It seems like an ethernet connection will always be faster for many people than a wireless connection, and that’s a fair assumption. A wireless connection running on the same network as an ethernet connection will be slower as a wireless connection is subject to more interference than a direct-wired connection.
If your wireless signal is faster than your ethernet, it may be a glitch, or a few different things may be happening to cause it.
Which is Faster: Wi-Fi or Ethernet?
The fastest connection is a connection that has a higher speed cap. For example, I get around 500 Mbps download speed on a wireless network while my best friend gets less than 100 Mbps on ethernet – but we live in two places with two internet plans that have differing speed caps.
Within my household, people who connect directly to the router get faster speeds than those who consistently use wireless.
However, that isn’t the case for everyone. Many factors affect your internet speed, from the equipment you’re running to where certain things are positioned in your house.
For most people, though, ethernet connections are faster than Wi-Fi. If you’re hoping to get the best possible connection to a device, hook it up to a wired connection. When ethernet isn’t working in the way you expect, you need to investigate to find out what’s wrong and create a better network connection.
Why is Ethernet Faster?
Ethernet is faster because it’s a direct-wired connection. It isn’t as subject to interference and positioning issues because the signal doesn’t have to transmit through the air.
Why is My Wi-Fi Faster than Ethernet
There are many reasons why your Wi-Fi signal might be faster than your ethernet signal. To figure out which one it is, you can do a few things.
Check Your Ethernet Cables

If your equipment is outdated, you may not be getting your optimal speeds. For example, an old cable or one that has been damaged somehow might not transmit the speed your service is capable of.
For most people, the length of the ethernet cable shouldn’t be a significant concern. If you’re using an exceptionally long one, though without the need to do so, consider switching to a shorter cord. Sometimes you can experience data loss and slower speeds as the cable length increases.
A damaged or degraded cable is a much larger concern. Before purchasing a cable, check to see whether it supports your internet speed. If you’re running a connection faster than 1 Gbps, you will want a cord that supports that speed. Look for a cable that’s rated Cat 6 or higher. Some people recommend against using Cat 7 cables, so it might be best to look for 6 or 8.
You might also want to look for cords from a higher category because they have an increased bandwidth capability. When you are moving large amounts of data, these can help improve your speed.
Different Device Capabilities
If you’re testing your speed on two different devices, the problem might be that each device can maintain different speeds. They have capabilities that come from their parts, and since they don’t have the same features, they don’t have the same capabilities.
Inside your computer is a wireless card that receives a wireless signal and provides your computer with incoming internet. An upgraded wireless card can deliver blazing fast speeds.
If the ethernet port in your computer is not as upgraded, it may not be able to sustain the same kinds of speeds. Each part is rated to handle a certain amount of speed. Check to see what kind of speeds your equipment can take, and you might find your answer to why your ethernet is slower than you expect.
Equipment Issues
There may also be a problem with the equipment you’re using. If the ethernet port on your computer, router, or modem is damaged, it might be impairing the signal.
When the ethernet port is damaged, that doesn’t mean that the wireless device inside your computer, router, or modem is damaged. So you will still be seeing high wireless speeds while your ethernet speed suffers from equipment malfunction.
Most devices come with multiple ethernet ports. Try unplugging your ethernet cable from one port and plugging it into another. Do it on both devices, and then restart your computer to see if the speed is faster once it restarts. If it is, you may need to consider replacing the modem, router, or backplate on your computer if you need the additional ports.
Check Your Network Adapter
In Windows, you can set your adapter to limit you to a certain connection. That isn’t always a bad thing. It can help you ensure there’s enough bandwidth to go around in multi-person households. Check yours to see if that’s why your ethernet is slower than Wi-Fi.
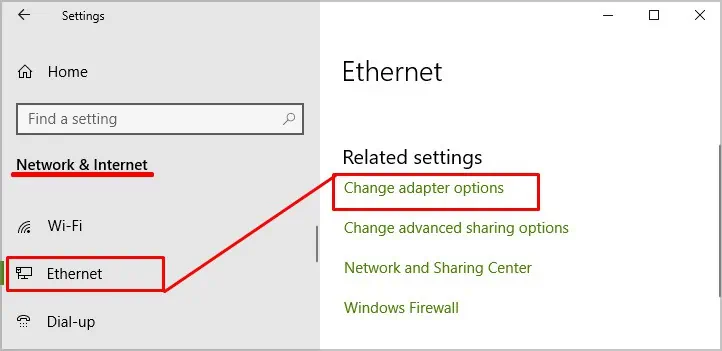
- Press the Windows key + X.
- Choose Settings.
- Choose Network and Internet.
- Choose Ethernet.
- Click Change Adapter Options.

