Slow WiFi is most often caused by interference from other WiFi networks and old devices in the vicinity. Solid metal objects or concrete walls also block WiFi radio waves pretty hard, making for an even weaker signal.
Fixing this is as simple as repositioning your router and changing the channel. But of course, this likely isn’t the only reason why your WiFi suddenly slowed down. We’ve got you covered, though.
Our comprehensive guide covers everything from what makes WiFi suddenly slow to how you can solve the issue.
What Makes WiFi Suddenly Slow?
As we just said, the main culprit that makes WiFi suddenly slow is a weak signal. This is typically caused by interference from various sources. Some other common causes include:
- Bandwidth congestion
- Bandwidth Throttling/Shaping by ISP
- Background Processes/Updates
- VPN Server
- Proxy
- Faulty DNS Server
- Malware
- Wireless adapter set to low performance
- Old Router, PC, or Phone
- Outdated Network Drivers
How to Fix if WiFi Suddenly Slow?
The easiest way to fix WiFi problems is to restart your router and modem. Unplug the power cables and turn them off. Wait for about 30 seconds and turn them back on. This is especially likely to help if your device has been up and running for a long time.
Before getting into the technical details, try to narrow down the variables to find the root of the problem. Check if your WiFi is only slow on a specific website/app or throughout the system. Also, test the WiFi speed on multiple devices.
Now let’s check out the solutions.
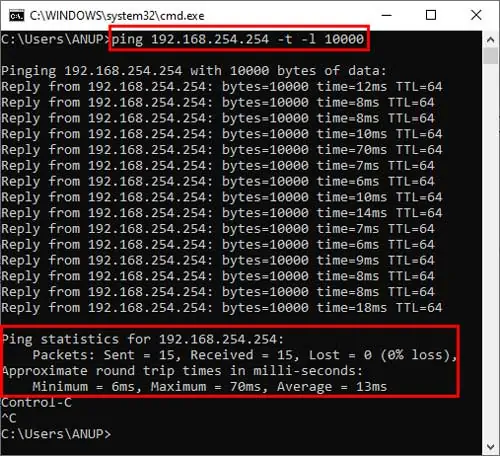
Use Ping Test to Determine the Cause of the Issue
You should first determine, if the issue is on the user’s side or the ISP’s, using a ping test. Ping is a tool to test the average time taken for a packet of data to reach the host from the client and also receive the acknowledged (ACK) handshake.
We recommend using a large packet size (10000 bytes) for the test as packet loss won’t always be apparent with the default size. To do so:
Windows
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type cmd and press Enter to launch Command Prompt.
- Type ipconfig and press Enter to show your network adapter info.
- Note the Default Gateway. Use this value in the next step.
- Type
ping Default Gateway -t -l 10000and press Enter. - After around 15 pings, press Control + C to stop the ping test.

