The C drive is where the Windows operating system is predominantly installed by all computer manufacturers. As the OS drive, the C drive handles and stores a lot of system important files. However, you may sometimes find its storage space filling up unusually fast.
This issue can crop up due to a variety of reasons like malware, problematic drive, improper storage management, old user account folders, large temporary files, and so on. As the C drive must have free space for the smooth operation of your Windows OS, you need to make sure its storage space is properly managed.
Scan for Malware
One of the main reasons why your C drive is getting filled up so fast may be due to malware infection. If your computer is infected with malware, it can possibly occupy large storage spaces or mess with your system and show low free space on your drive.
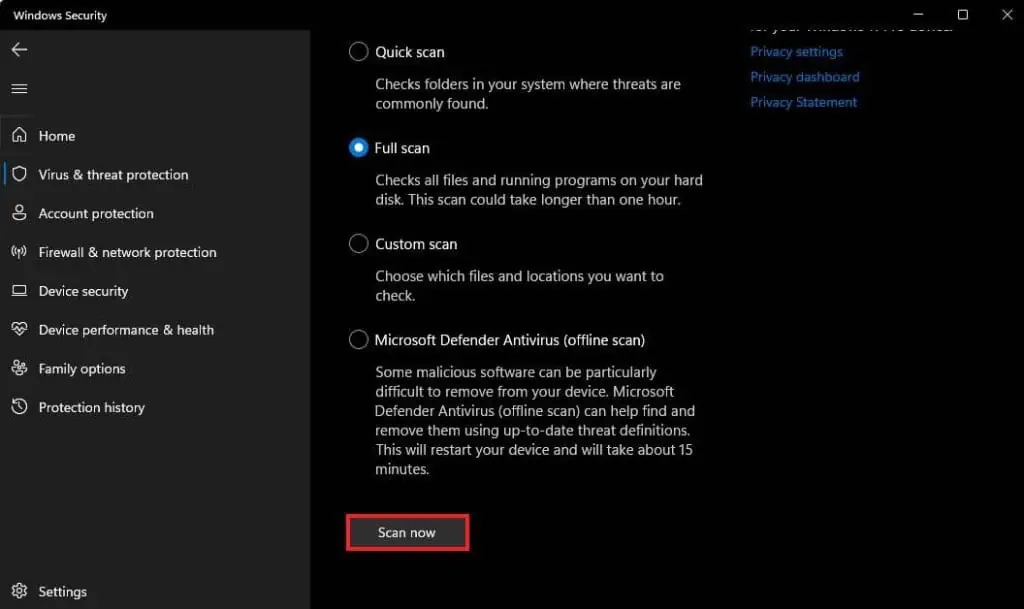
So, to check if a malware infection is behind the cause of your issue, you can try performing a full system scan from Windows Security.
- Press Windows + I hotkey to open Settings.
- Navigate to Privacy & security > Windows Security.
- Click on Virus & threat protection.

- In Virus & threat protection, click on Scan options.
- Select Full scan and click on Scan now.

