Microsoft regularly provides Windows updates to all supported versions to introduce new features and resolve previous bugs. However, sometimes while presenting new features, it may also introduce new bugs that cause varieties of issues.
Your computer crashing during or after an update is one of such issues. It usually happens because of conflicts with pre-existing software.
Microsoft will naturally create patches or fixes for the issue in the next major or minor update. But there are a few things you can do at the moment to stop the system crashes.
Causes for Windows Update Crashing Computer
Here are the causes for Windows Update Crashing Computer, whether the crash occurs during the update or after:
- Bugs in the update files.
- Power failure during the update causing incomplete installation.
- Lack of storage space to store the update.
- Internet connection issues
How to Stop Windows Crashing After Update
If your Windows started crashing after successfully performing an update, it’s usually due to a problem with the update. So, the best solution is to roll back your system. However, there are also some other things you can do depending on your issue.
Rollback Windows OS
The most common reason for this issue includes new bugs introduced by the update. We recommend updating your OS as soon as new system and optional updates are available to resolve such issues.
In the meantime, report your error to Microsoft and roll back your system to the previous version. You need to uninstall the latest updates to roll-back your system. To do so:
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type
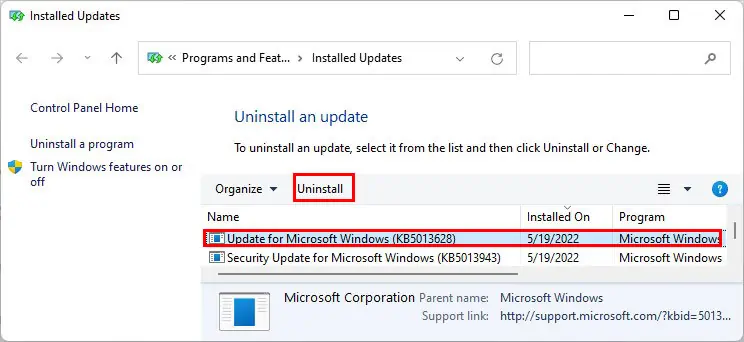
appwiz.cpland press Enter. - Click on View installed updates.
- Select the latest updates by checking the dates on the Installed On column.
- Click Uninstall and confirm with Yes.

If you are stuck in a crash loop after the update and can’t log in to your account, you need to uninstall the latest update from the Windows Recovery Environment.
Here’s how you can do so:
- Get to the Windows Recovery Environment using one of the following methods:
- Hard reset your PC three times. On the third boot, click Advanced Options on the Startup Repair screen.
- Boot your computer using a Windows recovery or installation media and click on Repair your computer on the Install screen.
- Go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options.
- Select Uninstall Updates and follow the on-screen instructions.

You can also go to Command Prompt to list out and delete your updates. You will also be able to know the name of the problematic update with this method. So you can search on the internet if there’s anything you can do except uninstalling it. To list and uninstall the update:
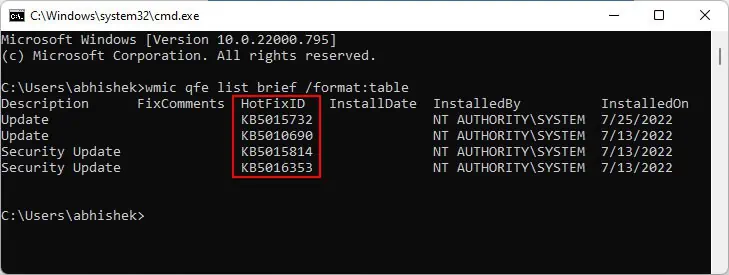
- On Command Prompt, enter
wmic qfe list brief /format: tableto list your updates. - Note the HotFixID for the latest update by checking the InstalledOn column for the dates.