Mac
- Open the Terminal.
- Type ipconfig and press Enter to show your network adapter info.
- Note the Default Gateway. Use this value in the next step.
- Type
ping Default Gateway -s 10000and press Enter. - After around 15 pings, press Control + C to stop the ping test.
Key Notes From Ping Test
- Check your Average Ping. It shouldn’t be higher than 15ms.
- Make sure there’s no Packet Loss.
- If possible, perform the test with an ethernet cable and check if you get better results compared to on WiFi.
- If you got high ping/packet loss or better results with Ethernet, the connection between your device and the router is facing a problem.
- To fix it, move closer to your router for a better signal. PC users can simply use an ethernet cable as well. It’s also worth resetting your router (press the Reset button for 10 seconds).
- If the ping and packet loss are fine, contact your ISP as the problem is likely on their end.
Adjust Router for Better Signal
Solid objects like walls or devices like microwaves block and interfere with the WiFi signal. If your signal strength is weak, there’s likely a lot of packet (data) loss, making your WiFi seem slow.
- Place your router high in the central part of your house where any large concrete/metal objects do not directly block it.
- Adjust the external antennas perpendicularly for max coverage.
- If you have an old router lying around, you can use it as a WiFi Extender / Repeater to improve the WiFi coverage. Of course, devices made specifically for this are also available in the market.
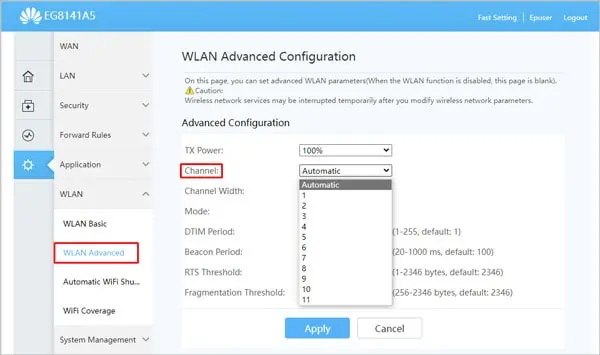
Change WiFi Channel
Frequency congestion can lead to high interference for your network making the WiFi slow. To avoid such situations, your router changes frequency orderly as necessary.
So, although you can select the WiFi channel as you prefer, we recommend setting your WiFi Channel to automatic. Your router will determine the ideal channel on its own in most cases. To do so:
- Open the Router Settings Page. Refer to the How to Access Router Settings section towards the end if you need help with this.
- Switch to the Wireless or WLAN tab (or similar). In some routers, these may be under advanced settings.

- Select Automatic and press Apply to save changes.
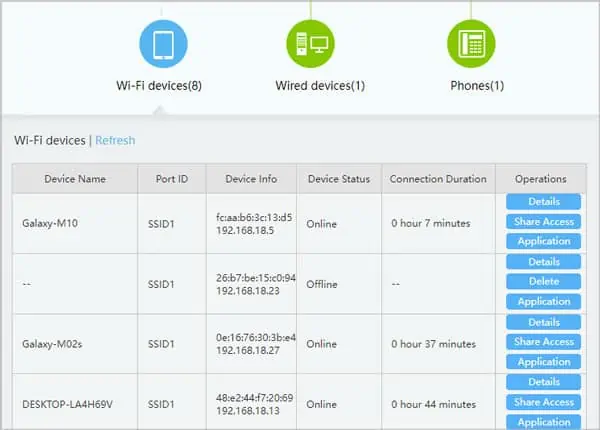
Check Other Devices on the WiFi
One device streaming high-quality video or downloading a large file can affect the internet speed for everyone else on the network. This can especially be a problem during peak usage hours (evening for e.g.) when everyone is using the WiFi at the same time.
To check the device list via Router settings:
- Open the Router Settings Page. Refer to the How to Access Router Settings section towards the end if you need help with this.
- Navigate to Status or Device/System Info or similar tab.
- Check the Connected Clients or Attached Devices or similar list.

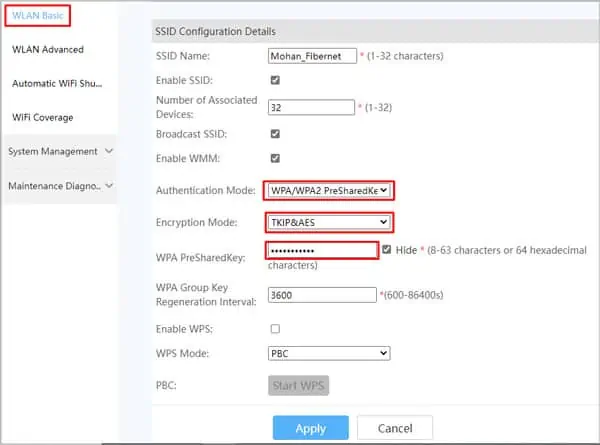
Secure your WiFi
When checking the devices list in the solution above, if you saw an unknown device(s), your WiFi connection might’ve been hijacked. Someone could be piggybacking on your network without your consent and making your WiFi suddenly slow.
To secure your WiFi, you should change your password and use WPA2 security with AES/TKIP encryption.
- Open the Router Settings Page. Refer to the How to Access Router Settings section towards the end if you need help with this.
- Navigate to Advanced Settings > Wireless or WLAN or similar tab.
- Set a new password and select WPA2 as security and AES/TKIP as encryption.