Manage Storage From Setting
The storage sense feature in Windows makes it quite easy to see what files are taking up space in your computer. You can then manage and delete unnecessary files from there to free up space in your drives.
- Press Windows + I shortcut key to open Settings.
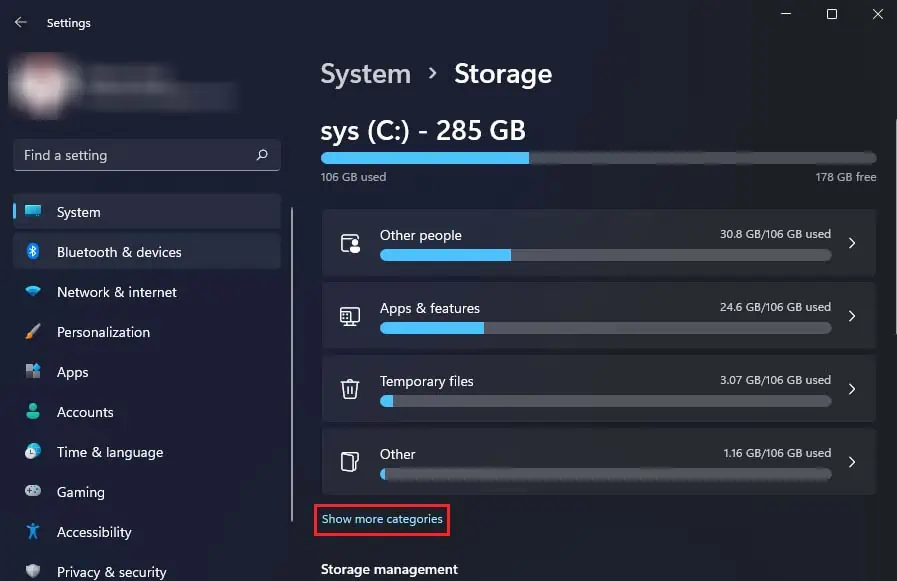
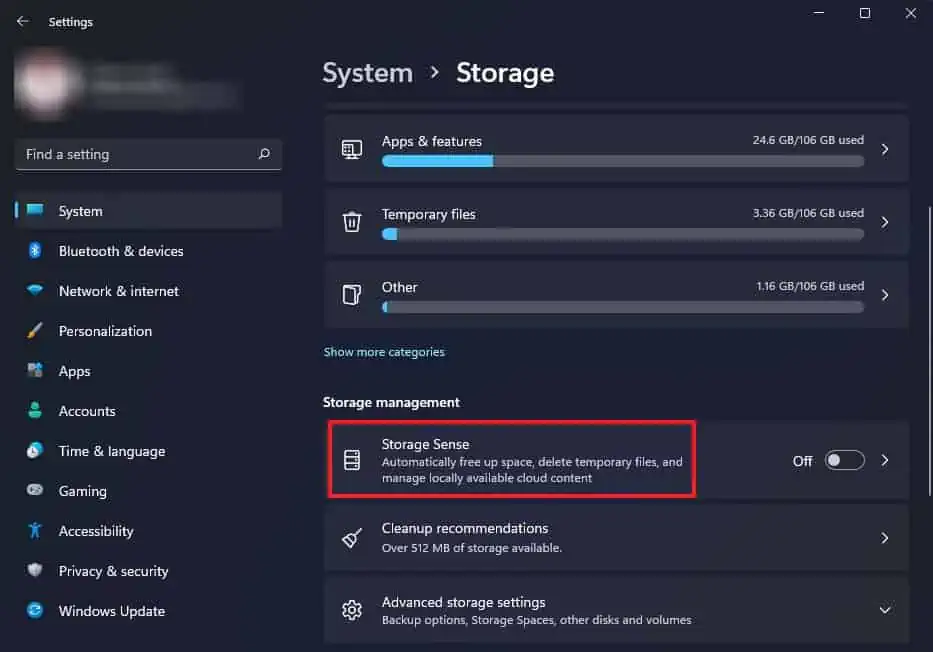
- Navigate to System > Storage and click on Show more categories.

- You can then see all the different things that are taking up space in your computer.
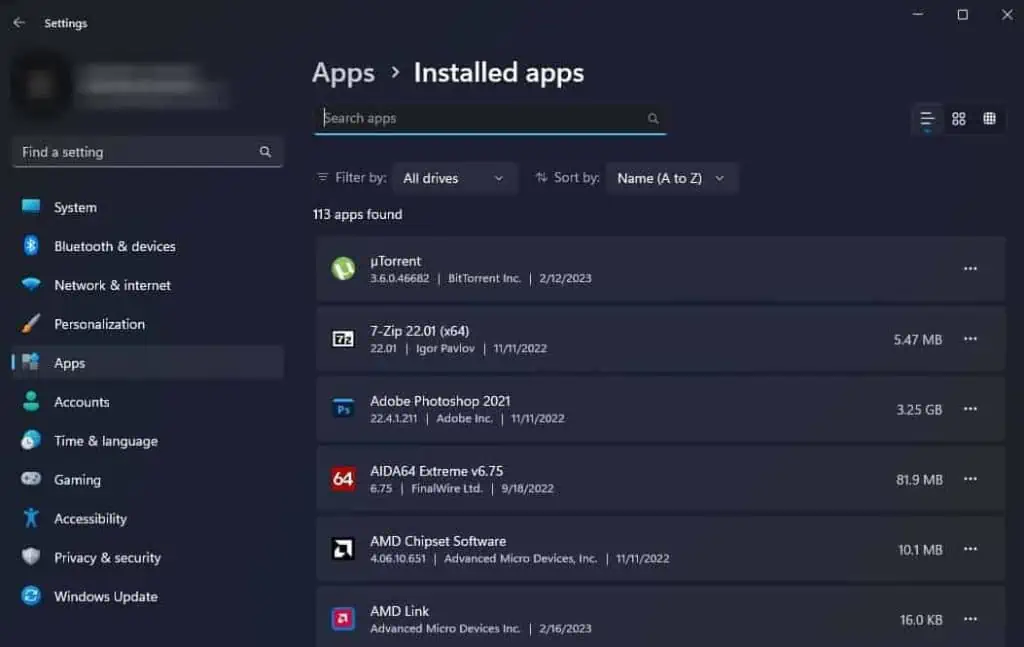
- If your Installed apps are taking up a lot of space, you can select Installed apps to uninstall unnecessary applications.