- Enter the command
cd %windir%\System32to change to the directory. - Then, type
wusa / uninstall / kb:“HotFixID”and press Enter. Don’t forget to replace “HotFixID” with the value you noted on step 2.
Restart your PC after rolling back your system and check if the issue resolves.
If you encountered this issue after upgrading your system, you have 30 days before you can roll back to the previous version. To do so, go to Settings > Windows Update > Advanced options > Recovery and select Previous version of Windows or Go back.
You can also perform a system restore to the roll back your system if you have a restore point from the time before the update.
Enable Some Windows Features
If your PC started crashing after the May 10, 2022 – KB5013943 update, you need to enable some Windows Features to resolve the issue. Microsoft has resolved most of the bugs with this update on the later ones. However, one particular feature that affects .NET Framework 3.5 apps has not been addressed.
This issue leads to a some problems, including system crashes while opening the .NET Framework 3.5 apps. An update troubleshooter should be enough to resolve the issue. But you can also fix it by enabling the following optional features:
- .NET Framework 3.5
- Windows Communication Foundation (WCF)
- Windows Workflow (WWF) components.
Here’s an easy way to do so:
- Open Run (Win+ R).
- Type
cmdand press Ctrl + Shift + Enter. - Enter the following commands:
dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:netfx3 /alldism /online /enable-feature /featurename:WCF-HTTP-Activationdism /online /enable-feature /featurename:WCF-NonHTTP-Activation
Disable Driver Signature Enforcement
Windows includes the feature, Driver Signature Enforcement, which is enabled by default to improve security. When this feature is On, the presence of any drivers without a digital signature will prevent your system from booting properly. So, you’ll be stuck in a startup crash loop.
Sometimes, a problematic Windows update can corrupt some drivers’ digital signature and cause crashes during the startup. The crash message also shows “the digital signature of a file couldn’t be verified” in such cases.
The temporary solution is to disable the driver signature enforcement. You can disable it during startup by pressing the corresponding key on the Startup Settings.
However, you have to do so on every boot. To permanently disable this feature,
- Get to WinRE and go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Command Prompt.
- Enter the command
bcdedit /set nointegritychecks on - Enter
exitto get out of the Prompt and restart your PC.
If you want to re-enable this feature, use the same command, but with off instead of on.
How to Stop Windows Crashing During Update
Make sure there are no issues with your internet connection before starting the update. We also recommend plugging in the AC cord on your laptop to account for potential power failures due to low battery.
You should also create a restore point before initiating the update to revert your system in case you encounter some serious issues.
Then, apply the possible solutions below and try updating your system again.
Free up Storage Space
Lack of sufficient storage space is one of the main reasons for the computer crashing while updating Windows OS. So, make sure you have sufficient available space in the system drive.
You can check out our article on How to Clean C Drive to learn how you can free up space on the disk.
Run Windows Update Troubleshooter
Windows includes dedicated troubleshooters to scan and repair issues with your system components. You should run the update troubleshooter whenever you encounter any update issues. To do so,
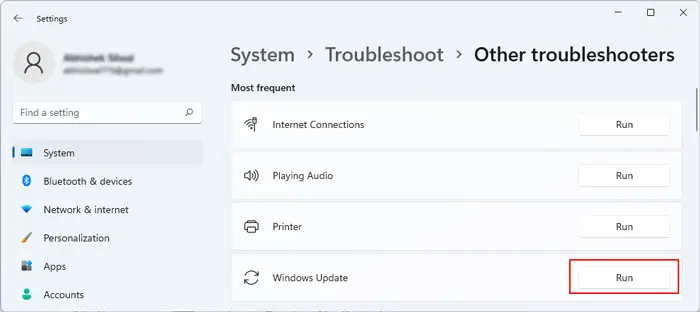
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type
ms-settings:troubleshootand press Enter. - Select Other troubleshooters or Additional Troubleshooters.
- Click on Windows Update and select Run or Run this troubleshooter.

- Follow the on-screen instructions.
You can also run the Network adapter and Internet Connection troubleshooters in case there are some issues with your internet.
Reset Windows Update Components
Resetting Windows Update Components is a good solution for most common update errors. In this process, you perform two operations at once:
- Resetting the services you need for Windows Updates.
- Deleting the potentially problematic update files your system downloaded previously along with additional cache files. It allows your system to re-download the files.
These processes will troubleshoot the issue if it’s due to incomplete or buggy update files.
We also recommend you reset your winsock catalog afterwards to account for other connection issues.
Here are the complete steps for the both processes:
- Open Run.
- Type
cmdand press Ctrl + Shift + Enter. - Enter the following commands:
net stop wuauservnet stop bitsnet stop appidsvcnet stop msiservernet stop cryptsvcnet stop trustedinstallerdel "%ALLUSERSPROFILE%\Application Data\Microsoft\Network\Downloader\qmgr*.dat"ren C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution SoftwareDistribution.oldren C:\Windows\System32\catroot2 catroot2.oldnet start trustedinstallernet start wuauservnet start cryptsvcnet start appidsvcnet start bitsnet start msiservernetsh winsock reset
Update or Reinstall Network Drivers
Errors with your network drivers can also lead to buggy update files due to unstable internet connectivity during their download. We recommend keeping your drivers fully updated to prevent such issues.
To update the network drivers,
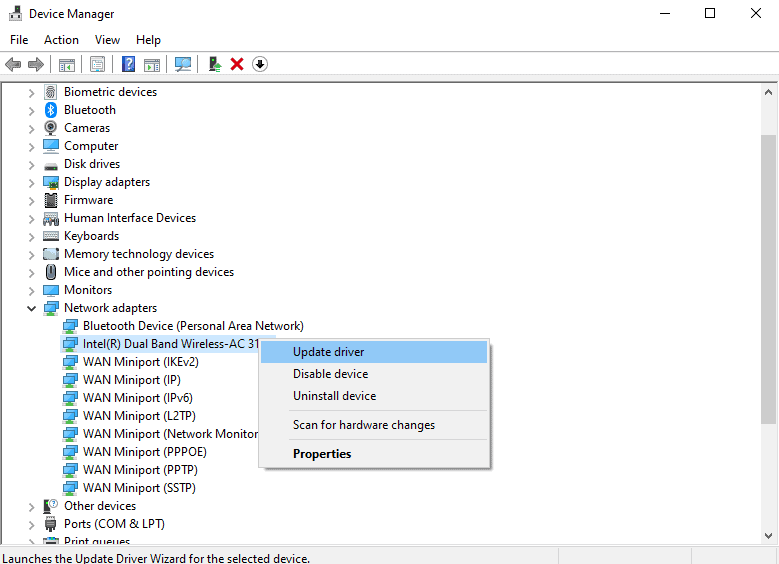
- Press Win + R and enter
devmgmt.msc - Expand Network adapters and right-click on your network device.
- Select Update driver and then Search automatically for drivers.