- Press Apply to save the changes.
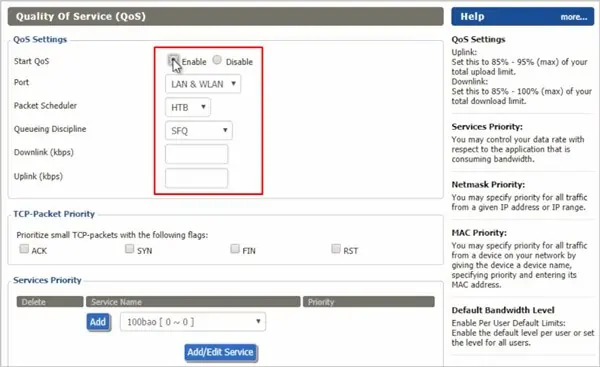
Use Quality of Service (QoS)
You can use QoS to make sure one device/app isn’t hogging most of the bandwidth and making the WiFi slow for everyone else.
Uplink/Upstream – Your Upload Speed
Downlink/Downstream – Your Download Speed
Dynamic QoS – A feature in some routers that automatically configures QoS settings for you.
QoS Rules – Rules to determine the bandwidth allocation and priority order according to the app, device, or service.
- Open the Router Settings Page. Refer to the How to Access Router Settings section towards the end if you need help with this.
- Switch to the QoS settings tab and select Enable or Activate.

- Select WAN as the port.
- Enter the Upload and Download speeds as you require into the uplink and downlink fields.
- Click Apply Settings to save the changes.
End Unnecessary Background Processes / Updates
Your device/system may be updating in the background without your knowledge. Windows Update, for instance, is necessary for security and performance, but it can certainly take a toll on your WiFi. On Android/iOS, your apps might be auto-updating and making the WiFi seem slow at the time.
To check and end unnecessary background processes:
Windows
- Press Windows + Shift + Esc to launch the Task Manager.
- Check the Network tab.
- Select any unnecessary processes causing high network usage and click End Task.
macOS
- Press Command + Shift + U to open the Utilities folder.
- Launch the Activity Monitor and check for any unnecessary processes causing high network usage.
- Select the app/process you want to quit and click Stop (X) at the top left.
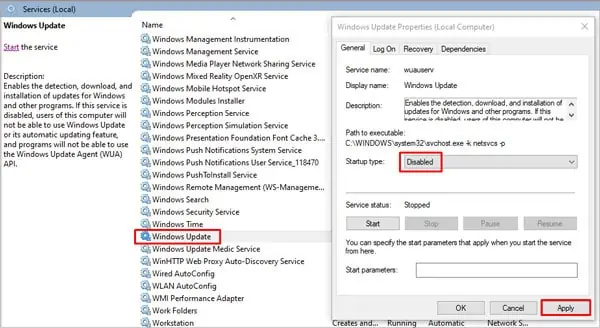
Next, to turn off Automatic Updates on Windows:
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type
services.mscand hit Enter. - Scroll down to Windows Update and double-click to open Properties.
- Set the Startup Type to Disabled.