- If your Pictures, Music or Videos are taking up a lot of space, you can relocate them to a separate drive.
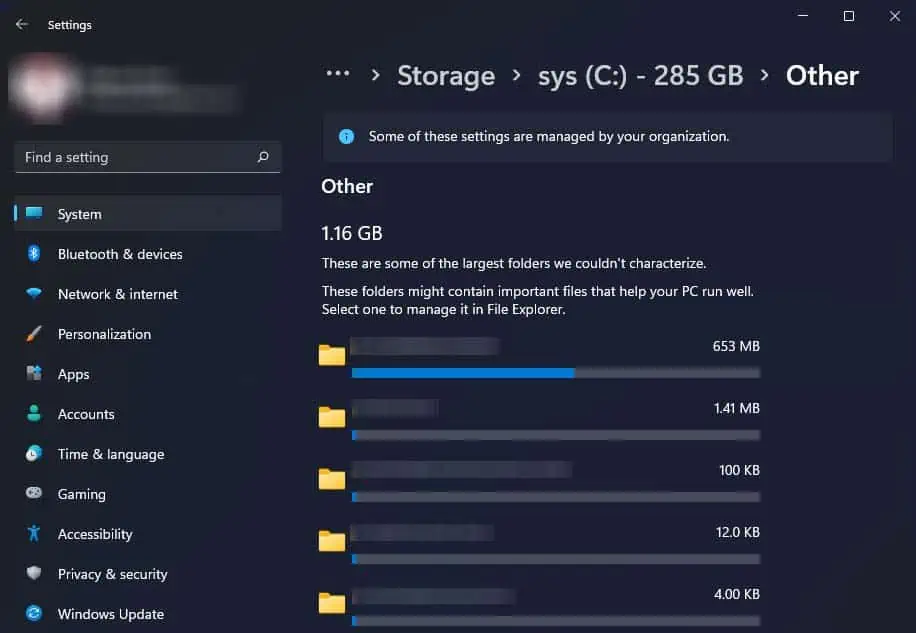
- If the Other section is taking up a lot of space in your drive, you can click on it to see the large folders that are occupying your drive space.

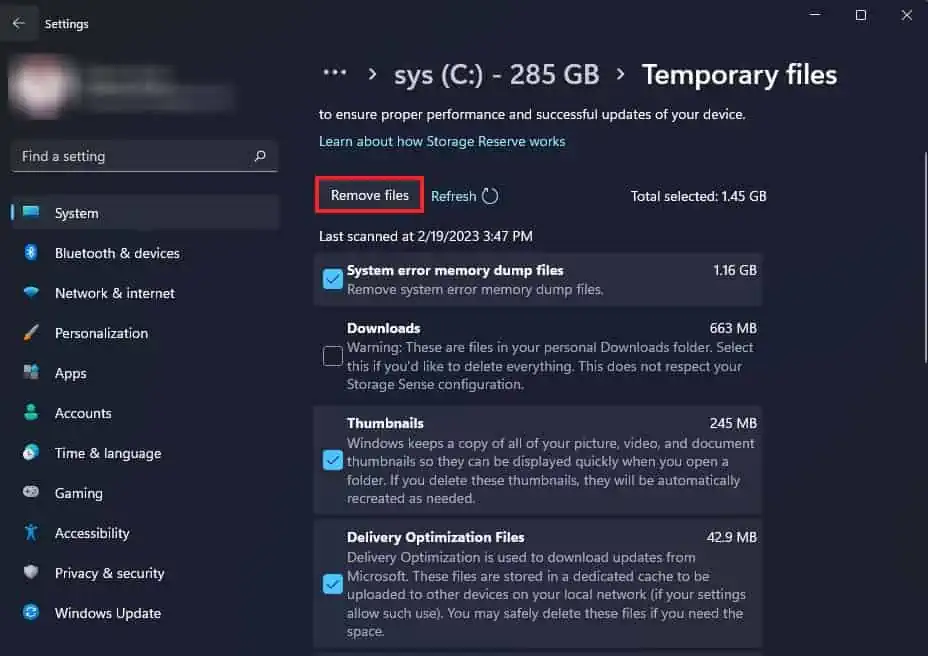
- To delete your Temporary files, click on it and select the files you want to delete. (If you have a previous installation of Windows which you don’t need currently, you can also select it.)
- Make sure to select Temporary files, Thumbnails, Temporary Internet files, and Recycle bin. (For the remaining files, you can check their description to decide whether you want to delete them.)