If you have the latest network driver, you’ll need to reinstall it to resolve any errors within. To do so, uninstall it and restart your PC. Your system will install any missing drivers during the reboot.
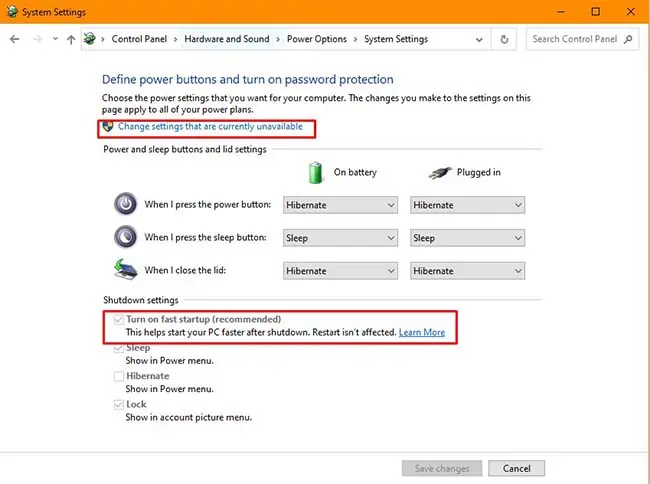
Disable Fast Startup
The Fast Startup feature does not refresh the kernels during a reboot. If any updates are related to security or kernel, the chances are very likely that fast startup will cause an issue.
So, if there are any related updates, they may not install correctly. It’s always better to restart your PC instead of shutting down after you install any updates.
However, you can also disable this feature altogether to avoid such complications. Here’s how you can do so:
- Open Run and enter
powercfg.cpl - Go to Choose what power buttons do and the click on Change settings that are currently unavailable.
- Uncheck Turn on fast startup and click on Save Changes.

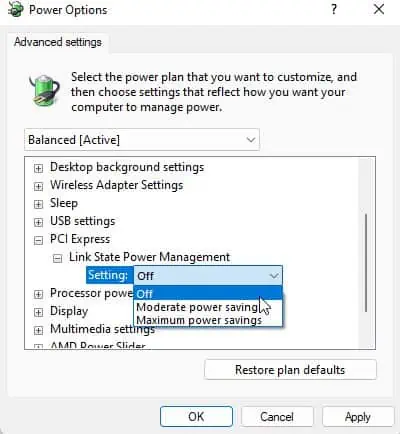
Disable Link-State Power Management
Link-state Power Management helps improve battery life by suspending power to idle PCIe devices. However, this feature can cause crashes, especially with a GPU installed. It usually happens because this setting affects power transition to your hardware components.
You can try disabling this feature and see if your computer stops crashing. To do so,
- Open Run and enter
powercfg.cpl - Go to Change plan settings next to your selected plan and select Change advanced power settings.
- Expand PCI Express > Link State Power Management.

