Copying files in Windows or Linux is simple enough. Copying files between them, though, not so much. The classic copy-paste with a USB stick method does work, but it’s not very efficient.
Instead, you can transfer files using protocols like SMB and SSH and using FTP applications such as FileZilla. We’ve listed step-by-step instructions for these and more methods in the sections below.
Ways to Transfer Files between Linux and Windows
Before you start, do keep in mind that, unlike Windows, Linux is case-sensitive. When entering the commands or file paths, users often forget this and can’t figure out why the file transfer doesn’t work despite following the steps correctly.
With that said, here are the various ways to transfer files between Linux and Windows.
Transfer Files Using SMB
The Server Message Block (SMB) protocol is a client-server communication protocol built into most Linux distributions. Here are the steps to transfer files using SMB:
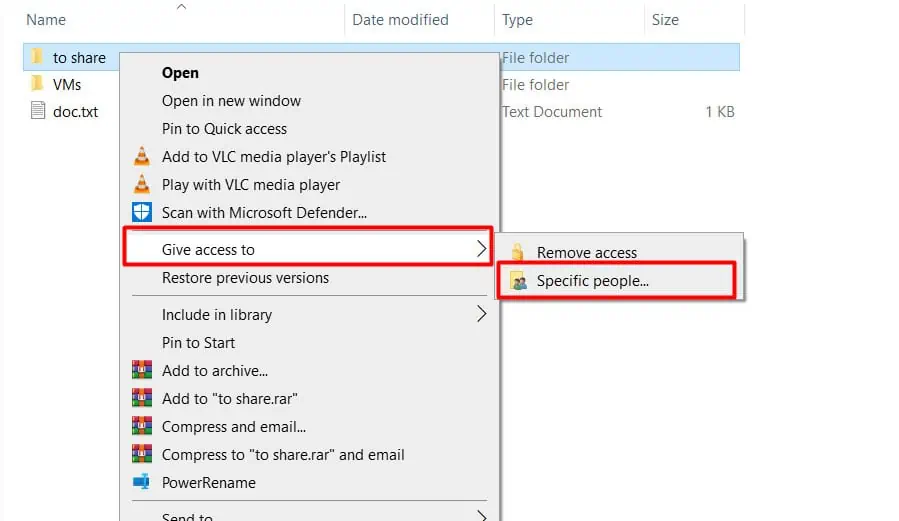
- On your Windows system, locate the folder you’re trying to share.
- Right-click the folder and select Give access to > Specific People.

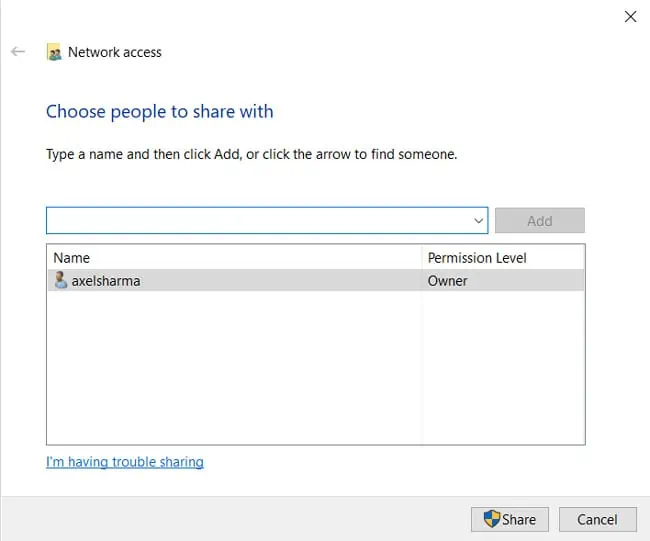
- Click on Share and press Done on the next screen.