- Click on Remove files to clear your temporary files.
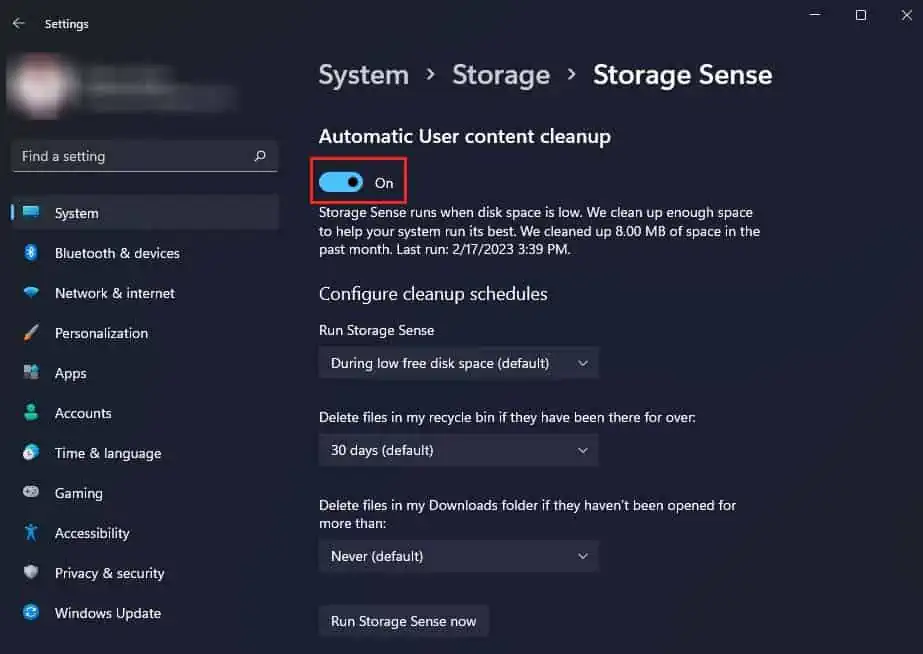
Additionally, you can also enable storage sense to automatically clear some space when your disk space is low.
- Open Settings and go to System > Storage.
- Click on Storage Sense.

- Toggle on Automatic User content cleanup.

- You can also configure cleanup schedules according to your liking or Run storage sense now.
Clear User Temporary Files
Temporary files, as their name suggests, are for temporarily storing data for various purposes. While they are small in size individually, they can accumulate and stack up to tens of gigabytes in size. Furthermore, some temporary files like the ones created by applications in user folders do not get automatically deleted.
So, clearing the temporary files in your system can relieve quite a bit of used disk space, especially if you haven’t done so in a while.
- Press Windows + E to open File Explorer.
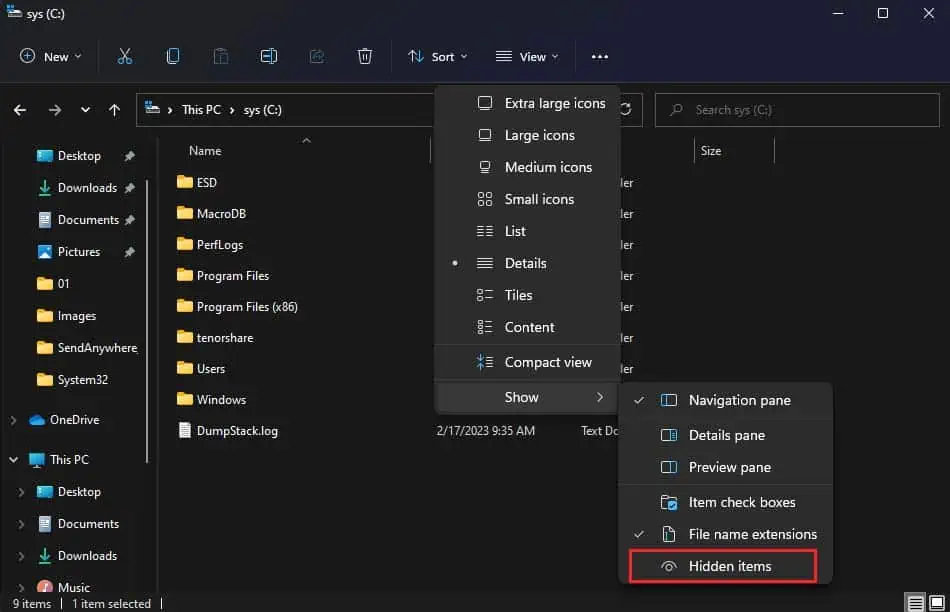
- As the path to the temporary files is hidden, you’ll first need to enable show hidden folders.
- Click on View in the menu bar and select Show.
- Select Hidden items.

