When your router doesn’t connect to your Internet, it makes it impossible to use the devices that rely on it for the connection. Though you can connect a PC directly to the modem in most cases, that doesn’t provide Internet access for the rest of the devices in your house.
Why Won’t My Router Connect to My Internet?
There are a few reasons why your router won’t connect to the Internet, but they boil down to a few things.
- Settings issues are preventing the router from establishing a solid connection. There are a lot of settings on a router that might be confusing to those unfamiliar with them. If you’ve made changes, one of them might be the problem.
- Hardware issues could also be at fault. Your router or other accessories may break down, causing your connection to suffer. If your router is connected to a separate modem, that may also be an issue.
- Your Internet service provider might be experiencing issues. If they are, you probably won’t connect to the Internet until the problem is fixed.
Troubleshooting a router means working through each of these potential issues to see which one is blocking your connection.
Remember: If your connection works on most devices but not on one computer, you might need to troubleshoot that PC instead of the router. Check to see which devices work before you start working on the router, just in case.
How to Fix Router Not Connecting to the Internet
Start by resetting everything to ensure that it’s not just an issue that will disappear as soon as the Internet is reset.
You should do two things to check whether your router is working:
- Speed Test: The speed test will tell you whether you have your regular download and upload speed.
- Ping Test: The ping test will let you know that the connection between your device and your router is strong.
Reset Your Internet

Properly resetting your Internet isn’t as simple as turning your router on and off. You need to reset the entire system and let it load fully before checking whether the connection works.
It’s not a bad idea to disconnect most connected devices on your router. Having fewer devices sharing the connection might help make it more stable for testing.
- Unplug the router from the wall.
- Unplug the modem from the wall.
- Wait for two minutes, and plug the modem back into the wall. If it has a power button, press it now.
- Wait for two minutes, and then plug the router back in. If it has a power button, press it to turn it on. It’s important to remember that not every modem and router will have a power button. Many start working as soon as they’re plugged in.
- Wait two minutes before you attempt to connect with your computer to test. This gives the router time to grab the connection from the modem and start sharing it with your devices.
- Run a speed test and a ping test.
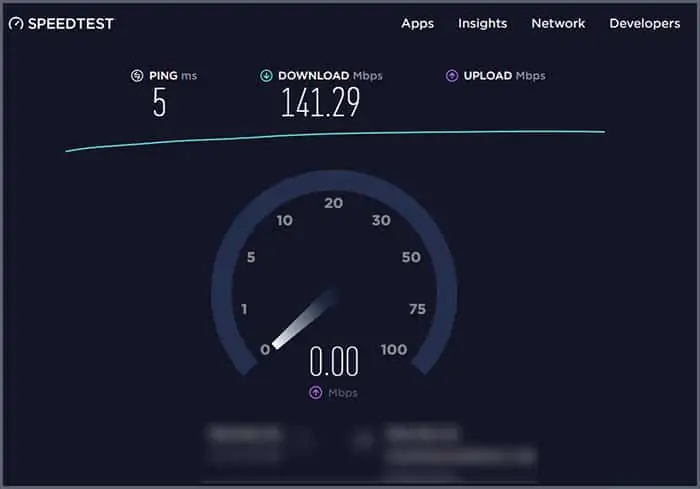
A speed test checks your Internet speed. You can use a website to perform one. You’ll see what server it’s using to test, your ping, the upload speed, and the download speed.
Don’t start a speed test while using other connection-hungry applications on your computer, like media streaming or gaming.
- Navigate to Speedtestor any speed test site of your choice. Each site will have its own specific way to test the connection.
- Press Go.
- Wait for the test to complete. Your Internet connection probably won’t be as fast as the limits of your plan from your ISP, but it should be about the same speed you usually experience to show that it’s working.