- Click Apply and restart your PC.
To re-enable automatic updates, just set the startup type to Manual/Automatic.
macOS
- Open the App Store and open Preferences from the menu bar.
- Deselect Automatic Updates.
iOS
- Go to Settings > App Store.
- Tap the slider to turn off App Updates.
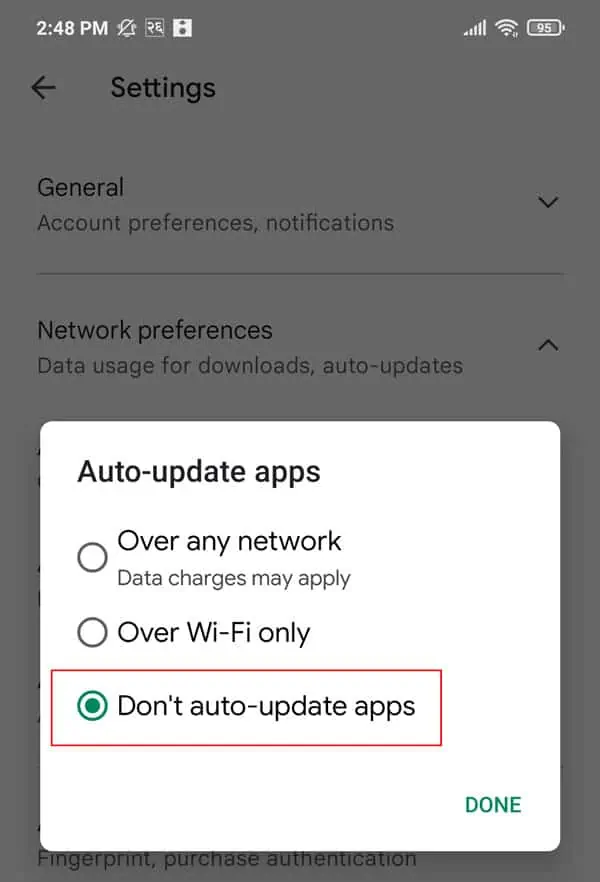
Android
- Launch Google Play Store.
- Tap your profile picture and go to Settings > Network Preferences > Auto-update apps.
- Select Don’t auto-update apps and press Done.

Disable/Change VPN and Proxy
Disable your VPN temporarily and test the WiFi speed. Change to another server if the VPN seems to be the issue. Or use a different VPN altogether. The same goes for proxies. You can follow the same steps to re-enable these later.
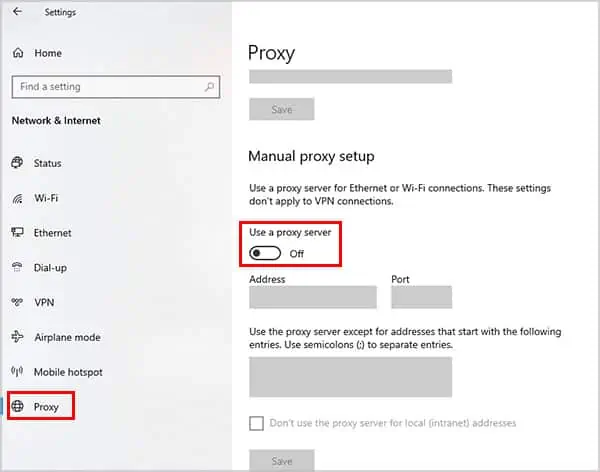
Windows
- Right-click your VPN from the taskbar and click Stop Service or Disconnect.
- If that doesn’t work, instead press Windows + I to launch Settings.
- Go to Network and Internet > VPN.
- Select your VPN connection and press Disconnect.
- Switch to the Proxy tab from the left menu.
- Press the Use a Proxy button and turn it off.

macOS
- Press the Apple logo from the top left and open System Preferences.
- Click on Network.
- Select your VPN from the left pane and click Disconnect.
- Next, select your active Wi-Fi connection.
- Press the padlock and enter your admin credentials if prompted.
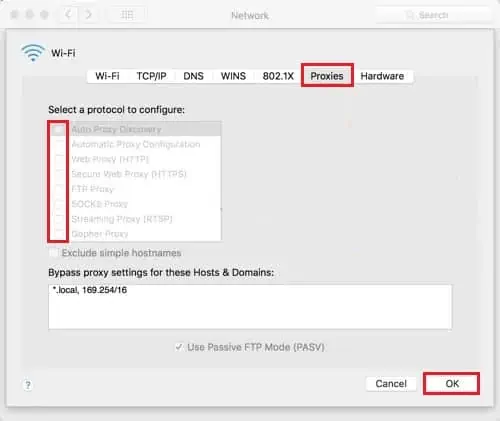
- Go to Advanced > Proxies.
- In the proxies tab, disable all proxies and press OK.