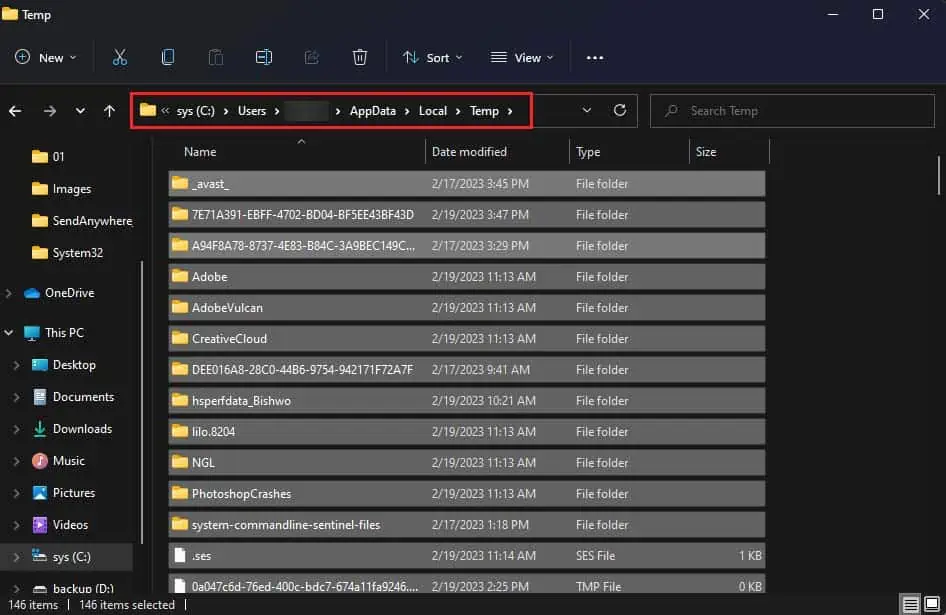
- Now, navigate to
C:\Users\USERNAME\AppData\Local\Temp. (Replace USERNAME with your account username.)
- Press Ctrl + A to select all of them and hit the Del key to delete them.
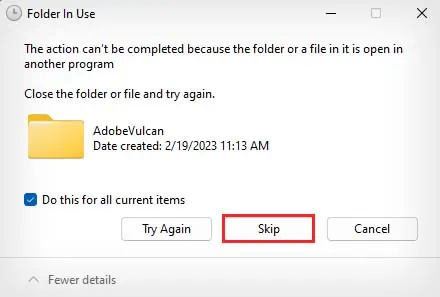
- If you need to provide admin access to delete the files, click on Do this for all current items and click on Continue.

- If some of the files can’t be deleted because they’re open, select Do this for all current items and hit Skip.