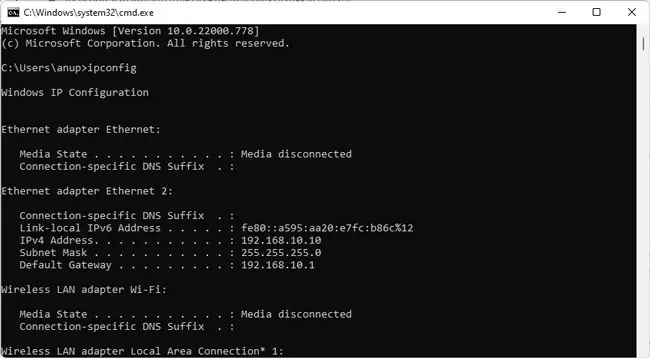
- Next, press Win + R, type
cmd, and press Enter. - Type
ipconfigand press Enter. Note the IPv4 address of the first adapter on the list.
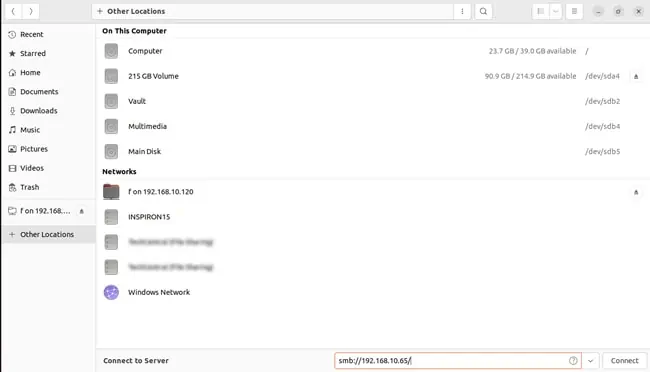
- On the Linux system, launch the File Browser and click on + Other Locations.
- In the Connect to Server field, enter the IP from Step 5 in the following format:
smb://IP
- At the authentication prompt, enter your Windows account credentials and press Connect. You can now use this folder to transfer files between Linux and Windows.
Transfer Files Using SSH
Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol commonly used for remote login. With an SSH client such as PuTTY, you can transfer files between Linux and Windows via the command line. Here are the steps to do so:
- On the Windows system, download and install PuTTY if you haven’t already.
- On the Linux system, press CTRL + Alt + T to launch the Terminal.
- Install and enable SSH with the following commands on Debian-based Linux systems such as Ubuntu:
sudo apt install ssh
sudo systemctl enable ssh --now - On RedHat, CentOS, Fedora, and other systems, use these commands instead:
sudo apt install OpenSSH
sudo systemctl enable sshd --now - In case you’re getting blocked by the firewall, use the following command:
sudo ufw allow 22/tcp - Enter
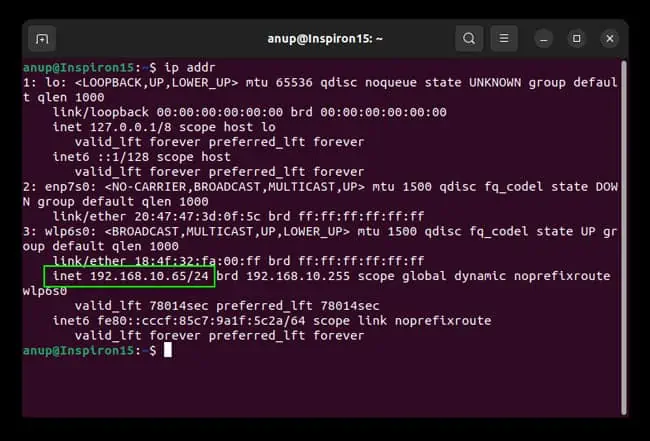
ip addrand note the IP Address.
- On the Windows system, open Command Prompt and use the commands listed below as appropriate.
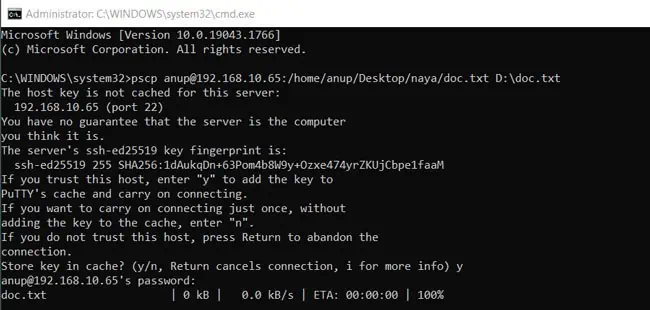
- The following command is to copy a single file. The example shows the file named
doc.txtbeing copied from a remote Linux system to the D drive on the Windows system.pscp user@host:remote_path/file_name host_path\file_name
- To copy all files in a folder:
pscp user@host:remote_path/* host_path\
eg: pscp anup@192.168.10.65:/home/anup/Desktop/naya/* D:\testfolder\ - To copy all files & folders in a folder:
pscp -r user@host:remote_path/ host_path\
eg: pscp -r anup@192.168.10.65:/home/anup/Desktop/naya D:\testfolder\
Transfer Files Using SFTP
You can also use a third-party tool such as FileZilla to transfer files using SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol). Here are the steps to do so:
- On the Linux system, follow Steps 1 – 6 from the section above to set up SSH.
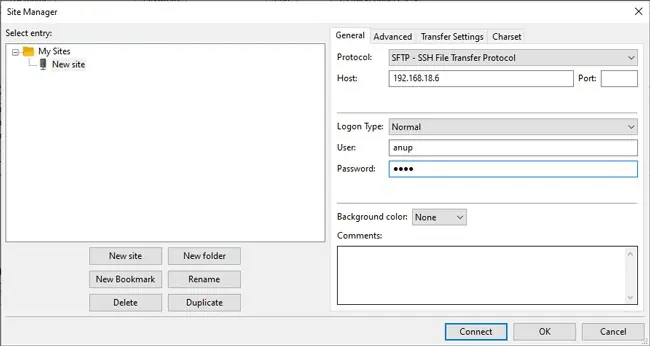
- On the Windows system, launch FileZilla and select File > Site Manager > New Site.
- In the Protocol field, select SFTP – SSH File Transfer Protocol.

- In the Host field, enter the Linux IP Address from Step 6 of the section above.
- Fill in the login credentials of your Linux system and press Connect.
- If prompted, enable the Always trust this host option and press OK.
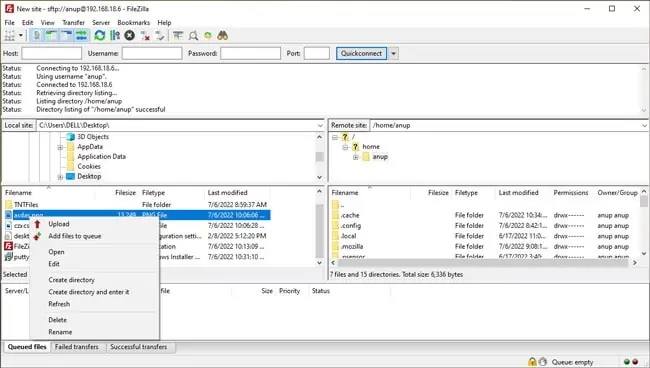
- Now that the connection is established, you can transfer files between Windows and Linux by dragging and dropping or right-clicking the file and selecting Upload/Download.

How to Transfer File from Linux to Windows VM?
You can easily transfer files from Linux to a Windows VM using a USB Stick. Of course, that’s just one easy method. We have an article that details multiple ways to transfer the files for your further reading.