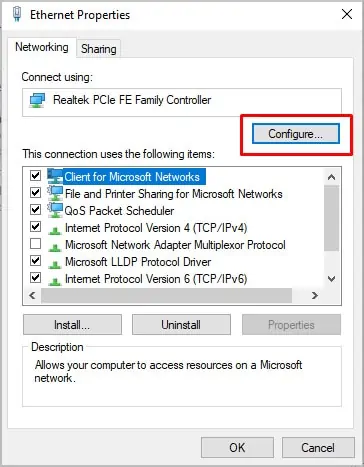
- Right-click your ethernet adapter and choose Properties.
- Choose Configure.

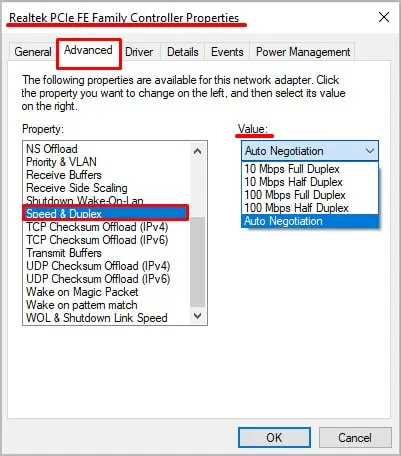
- Click Advanced.
- Choose Speed and Duplex.
- Look at the options under the Value drop-down menu.

You can choose any option you want. If you don’t want to manage it yourself, choose Auto-Negotiation. If the value is set to a lower value than the wireless speed you’re seeing, that is why your ethernet is slower than your wireless speed.
While you’re in your settings, try to look for updates for your wireless adapter too.
- Press Windows key + X.
- Choose Device Manager.
- Click the arrow next to the computer name to expand it and see a list of devices.
- Expand the Network Adapters menu.
- Right-click your ethernet adapter.
- Choose Update Driver.

- Follow the steps to look for driver updates.
Since driver updates can fix problems and improve performance, you might see a bump in your speeds if a new adapter is available and you can install it.
Connect Directly
Try connecting directly to the modem rather than the router and test your speeds. If you’re getting the speed you expect from ethernet from the modem, the problem might be with the router.
Check the pins and sockets in the ethernet ports to see whether they’re dirty. You can clean them with a q-tip and rubbing alcohol if they’re dirty.
If you’re still seeing a lower speed, check the status of your network adapter to see what it says. It might indicate that a network card or cable is broken if it’s lower than it should be.
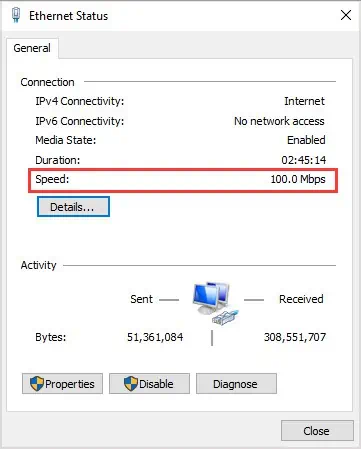
- Press the Windows key.
- Type Network Status.
- Click Change Adapter Options.
- Right-click on Ethernet Adapter.
- Click Status.

- Check to see what the speed reads.
Expect the speed to be lower than what you’ll see in speed tests. Mine is around double my speed on Wi-Fi. If it seems much lower than it should be for your network and the speed you expect, something in your devices or cables is probably not working. It could be the adapter in your computer, the networking devices, or the cables.
Reset Your Networking Devices

Sometimes your networking devices need to be reset to make them function at their best. Simply unplug both your router and modem, wait a few minutes, and then plug them back in again once you’re done.
Don’t go too fast. Let the modem get the connection before the router. Give everything time to load up before testing your speeds again.
Check Your Router Settings
If your router or modem has a web interface, log in and check your router settings. Make sure that you prioritize the computer with speed problems and that your bandwidth isn’t being directed to other computers.