Additionally, every user account in your computer has separate application temporary files. You can use the above method to clear the temporary files of other user accounts.
Delete User Accounts Folder
If you had created multiple user accounts in the past and deleted them, you might expect all the data stored in those accounts to get deleted as well. However, the deleted user account’s data still gets stored in your C drive.
So, you should make sure to delete the user accounts folder as well to completely get rid of the old data.
- Open File Explorer.
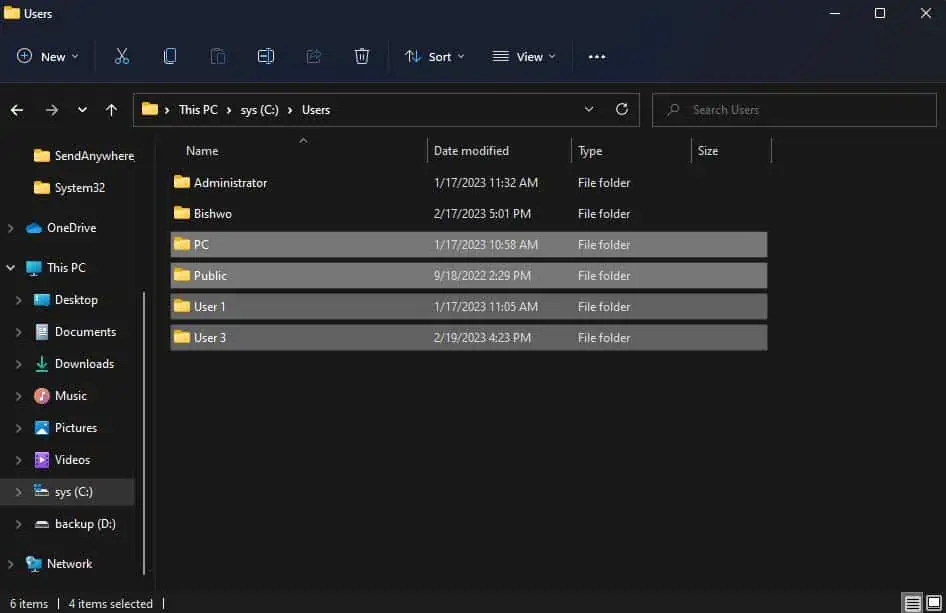
- Navigate to C drive. Click on the Users folder.

- If you see any of your old deleted user accounts folders, click on it and hit the Del key.
- Click on Continue to provide admin access to delete the user account folder.
Manage System Restore Points
System restore allows you to revert the state of your Windows PC to a previously saved state called system restore point. The saved system restore points occupy a set amount of space in your C drive, and if you let it run on automatic, the set amount of space can quickly get filled up.
- Press Windows + R to open the Run Utility.
- Type
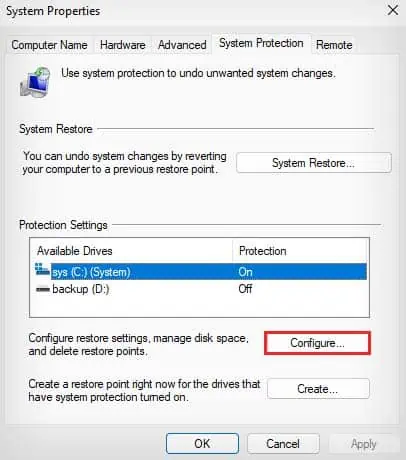
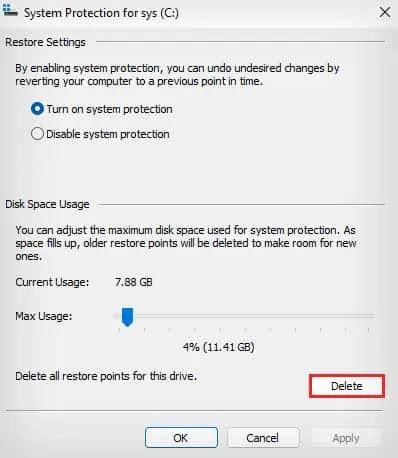
SystemPropertiesProtectionand press Enter to open System Properties. - In the System Protection tab, select your C drive, and click on Configure.

- Click on Delete in the new window.

- If you do not want your computer to automatically create a system restore point, also select the Disable system protection option.
- Select Continue to confirm and click on Close.
Manage Pagefile
Another thing that takes quite a bit of storage space in your C drive is the pagefile. It is an area in your hard drive that is used as RAM and is created by default in the OS drive. The pagefile is more commonly known as virtual memory.
To conserve space in your C drive, you can altogether disable the pagefile if you don’t need to run RAM-intensive programs or move to another drive.
- Launch Run dialog box using Windows + R hotkey.
- Type
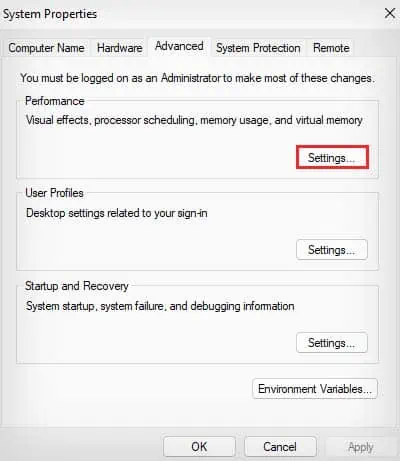
systempropertiesadvancedand hit Enter. - Under Performance, click on the Settings option.