iOS
- Open the VPN app and click Disconnect/Disable.
- If that doesn’t work, go to Settings > General.
- Tap VPN or VPN & Device Management.
- Switch off the VPN.
Android
- Open the VPN app and click Disconnect/Disable.
- If that doesn’t work, go to Settings > Connections.
- Scroll down to More Connection Settings.
- Select the VPN and tap on the blue settings cog next to the VPN name.
- Press Delete VPN profile.
Use a Different DNS Server
If your DNS server is slow or problematic, it can cause the page you’re trying to open to load very slowly as well. Your computer obtains the DNS automatically, and normally that’s fine, but it’s better to use a custom DNS in situations like this.
The free public DNS servers from Google or OpenDNS are a good place to start.
| Preferred DNS: 8.8.8.8 Alternate DNS: 8.8.4.4 | |
| Cloudflare | Preferred DNS: 1.1.1.1 Alternate DNS: 1.0.0.1 |
| OpenDNS | Preferred DNS: 208.67.222.222 Alternate DNS: 208.67.220.220 |
Windows
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type ncpa.cpl and press Enter to launch Network Connections.
- Right-click on your active Wi-Fi/Ethernet connection.
- Press the Properties button.
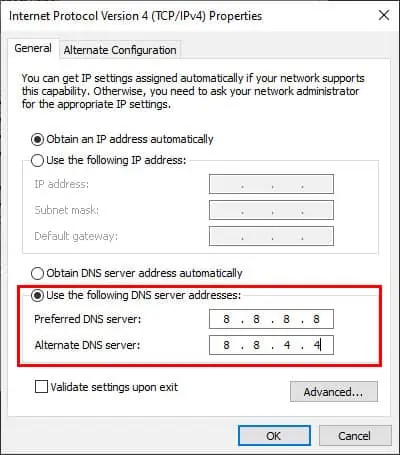
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and press the Properties button.
- Go to Use the following DNS server addresses.

- Enter 8.8.8.8 in the Preferred DNS server box.
- Enter 8.8.4.4 in the Alternate DNS server box.
- Click OK to apply the new settings.
macOS
- Click on the Apple icon at the top left to expand the Apple menu.
- Open System Preferences > Network.
- Unlock the padlock at the bottom-left and enter the admin credentials if prompted.
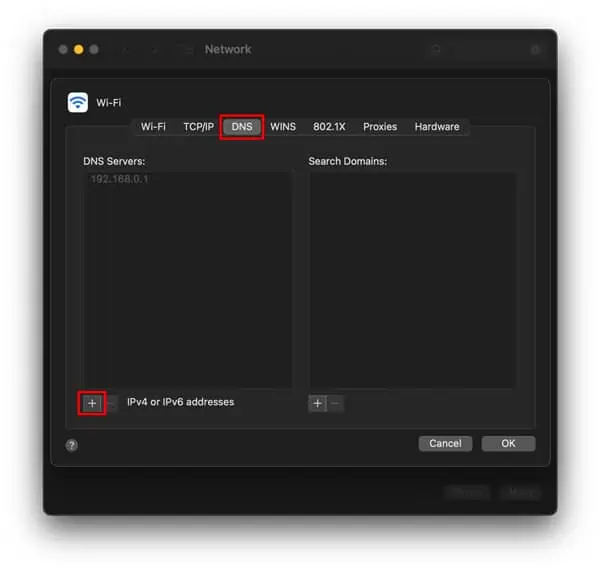
- Select Wi-Fi or Built-In Ethernet and click Advanced.
- In the DNS tab, press Add (+) and add the new DNS at the top of the list.
E.g., 8.8.8.8 and/or 8.8.4.4
- Click OK > Apply.
Set Wireless Adapter to Max Performance
Power Saving Mode in Windows adjusts your network adapter performance for longer battery life. To set it to max performance:
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type powercfg.cpl and press Enter
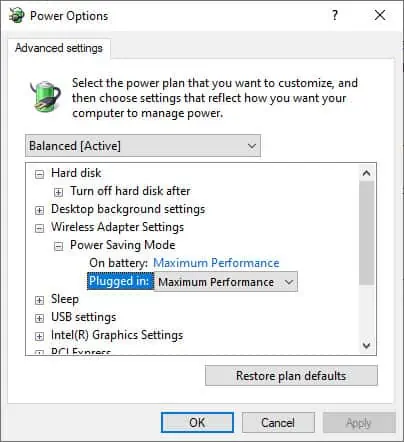
- Click on Change plan settings next to your selected plan.
- Open Advanced power settings and expand Wireless Adapter Settings.
- Set both On Battery and Plugged In to Maximum Performance.

