this article, we’ve written about all the differences between RAR and ZIP in the article below that may help you choose.
What is RAR?

Eugene Roshal developed RAR in the year 1993, naming it after himself. The Roshal Archive Compressed (RAR) is a WinRAR-registered compression technology, which is why RAR files specifically require the WinRAR program to create them.
It can bundle multiple types of files into a single archived file using its special compression technique. The .rar extensions also include other file extensions like .rev, .r00, and .r01.
- Better security
- Faster compression and decompression
- Supports larger files
- Requires WinRAR to create
- Requires third-party app to read or extract
What is ZIP?

A Zip file is the most standard compression technology that can compress data into a smaller file with no data loss. It is a free, open-source compression format that was introduced by Phil Katz in 1989. Most tailored software packages compress their files into a Zip folder to distribute to their users.
Older versions of ZIP used the ZIP 2.0 encryption to put a simple password barrier between the files and the user. But this encryption proved to be weak at protecting data. Simple password recovery software could easily break this layer of security making it redundant. Better encryption technology later replaced ZIP 2.0.
The .zip64 and .zipx are also a variation of the ZIP format. The ZIPX is a newer version of ZIP that includes better data compression algorithms and stronger encryption. It also has a better compression ratio, which is on par with RAR. Although ZIPX is better at data compression, it is yet to be integrated into other compression software.
- Does not need third-party software to extract/decompress
- Newer versions have good compression ratio
- Slower compression
RAR vs ZIP, What’s the Difference?
Both formats are compression technologies that are used to archive multiple types of files into a single file. The main difference that separates them is that RAR is a commercial format, whereas ZIP is open source and available to all. Here are some other noticeable differences between RAR and ZIP formats.
Compatibility

Although any of the archiving software can read RAR files, creating them specifically requires WinRAR. Some basic features of WinRAR are free, but you also can unlock some other exclusive features by buying the premium version of the app.
However, ZIP is open source which means you can use any archiving software to create a ZIP file. Unlike RAR, your operating system can extract from ZIP files without any help from extra software.
Max File Size
RAR format supports up to 9 ExaBytes(EB) of data compression. But the original ZIP format only supports around 4 GigaBytes(GB) of data. Although there is a massive difference between them, it is no surprise. Since the RAR is owned by WinRAR, they make improvements to the same format. But since ZIP is open source, newer versions of ZIP are preferred rather than improving on it.
ZIP64 and ZIPX are the later versions of ZIP that support up to 16 EB of archive size.
Headers
The headers of a file store information about the file itself, like file size, modification dates, file name, name length, etc. The RAR format can be differentiated by an 8-bit header. All RAR files share 0x 52 61 72 21 1A 07 00 header that records the file information. Whereas the ZIP has multi-byte values where the header may differ.
Compression Method
In simple terms, when compressing any file, it makes a data index and stores the location of the data rather than the data itself. For example, if you were to compress I LIKE POTATO, it will assign numerical values to the alphabet respective to the position. Then, it will create an index of values like I = 1, L= 2, K=3, and so on. So, rather than storing the repeated “O” itself, it will just point to the last location of O.
The RAR uses a lossless compression method that combines prediction by partial matching (PPMd) and Lempel-Ziv (LZSS) compression methods which are proprietary, to create RAR files. RAR has a higher compression rate in comparison to any other compression method.
Although ZIP may use many compression methods, the most common compression method is DEFLATE. DEFLATE combines LZ77 and Huffman coding to create a lossless compressed file. BZIP2 and LZMA are some of the other compression algorithms ZIP uses.
Compression Speed
As we’ve mentioned before, while compressing, it points to the last location of the character rather than storing the character itself. But it can only point to a location so far back. To make a pointer for something further than its capacity, it will have to make another index record.
Comparatively, RAR has a bigger pointer window than ZIP. This is why RAR requires higher memory but is faster at compressing and decompressing.
Compression Ratio
The compression ratio can be understood as the capability to downsize a file. For a general document file, RAR has a lesser compression ratio in comparison to the latest versions of ZIP(ZIPX). This may differ depending on the software you’re using to compress and the type of file. It means when you compress a file, the compressed file size of RAR is bigger than ZIP.
Encryption Algorithm
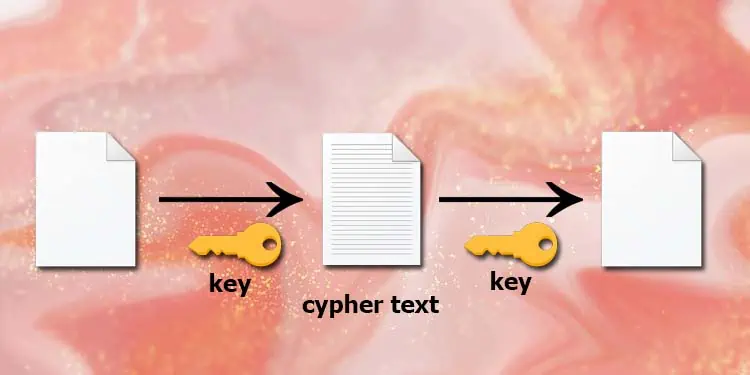
Encrypting means hiding information by randomizing the bits of data. A “key” is also created while encrypting, which the system uses to decrypt the encrypted data. This step-by-step process of encrypting data is known as the Encryption algorithm.
RAR uses the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption algorithm to encrypt the data. The keys are 128 and 256 bits for higher security standards. Longer keys mean a longer time to crack the encryption.
Similarly, newer versions of ZIP also use AES or AES-based encryption. But it may also use different encryption algorithms based on what software you’re using to encrypt your files. The level of security of your files also depends on the type of encryption you use.
What are the Similarities Between RAR and ZIP?
Unlike lossy compression, both RAR and ZIP are lossless data compression. This means that it does not lose any information while compressing and decompressing the data.
Both of them support AES Encryption technology that helps secure data from stealing and mishandling.
Which to Choose RAR or ZIP?
For general purposes, ZIP can be a better choice than RAR. Since you don’t need any new software to extract from ZIP files, it can save you the time needed to download and install the archiving software.
Another disadvantage of RAR is that WinRAR only provides its services for a limited period of time. After a certain time, you will have to pay to continue using the software. Whereas 7-Zip is free. As a free program, it lets you do everything WinRAR does, including creating better-encrypted ZIP files. It can also easily extract any other archiving format.
Here’s the summary of the features of both RAR and ZIP files:
| Features | RAR | ZIP |
| File Extensions | .rar, .rev, .r00, .r01 | .zip, .zipx |
| License | Proprietary or Commercial | Free, Open-source |
| Compression Ratio | Lesser Compression ratio | Better compression ratio, but depends on the software |
| Encryption Algorithm | It uses the AES encryption algorithm. | It uses AES/AES-based encryption algorithm but may vary depending on the software. |
| Compression Method | Proprietary compression method | Mostly DEFLATE but may use other compression algorithms too |
| Compression Speed | Faster compression and decompression | Relatively slower compression and decompression |
| Accessibility | It requires WinRAR to compress or extract compressed files | It requires software to compress but doesn’t require software to decompress. |
| Max Supported size | Supports up to 9 EB archive size | Original ZIP supports 4GB, but later versions like ZIP64 and ZIPX support 16 EB. |
| Min Size | The minimum file size of a .RAR is 20 bytes. | The minimum file size of a .ZIP is 22 bytes. |
| Data Recoverability | Features corrupt data repair and recovery records usage | Cannot repair broken data |