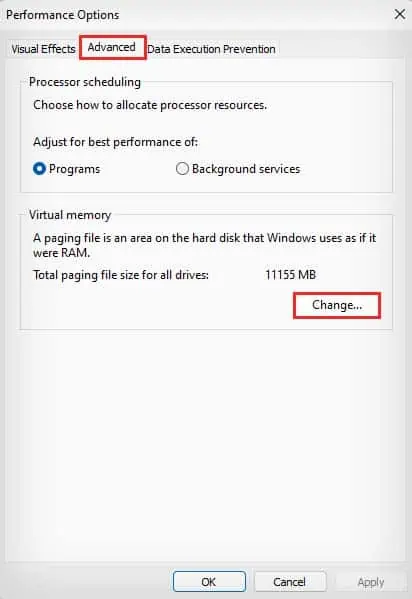
- On the Advanced tab, and under Virtual memory, click on the Change option.

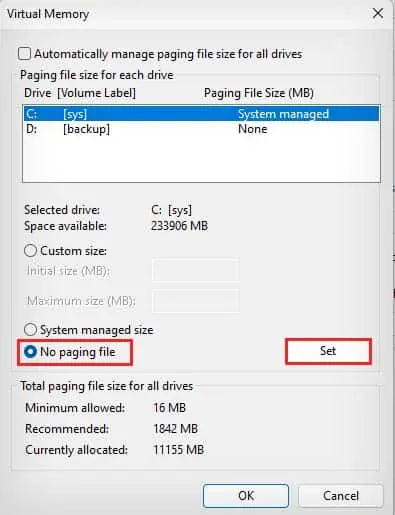
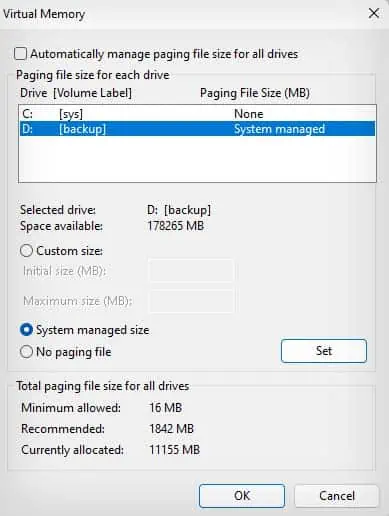
- Make sure the Automatically manage paging files size for all drives option is deselected.
- Click on your C drive, select No paging file, and click on Set.

- Select Yes to confirm.
- Now, you can either leave it so you don’t have a pagefile or set up the pagefile on another account.
- Click on the drive to set up a pagefile.

