Memory Rank refers to the number of 64-bit wide bus a single stick of RAM can use at a time. It is solely determined by the number of memory bus a memory module has.
Usually, a higher memory rank also means increased memory capacity in a single stick and lower latency as multiple ranks are accessed concurrently. But it also means complex internal architecture and lower memory bandwidth.
Most users confuse single-sided modules (memory chip on single side) as single rank and double-sided modules (memory chip on double-sided) as dual. But this reasoning is not entirely true. Single rank uses a single 64-bit bus, whereas dual rank module uses two 64-bit buses in interleaved mode.
Both single and dual-rank RAM have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. So let’s further dive into the topic to determine which RAM is better for you.
Understanding Single-Rank RAM
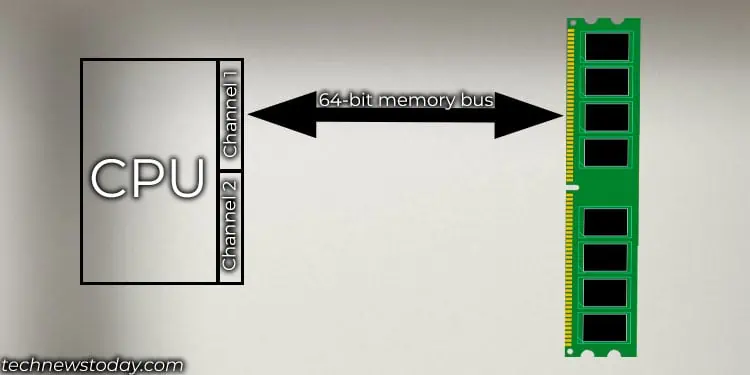
Every CPU connects to the memory using 64-bit wide memory buses (72-bits for ECC memory). A CPU may have 2, 4, or 8 of these memory buses. Now, each memory IC chip attached to your RAM communicates to the CPU using an x4, x8, or x16-bit memory bank.
This means the memory chip with an x4 memory bank connects to the CPU using a 4-bit memory bus, the x8 memory chip uses an 8-bit memory bus, and so on.
If RAM consists of x8 memory chips, it will require a total of 8 (64-bit memory bus/8 bit bus for single chip) memory chips or 9 in case of ECC memory. In this case, the 8 memory chip acts as a single rank and is usually soldered on one side of the memory stick.
For RAM composed of x16 memory chips, it will need 4 (64/16) memory chips. In this case, the four memory chips are considered one rank, or single rank, and are usually soldered on one side of the memory stick.
Lastly, if a RAM stick consists of memory chips that use x4 memory bank, it will need a total of 16 (64-bit memory bus/4-bit bus for single chip) memory chips. This means the total 16 chips can use the total 64-bit memory bus in one single rank.
In this case, the total 16 memory chips can be divided into half and soldered on each side of the memory module. For ECC RAM, two separate chip is added on either side (one on each side).
The memory chip on both sides might make it seem like it is dual-rank RAM, but actually, the entire 16-memory chip uses a total of 64-bit memory addresses. So, it is a single-ranked RAM.
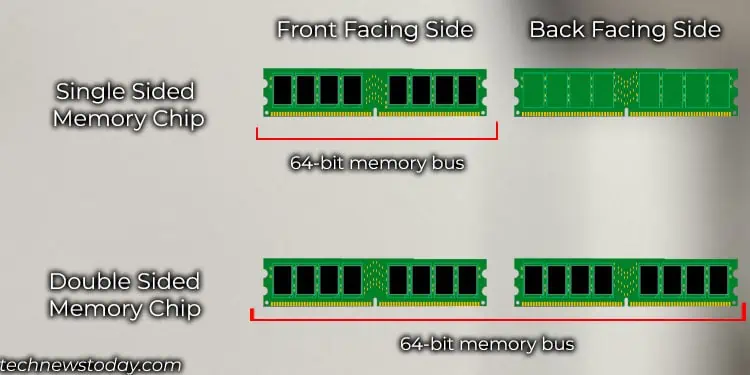
A group of memory chips (x4, x8, or x16) that adds up to the total of 64-bit bus width is one rank or single rank.
Most overclocking enthusiasts use four single ranks by filling up all four DIMM slots. This makes the RAM’s performance reach close to a dual-rank memory in a dual-channel setup.
However, if your system only has two DIMM slots, you would want two dual-rank memory to get the maximum performance.
To identify single-rank RAM, you need to check the RAM label or its specifications sheets. Check for writings like 1Rx4, 1Rx8, or 1Rx16 in the RAM label. Here, 1R means one rank or a single rank.
You can also install CPU-Z to check the number of ranks you have in your memory module.
