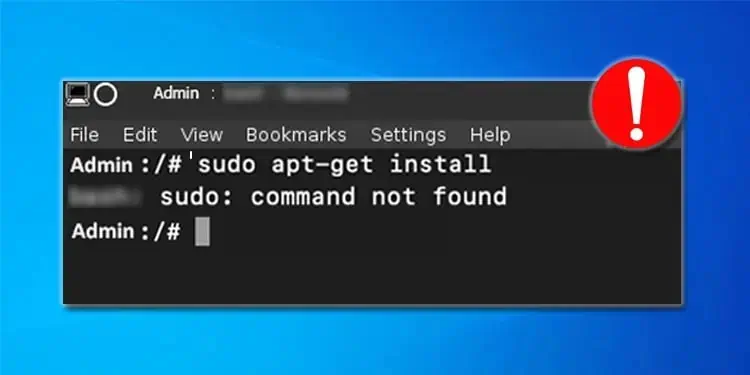
Sudo apt-get is a frequently used command line to manage the Debian packages. However, if you use this on a non-Debian device or if the apt package is not installed, you will get the Command not found error when trying to execute it.
Additionally, when this error pops up, users won’t be able to install, remove, update or manage the software packages.
In this article, we will cover this issue and help you find a resolution to this command error.
What is sudo apt-get Command?
The Linux repositories have different packages available for the users. These packages can be installed using the apt-get commands. apt is simply a package manager that is used to install, remove, and update packages.
Probable Causes of this Error
apt-get commands are supported only by Debian-based distros like Ubuntu. However, if you are trying to use apt packages on Rpm-based distributions, you will get the sudo apt-get command not found error. This error will also pop up if the location path for the apt package is missing.
How to Fix sudo apt-get Command Not Found?
The first step is to check if you are using a Debian-based operating system. To see which distro you are using, execute thelsb_release -a command. This will give the description of the distribution and its current version.
If you have confirmed that you are using Debian Linux, then use these fixes to resolve the problem.
Install apt-get
The major reason for the sudo apt-Get command not found error is if it is not installed. To install the apt packages perform these steps,
- Go to this link and search for the latest apt package.
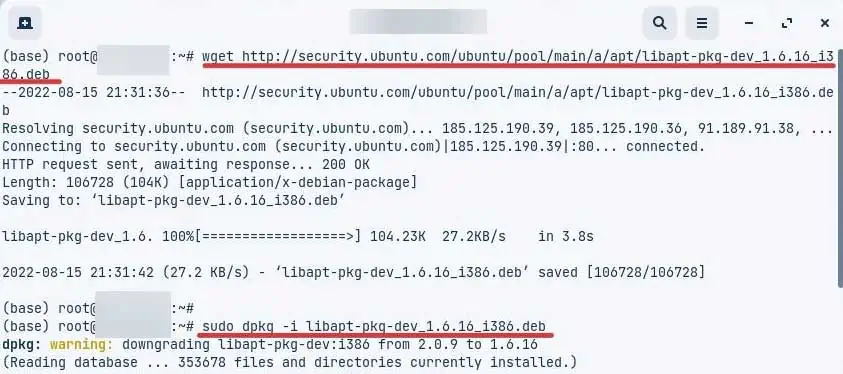
- Now, download the package using this command. Paste the name of the latest available package after the apt/ of this command. You might need to be logged in as a root user to execute these.
wget http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/a/apt/libapt-pkg-dev_1.6.16_i386.deb - Now install the package with this.
sudo dpkg -i libapt-pkg-dev_1.6.16_i386.deb
- If you are not able to use the commands because of the
sudoinvolved in it, try this alternative command-linepkexec dpkg -i libapt-pkg-dev_1.6.16_i386.deb - When asked for Press ‘Y’. This process will install the apt packages in the system.
Install Sudo
In the minimal Debian versions, the sudo isn’t installed by default. You might get the command error in such a condition.
To install the sudo, follow these steps:
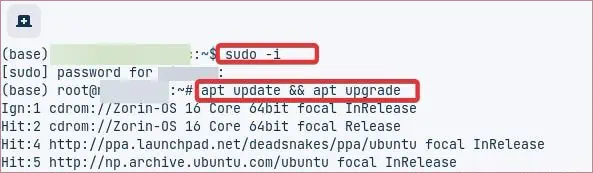
- First of all, update the apt cache with this command.
apt update && apt upgrade
- Now Install sudo.
apt install sudo
Use Native Package Manager
If you have a Linux distro other than Debian, apt-get package manager will not work for you. You have to use the native ones for your system. The list of different package managers with their compatible Linux distros is listed here.
| Package Managers | Linux Distributions |
yum | Red Hat Linux, Fedora, Cent OS |
pacman | Arch Linux |
tgz | Slackware |
dnf | Versions from Fedora 18 |
Zypper | OpenSUSE |
Perform a Fresh OS Install
If none of the fixes work, you must perform a fresh install of the OS. It is recommended that you download a non-minimal Debian distro and install it. These distros come up with lots of features and packages pre-installed. Ubuntu, Pop!_OS, and Zorin OS are some of the popular Debian Linux distributions.
How to Fix Sudo apt-get Command Not Found on Mac?
The macOs Terminal doesn’t directly provide support to the sudo apt-get command. However, you can use the Homebrew package manager to get it working. If you are trying to use the apt-get without having installed a supporting package manager, you will get the command not found error.
To install the Homebrew,
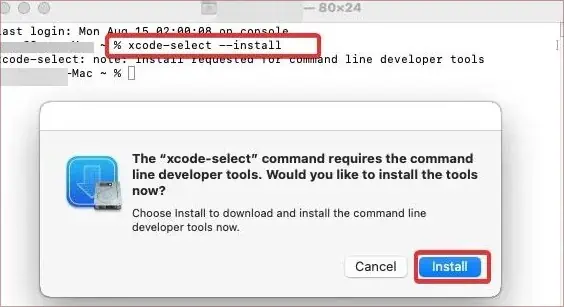
- First of all, install the Xcode IDE with this command.
xcode-select --install - When asked for confirmation, Click on Install.

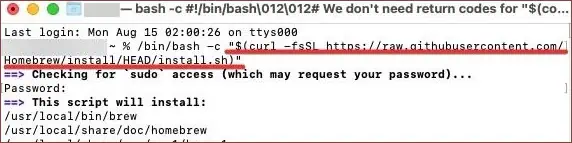
- Now, that the Xcode is installed, use the
curlcommand to install the Homebrew package manager.$ /bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
- Enter the system password when asked. This will start the installation process.
- Restart the terminal, and now you will be able to use the
sudo apt-getcommand on your mac.