- Select the System managed size or the Custom size.
- If you select the custom size, Initial size should be the recommended amount, and the Max size should be 1.5, 2, or 4 times your RAM size.
- Click on Set and close all the dialogue boxes.
- Restart your Computer.
Disable Hibernation
The Hibernation mode in Windows computers is a power-saving state, which doesn’t shut down the computer, but uses much less power than sleep. It saves the state of everything, including user sessions, running applications, user-mode and Kernel-mode drivers, and Windows kernel into hiberfil.sys in the C drive, so you can continue where you left off before hibernation.
However, the Hibernation mode rarely gets used most of the time, as users prefer putting their computer to sleep. If you also don’t use Hibernation mode, it is better to disable it to save the space it uses in your C drive.
- Open the Run box using Windows + R shortcut key.
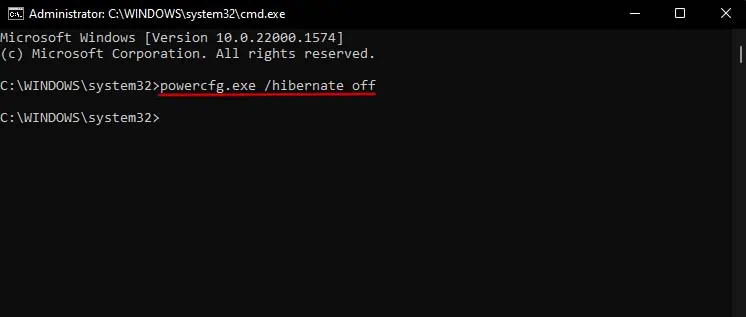
- Type
cmdand press Ctrl + Shift + Enter. - In Command Prompt, enter the following command:
powercfg.exe /hibernate off
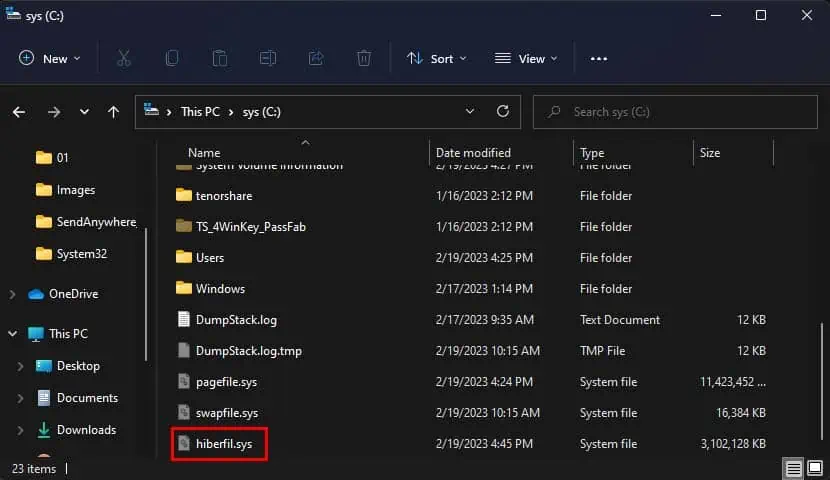
- This should delete the
Hiberfil.sys(The location where the RAM contents get stored) from the C drive.
Additionally, disabling Hibernation will also disable Fastboot as they use the same Hiberfil.sys file. However, you can also disable only Hibernation without disabling Fastboot.
Optimize C Drive Storage
Whenever you download or install any new content on your computer, they get stored in the C drive by default. For instance, the downloads folder is the default location in your C drive where all the things you download online are stored.
If you regularly download online content, you can try changing your default download location to another drive, so your C drive doesn’t get cluttered.
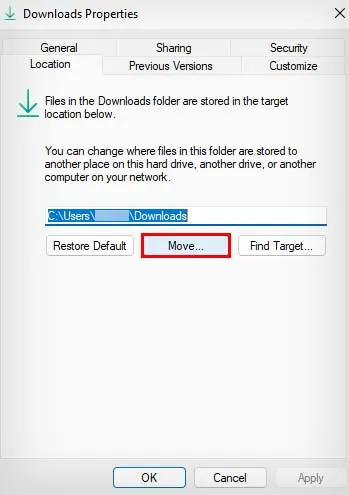
- Launch File Explorer.
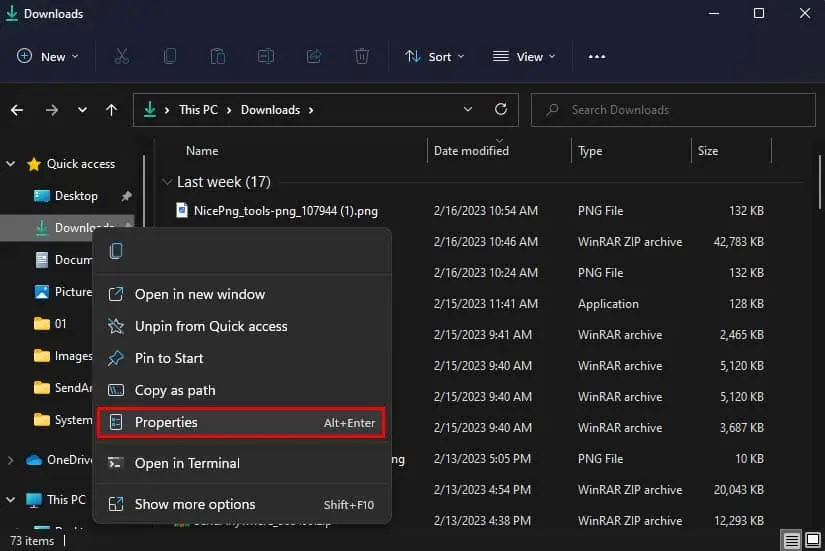
- Right-click on the Downloads folder in the left sidebar.
- Select Properties.

- Go to Location and click on Move.

- Browse to a location of your choosing and click on Select Folder.
- Click Apply and OK.
In addition to that, you can also choose to install all new applications or games to another drive instead of C. If you already have a lot of games in your C drive that you don’t want to uninstall, you can relocate them to another drive.
Lastly, make sure to be on the lookout for programs that create large data files. Software like Microsoft Outlook can store mails offline and create some pretty large data files. You can choose to relocate them.