Understanding Dual-Rank RAM
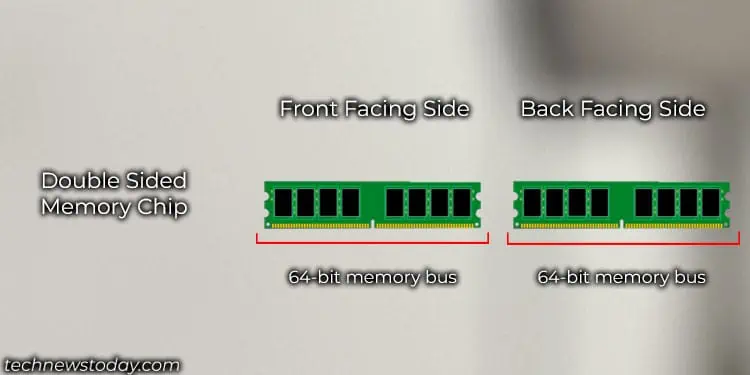
Dual Rank RAM has two independent sets of memory IC chips that run on two separate 64-bit memory buses. However, having two separate 64-bit buses on a single memory stick does not mean that the CPU can access both of them simultaneously.
Instead, the CPU uses one of these two 64-bit buses in interleaved mode. In this mode, the CPU can access one RAM rank while the other rank fetches the data or refreshes itself to be accessed again.
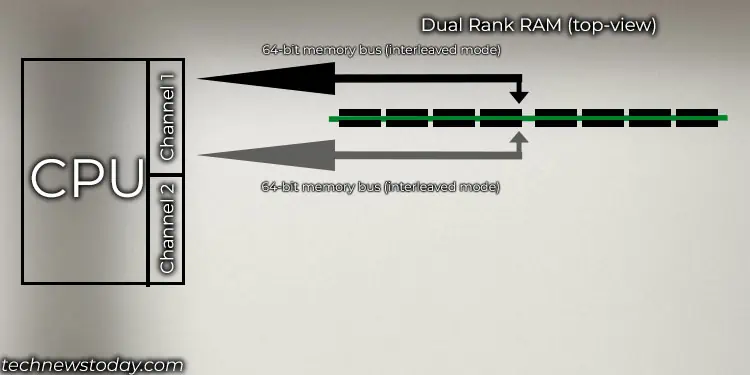
This reduces overall memory latency as the CPU does not have to wait on RAM. It also makes the module much more efficient.
One disadvantage to using more memory rank is that it lowers your memory overclocking capability. More ranks mean the memory controller requires more connection for several memory chips. This lowers the frequency at which the memory module operates.
So, although the memory works efficiently, the memory speed will take a hit.
This should make single-rank memory better, right? Well, it depends. Although RAM’s frequency is a crucial factor in determining its speed, it does not always scale that well. This means that increasing the memory bandwidth does not always mean the CPU can finish a process quickly.
If a task requires half an hour to finish on a 2133 MT/s RAM, it does not mean a 4266 MT/s RAM can finish the same task in fifteen minutes. You can only see such performance improvement in some workloads where an application is sensitive to RAM speed.
In order to identify dual-rank RAM, check the RAM specification for 2Rx4, 2Rx8 or 2Rx16 labels. In this case, 2R means two ranks or dual rank.
Single Rank Vs Dual Rank RAM
| Single Rank RAM | Dual Rank RAM | |
| Architecture | The module contains two sets of memory chips that uses two separate 64-bit memory bus. | The module contains two sets of memory chips that use two separate 64-bit memory bus. |
| Performance | Dual-rank RAM can access two different ranks of memory in interleaved mode and can access data much quickly. | Dual rank RAM can access two different ranks of memory in interleaved mode and can access data much quickly. |
| Transfer Rates | Transfer rates on single-rank RAM are higher compared to dual-rank. | Due to more memory chips on dual-rank RAM, it runs at a slightly lower speed than single-rank RAM. |
| RAM Capacity(This number may change as more memory IC chips are manufactured) | Memory capacity usually maxes out at 8GB. | Memory capacity usually maxes out at 32GB. |
| Identification | Having two sets of memory IC chips, dual-rank RAM tends to be more costlier. | Dual Rank Memory chip says 2Rx4, 2Rx8, or 2Rx16 on the RAM label. In this case, 2R means two ranks or dual rank. |
| Temperature and Overclocking | Generates more heat due to a higher number of memory chips. Overclocking may lead to memory reaching extreme temperatures. | Due to the lower number of chips, single-rank RAM runs significantly cooler and is more stable. Therefore, the optimal choice for overclocking |
| Pricing | Due to the lower number of chips, single-rank RAM runs significantly cooler and is more stable. Therefore, optimal choice for overclocking | Due to the lower number of chips, the cost of single-rank RAM is slightly lower. |
Single or Dual Ranked RAM
If you want a higher capacity single-stick RAM on your system, for now, there is no choice other than using a dual-rank RAM. But if you are choosing between a single rank 16 GB and dual rank 16 GB memory kit, it depends on your workload.
Single rank is faster as it does not have to switch through multiple memory ranks. The lower number of memory chips also means it runs at low temperatures, which is best for overclocking the memory speed. These types of RAM are great for casual day-to-usage and even gaming.
Dual-rank RAM, on the other hand, has two 64-bit buses. This offers lower latency as the CPU does not have to wait on RAM to access data. This type of RAM is especially for systems, such as huge workstation computers or database servers, which handle numerous data simultaneously.
But this does not mean dual-rank RAM is specifically designed for such purposes. An average consumer can also use these types of RAM in their personal system.