If your connection is what you expect, run a ping test. Ping tests send a message to the router, and then the router responds. Once the router responds, it tells you the latency of the connection.
- Press Windows key + X.
- Choose Windows PowerShell (Admin).
- Click Yes.
- Type
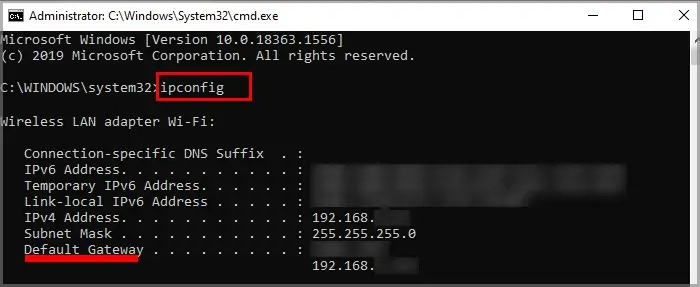
ipconfigand press Enter.
- Look for the Default Gateway listing and make a note of it.
- Type “
ping X” but replace X with the number of your default Gateway.
- Press Enter.
- Wait for the test to complete so you can read the results.
You’re looking at a few different pieces of information here.
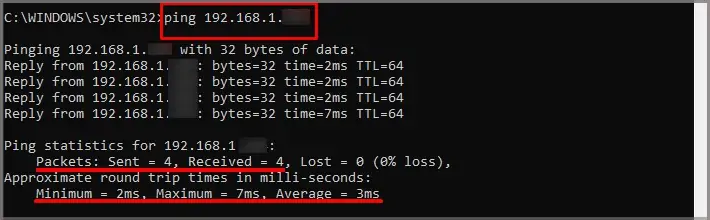
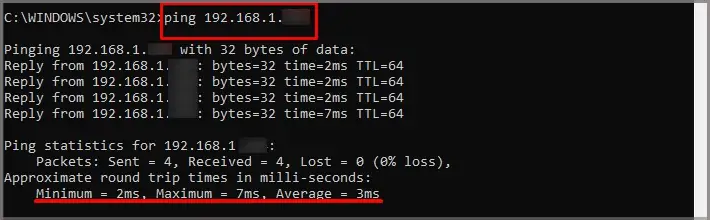
- Packets sent and received lets you know the number of calls the ping test made to the router and how many the router received. Most people shouldn’t experience significant packet loss unless there’s a problem with the network adapter or the computer.
- The round trip time in milliseconds tells you how long each ping took. You should see the minimum, maximum, and average time. For example, my ping test had a maximum of 7 ms, a minimum of 2 ms, and an average of 3 ms.
The average latency will vary depending on what kind of connection you have. For example, fiber might run around 40 ms while wireless might be 10 to 20 ms higher.
Satellite connections might be much higher than that. However, any connection with more than 100 ms latency can interfere with things like first-person shooter gaming or video streaming.
If you want to check and make sure your computer’s wireless card is working, do a ping test and ping the number 127.0.0.1, which is your loopback address. That does a ping test within your computer to let you know that the card is working.
If you’ve tested all of this and your router still doesn’t appear to be working, proceed to the next step. Remember, you’ll want to run all these tests with each step if you see an active connection on your PC.
Check With Your ISP
Your Internet service provider should have a phone number or website where you can contact them. Check for connectivity issues before checking to see whether the router has problems.
You can often find this on the ISP’s website under Status or Troubleshooting. If you can’t find it online, call them at their hotline and ask whether there’s a problem.
Many providers also offer an online troubleshooter for your internet connection. Check to see whether yours does or ask a customer service representative on the phone to perform one.
Move Your Router
Routers generate heat like most electronics. If your router feels particularly warm, unplug it and move it to a different location. After 30 minutes, try plugging it back in to see whether it shut down due to excessive heat.
If this works, you should find a new spot for your router that’s cooler and has more airflow.
If you have a different power cable, extension cord, or Ethernet cable available, try it out now, too. Sometimes a damaged cable can make it appear as if your router is broken when the cables aren’t functioning correctly.
Consult Your Manual
The lights on your router can give you messages about problems it’s having. Many models flash the lights when there’s an issue – while others usually flash.
The best way to know for sure is to consult your manual. You can probably find a copy online if you don’t have it at your home.
Log Into Your Router Settings
You can access your router’s settings by navigating to a specific address. It’s the same as your Default Gateway, but if you can’t find it, you can look it up online by searching for the manufacturer’s name and the words router address.
Sign in with your username and password. If you don’t know them, they’re probably the default for the router model.
- Reset the router to factory default. If you’re having issues with your router, this step can save you a lot of time and energy. It wipes out all your custom settings and replaces them with those applied when you first got the router. Instead of digging into your settings and teasing out which one is creating the problem, just reset it and wipe away any problematic settings.