- Set the drop-down boxes to Off.
If you are disabling this setting, it is also a good idea to disable PCI Express Native Power Management in your BIOS. There are different ways to get to BIOS and different BIOS interfaces for individual motherboards. So, we recommend checking their official website to learn the process.
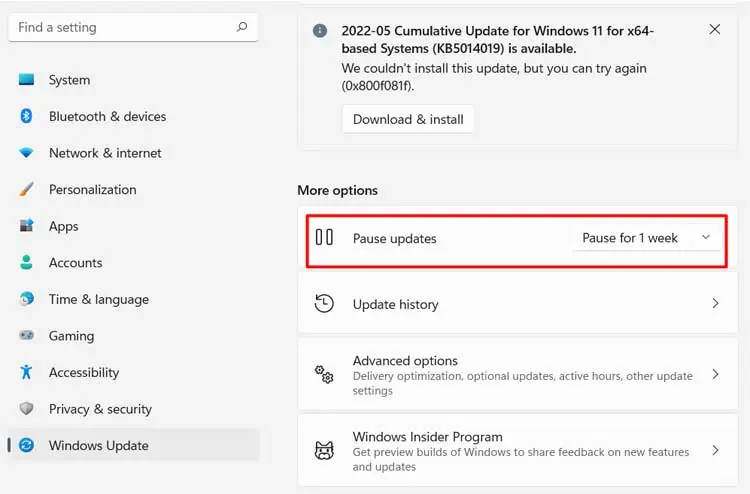
Temporarily Pause Updates
If your computer keeps on crashing during the update, it’s likely due to an issue with the update. The only thing you can do in such scenario is inform Microsoft.
Then, you should temporarily pause your updates until Microsoft releases a patch or bug fix. To do so,
- Open Run and enter
ms-settings:windowsupdate - Set the pause time per your preference and click on it.

You can resume the updates by selecting Resume updates.
Advanced Solutions for Windows Update Crashing Computer
Windows crashing after or during a system update may only be a coincidence and there might be other underlying causes unrelated to the update. You can also try applying other solutions for computer crashes. We have created an article dealing with Windows 11 Crashes, which you can visit to learn all possible solutions.
Apart from that, we recommend applying the advanced solutions below if those we mentioned previously were not enough to debug the issue.
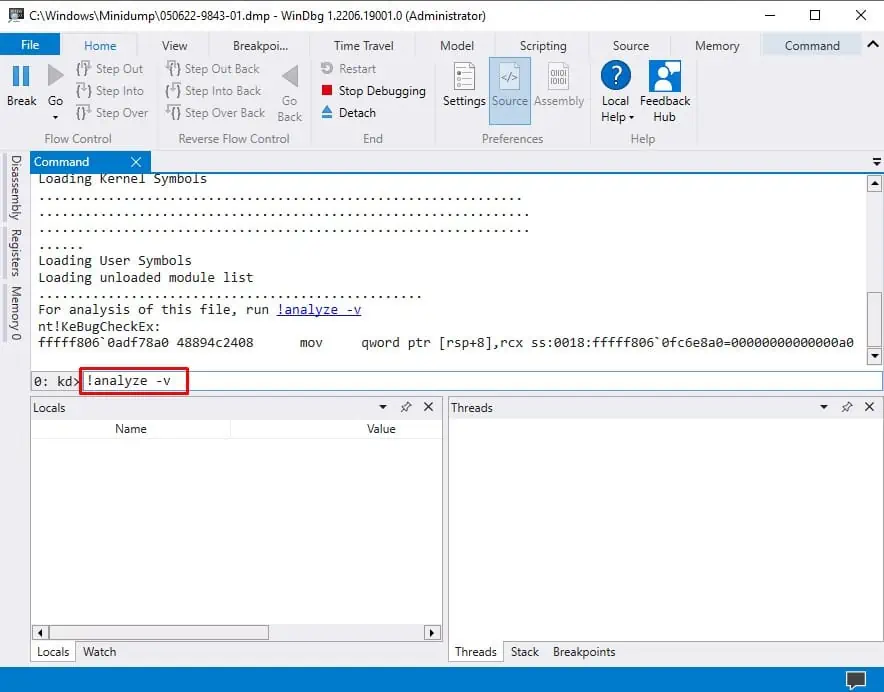
Check Minidump File
If the crash results in a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), you can try analyzing its minidump file. The crash creates the minidump in the %windir%\Minidump folder. You need a debugger to analyze it and determine the reason for your issue.
To analyze the minidump using Microsoft WinDbg Preview,
- Install Microsoft WinDbg Preview from the app store.
- Open the app as administrator.
- Press Ctrl + D and navigate to the
%windir%\Minidump directory. - Choose the latest minidump file and select Open.
- Enter
!analyze -von WinDbg’s command line.
- After the analysis, search for MODULE_NAME and probably caused by to check the cause.
You can also ask for help on the Microsoft forum if you have any trouble analyzing the file.
It’s also a good idea to run driver verifier to stress your drivers. After a problematic driver fails, you’ll encounter the Driver Verifier Detected Violation BSOD crash. So, analyzing the minidump file will help troubleshoot a buggy driver.
However, remember to create a restore point beforehand to account for further system issue.
Reset or Reinstall Windows
If you can’t resolve the issue after performing all previous solutions, your only choice is to reset or reinstall Windows.
First, reset your system using the steps below:
- Open Run and enter
systemreset - factoryreset - Follow the on-screen instructions.
If you want to know what each options in the process determine, you can check out our article on How to Reset Windows. You can also visit this article if you want to learn other methods of resetting your PC.
If resetting doesn’t resolve the issue, reinstall Windows OS using an installation media.