- Press OK to apply the changes.
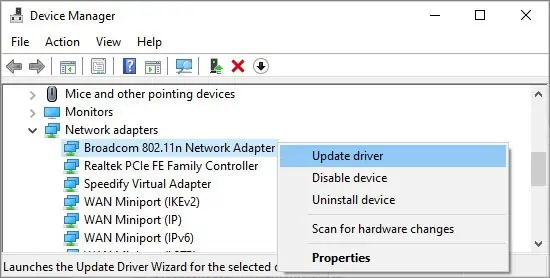
Perform Network Driver / System Update
Windows
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type
devmgmt.mscto open Device Manager. - Expand Network Adapters by pressing the arrow.
- Right-click your network adapter and click Update Driver.

- Click Search for Drivers Automatically when prompted.
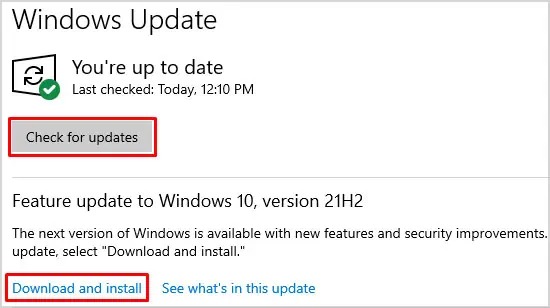
- Open Run once again by pressing Windows + R.
- Type control update and press Enter.
- Click on Check for Updates and download any available ones.

- Restart your PC if it doesn’t do so automatically.
macOS
- Click on the Apple logo from the top left to open the Apple menu.
- Open System Preferences > Software Update.
- Press Update Now

- Follow the instructions on-screen and install any updates available.
Android / iOS
- Go to Settings > About Phone / General.
- Tap Check for Updates / Software Update.
- Follow the instructions on-screen and install any updates available.
Scan for Malware
Malware is notorious for hogging resources. You can use third-party antivirus apps or built-in security tools to scan and remove viruses from your device.
Windows
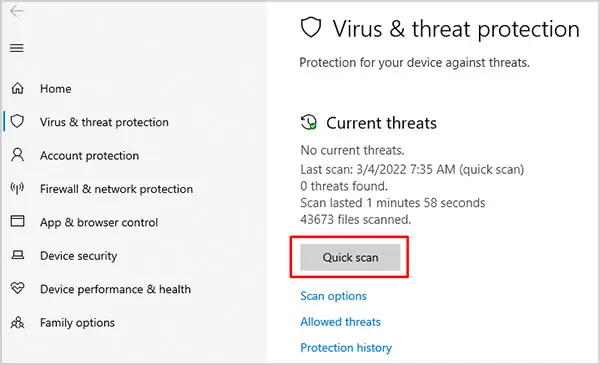
- Launch your antivirus software and run a full scan. If you don’t have one, Windows Defender is fine too.
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type or copy
ms-settings:windowsdefenderand press Enter. - Open Virus and Threat Protection. Press Quick Scan or click on Scan Options for a Full Scan.

macOS
Mac has various anti-malware tools and services running in the background including XProtect (for signature-based malware detection), MRT, and Notarization.
Mac’s inbuilt security system is great on its own, but you can always use a third-party antivirus for an extra layer of protection.
Android/iOS
Android and iOS devices don’t have reliable ways to scan for viruses. It’s best to use reputable third-party antiviruses for these as well.
Contact Your Network Admin/ISP
If you’re on a school or work WiFi, consult with your network admin about slow WiFi. For home users, check with your ISP regarding bandwidth caps and throttling.
If you’ve tried all the fixes on our list and the WiFi is still slow, it’s best to contact your Network Admin/ISP and ask for support.