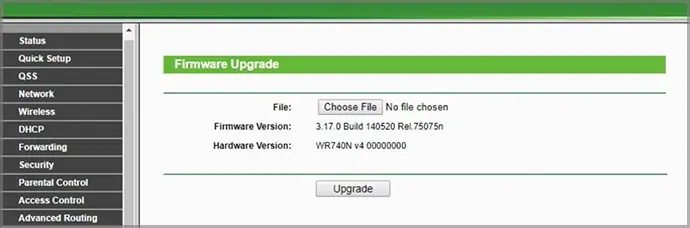
- Update your firmware once the router is reset. The location of each router setting will vary depending on the model you’re using, but each of them should have this as an option. It will upgrade your router to the most recent hardware as long as an update is available.

- Follow the steps from the beginning of the article to reset the router and modem. Once you’re done, rerun the tests to see whether the connection works.
- Check your Wi-Fi channel if you’re able to connect, but it’s slow or sluggish. The procedure will vary depending on your router but look for a place to change your wireless channel settings. Start with channel 1 and run a test to determine the speed and ping. Continue until you find your best possible connection.
- Turn off your Guest Network. You don’t need to be sharing your connection while it isn’t working solidly.
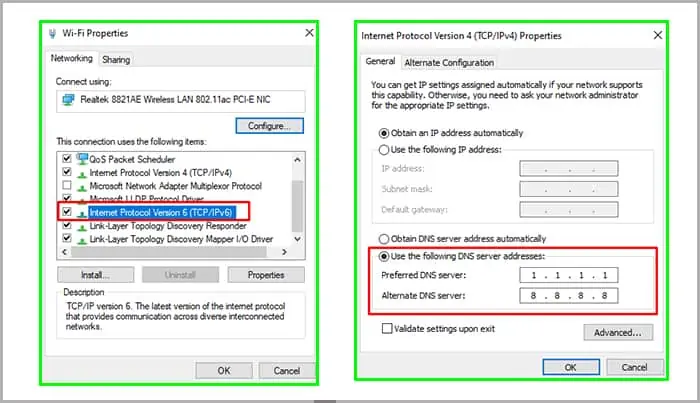
- Try manually setting your DNS in your router. Sometimes a DNS server is down and prevents a connection from completing. You can try 1.1.1.1 or 8.8.8.8. When you’ve changed it, reboot the router and try to connect again.

- Turn on IPv6 if it isn’t already on. This protocol supports more devices and a more robust network than most IPv4 connections. There’s no reason not to have it on as long as your router has the feature.
If you’re comfortable with your router settings, you can look through them and try to see whether something is out of place. However, if your settings were working one day and aren’t the next, it probably isn’t a change you made – and resetting it might fix everything.
Physical Router Issues
Your router might be too damaged to fix if it doesn’t turn on, light up, or do anything. Try to reset it using the physical reset button or pinhole on the device.
Consult your manual for details, but you usually press a reset button or use a small wire to press a button hidden inside a small pinhole. Either one should reset your router to default.
Beyond that, there isn’t much you can do if your router won’t turn on. Shopping for a new router – and potentially an upgrade – is your best bet if you’ve tested your cables and electrical plugs and it still isn’t working.
Physical Modem Issues
Sometimes the connection between your modem and router is damaged, even if it appears that the modem is working. Consider swapping out the modem for another to check whether that fixes the problem with your router.
If it does, then you probably need to get a new modem – though make sure you test that Ethernet cable that connects them.
If you use a combination modem and router that appears to work but won’t hold a stable connection, you also need to check the wiring in your house. Damaged wiring can cause significant issues with your connectivity. Talk to your ISP to see whether they’ll send someone out to assess any potential problems if all else fails.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does Connected but No Internet Mean?
This message means that your computer reaches the router, but the Internet connection isn’t working. Try to run the network troubleshooter on your computer or reach out to your ISP to see if there’s a network problem.
How Do I Know if My Wireless Router Is Failing?
If the router drops connection more often or you notice your speeds are falling, it might be time to replace your router. There usually isn’t an obvious sign that your device is dying. Instead, you just have to pay attention to your connection quality and judge whether it’s time for a new setup.
In general, you should consider replacing your router every five years – though that number may decrease if you have a lot of different devices connecting to it.